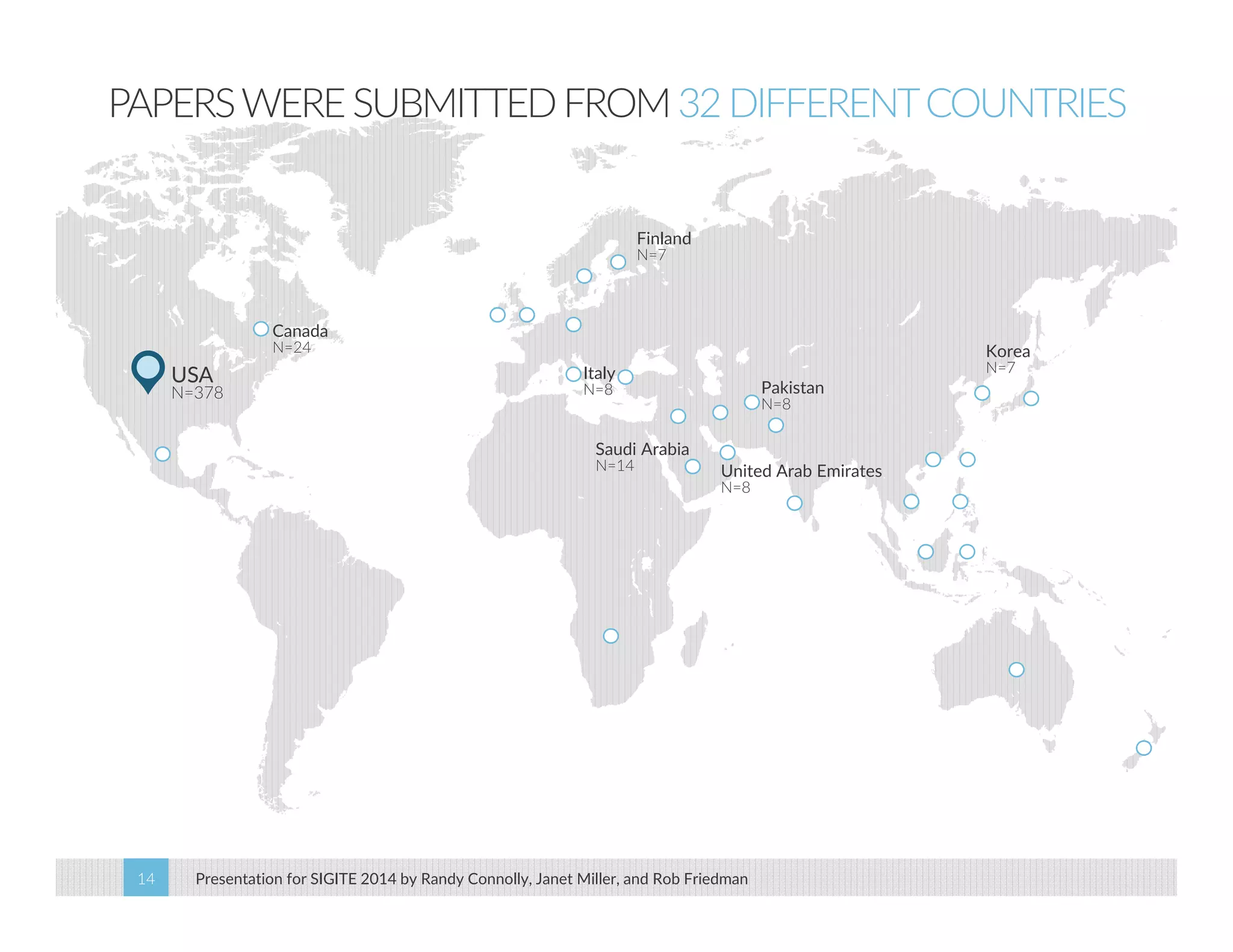
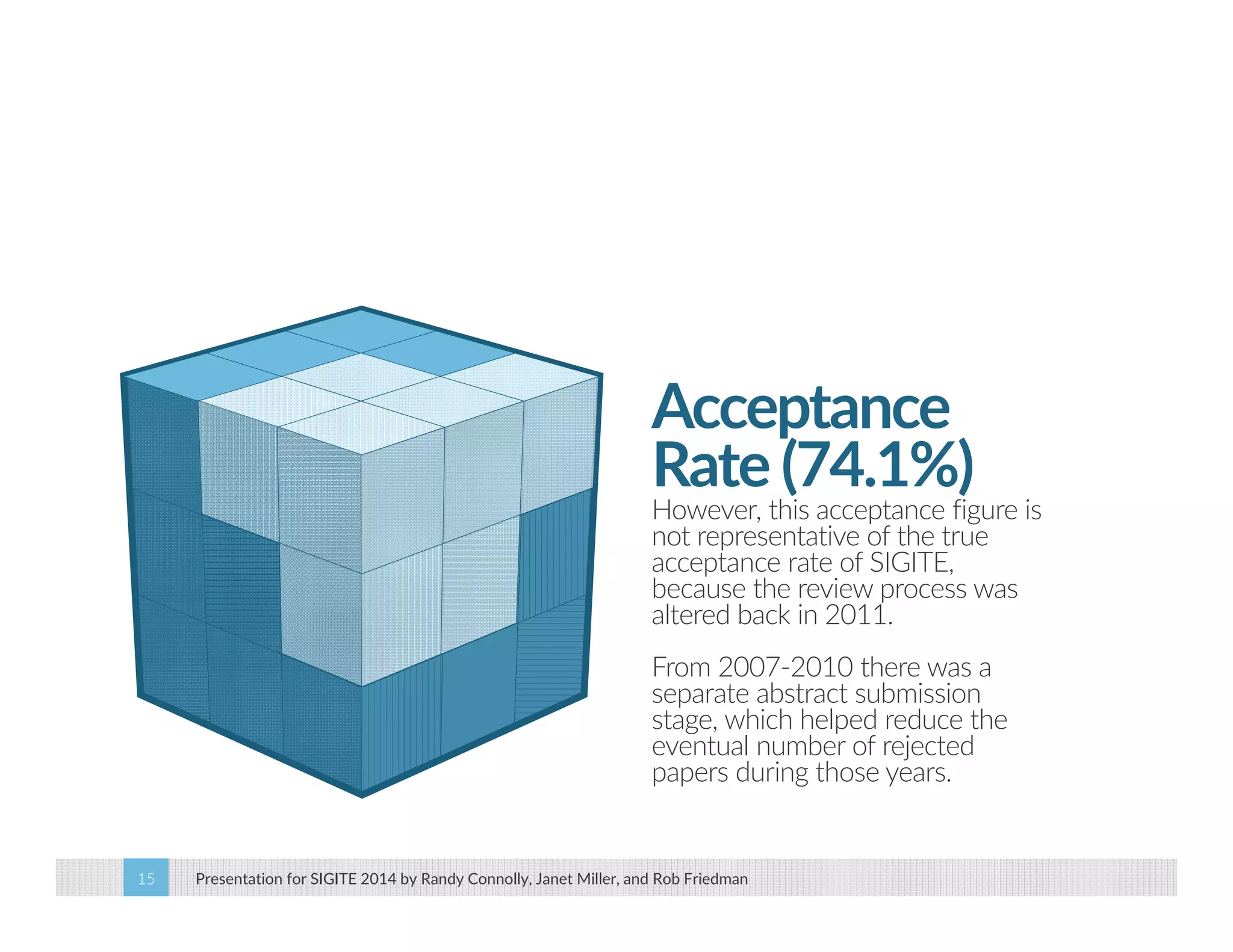
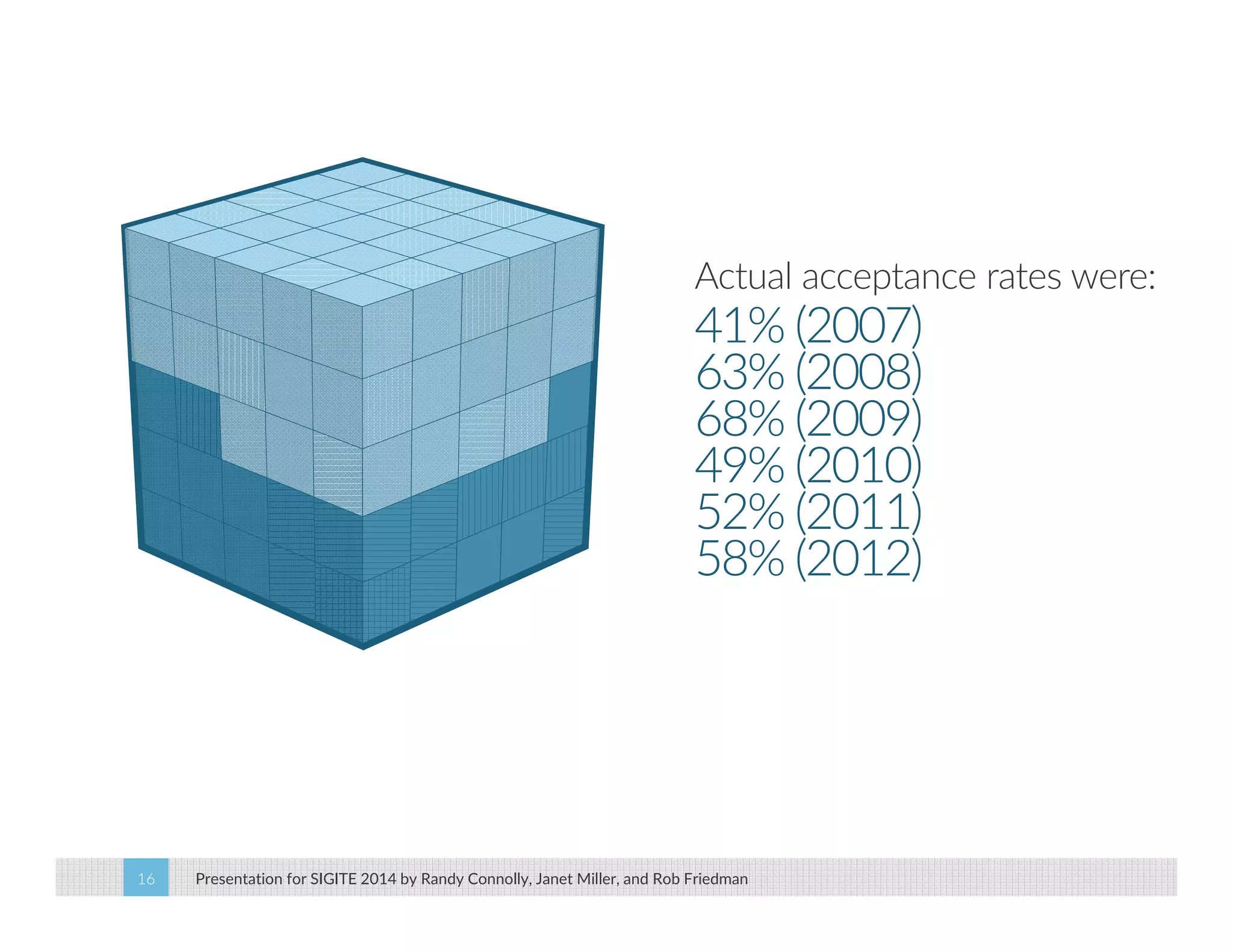
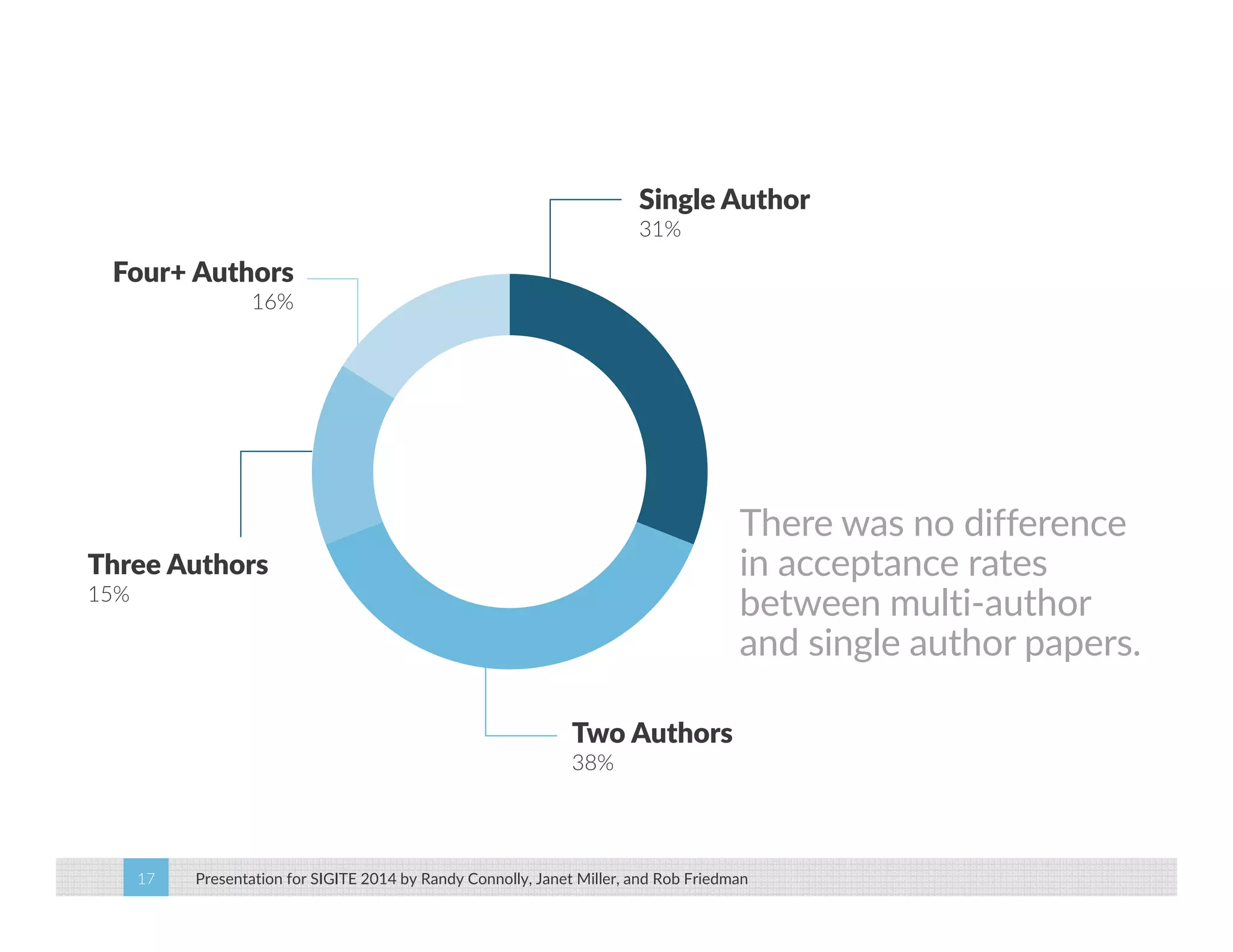
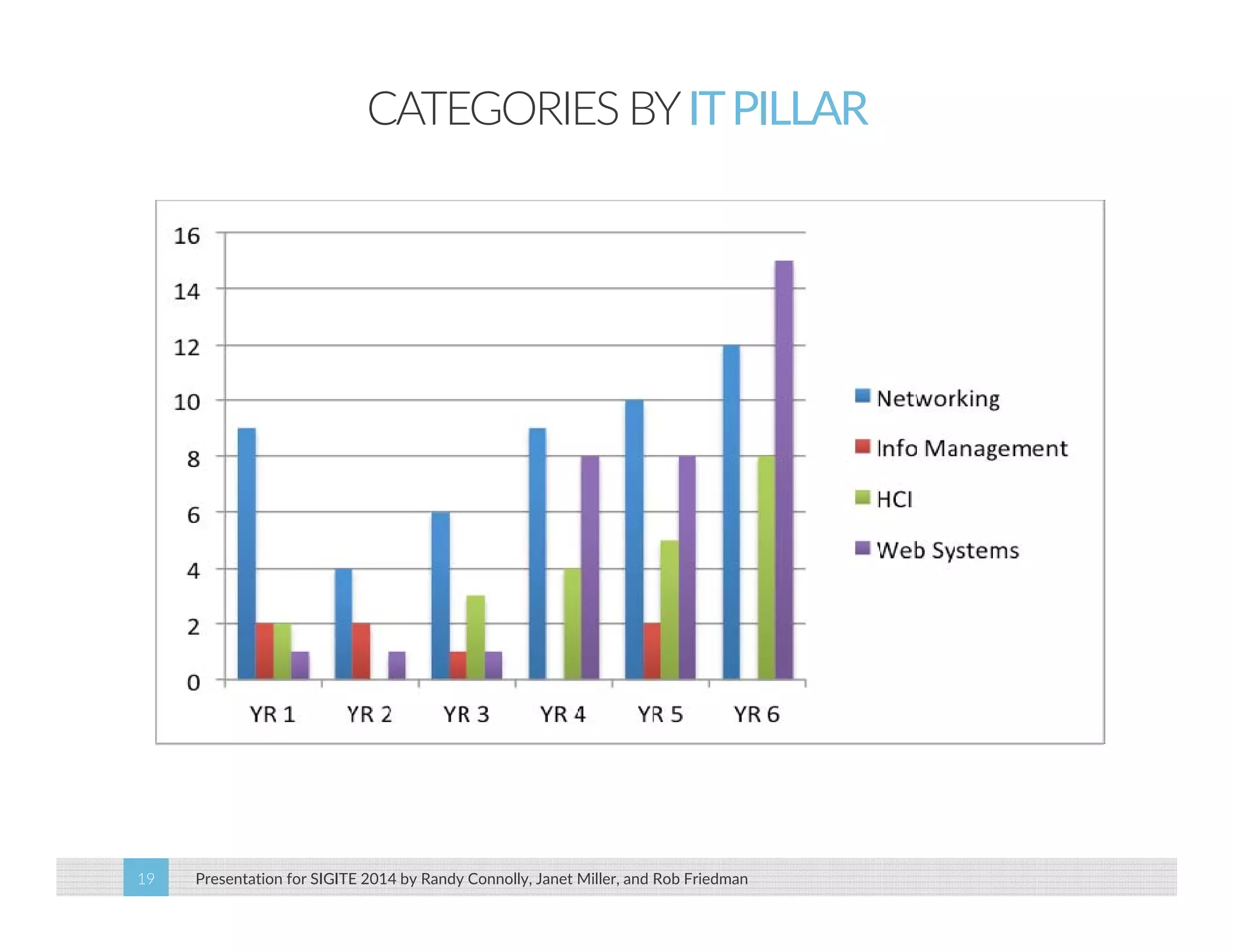
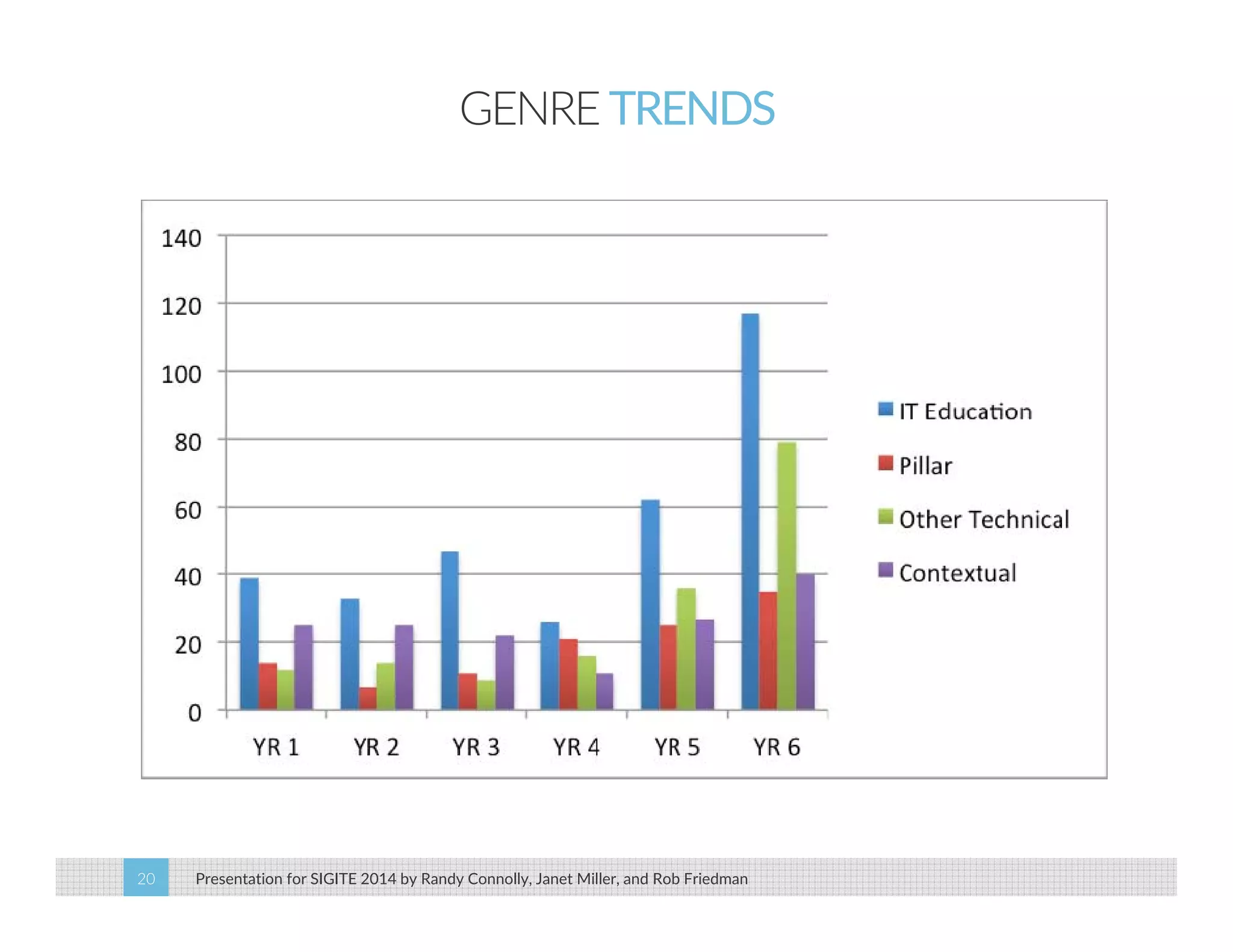
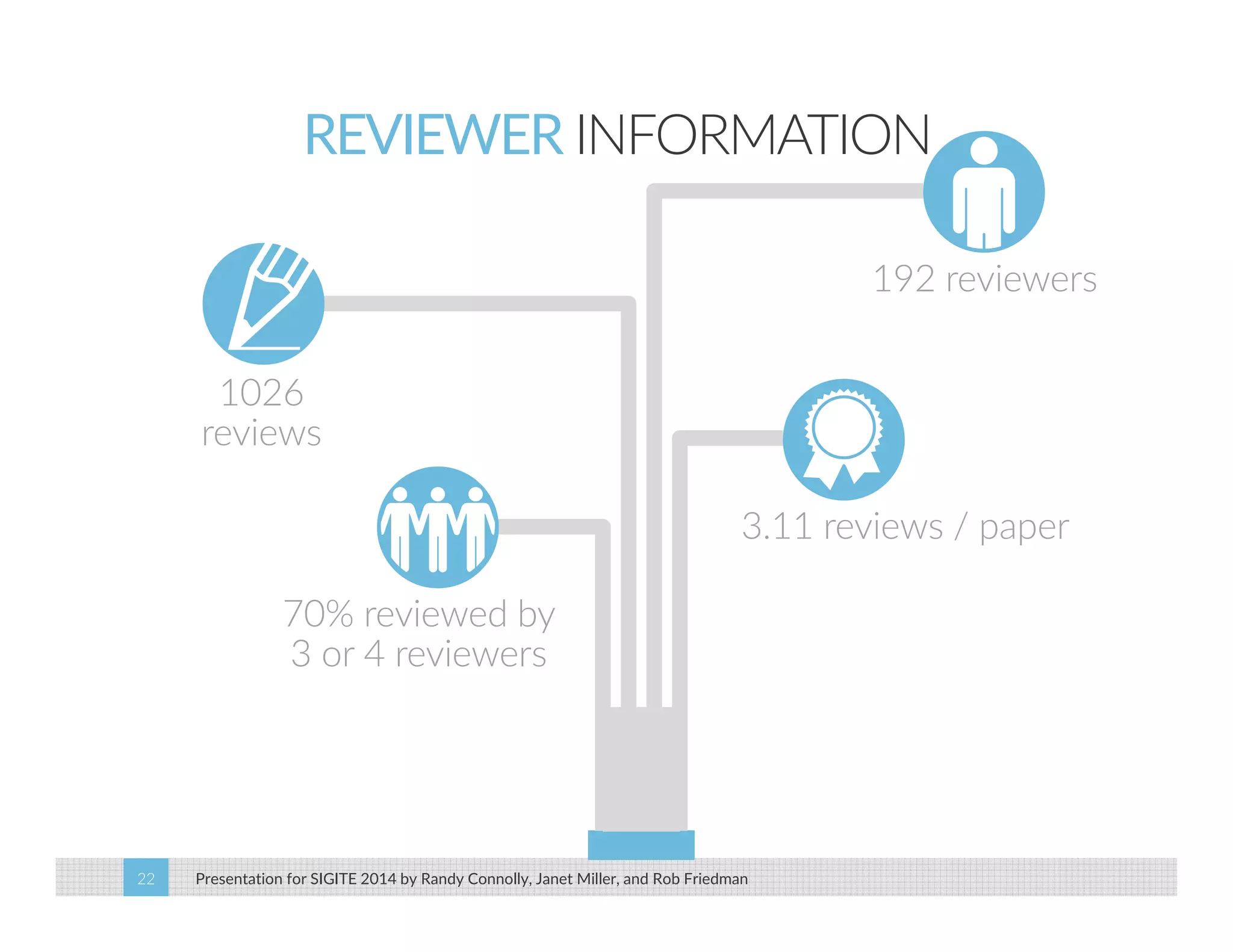
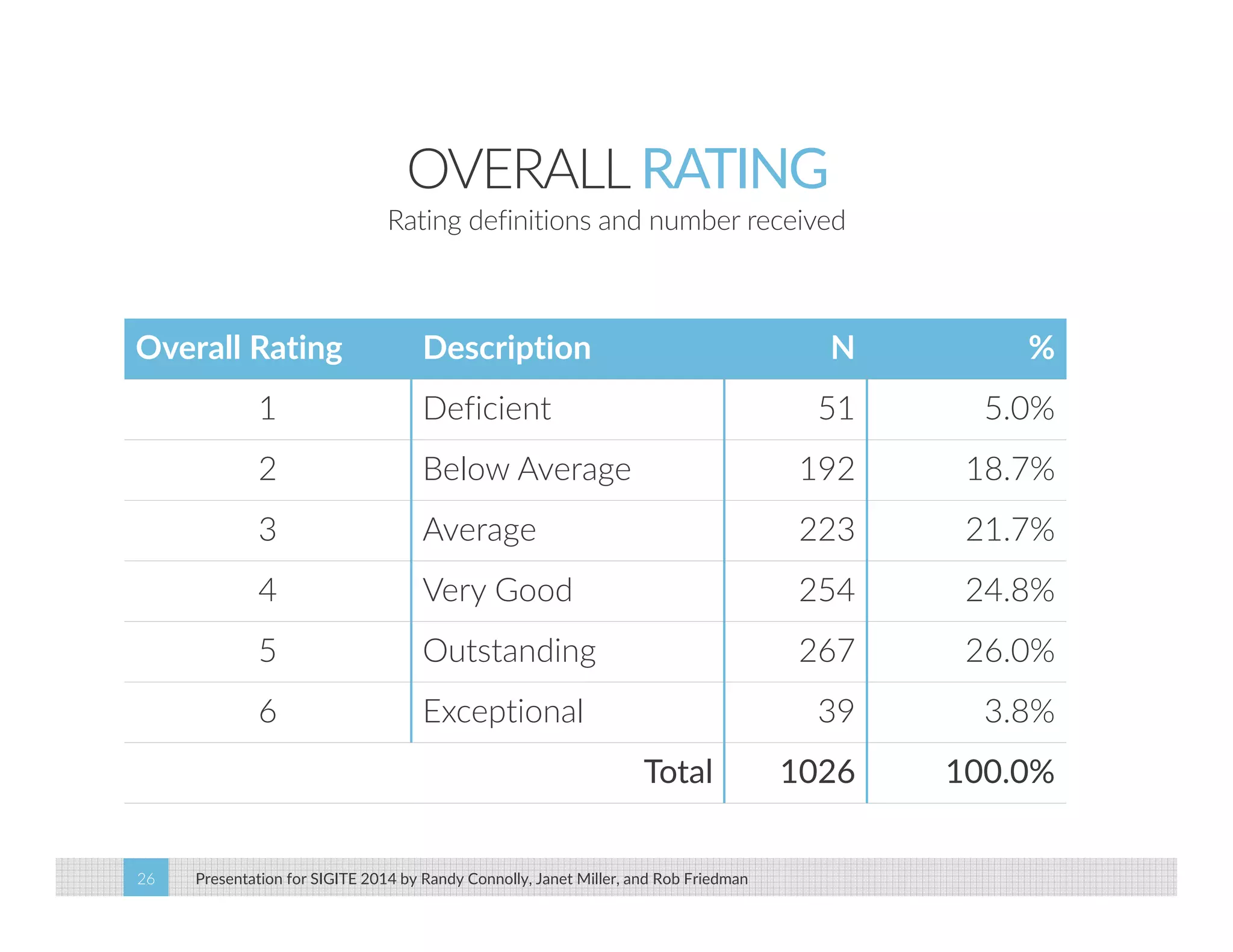
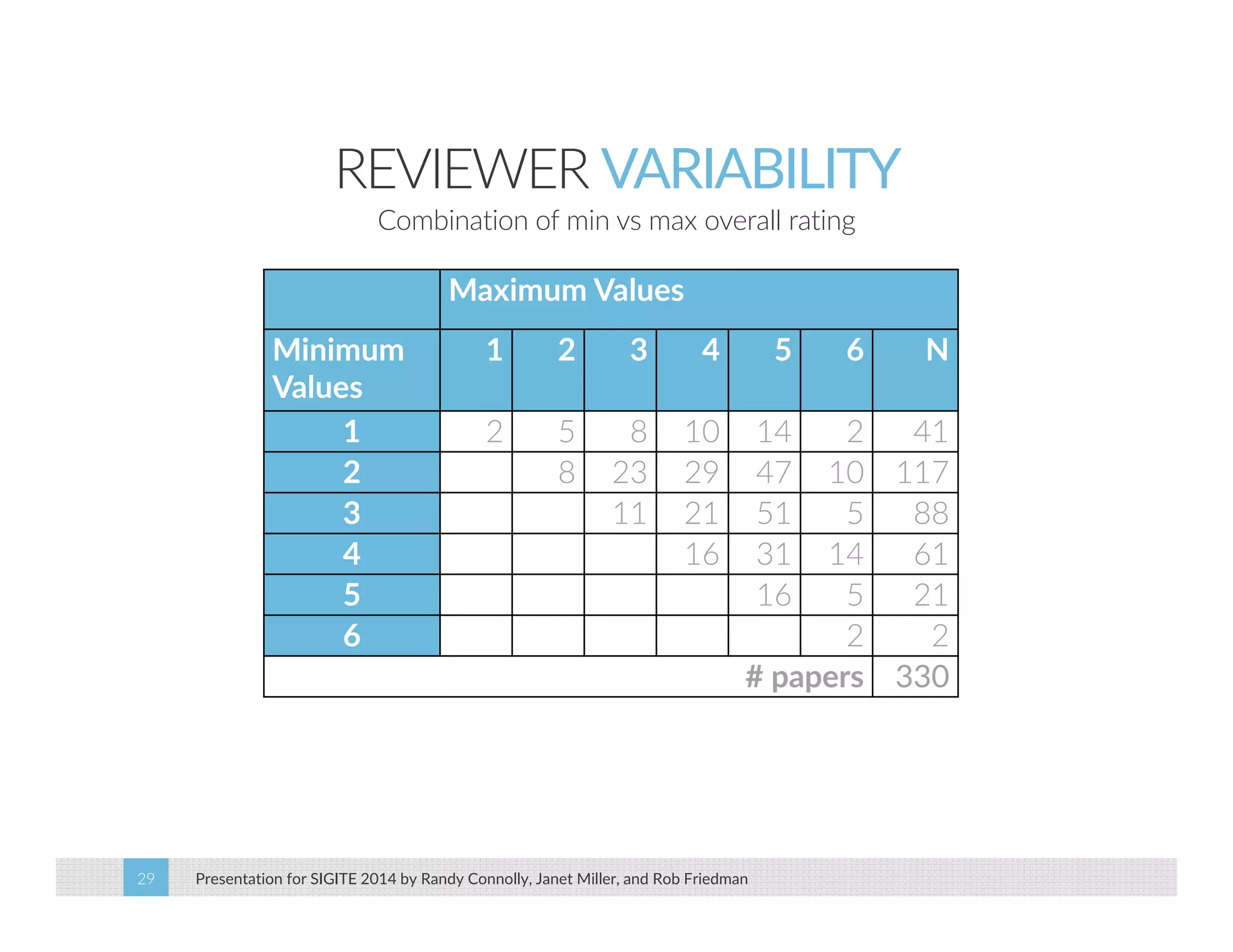
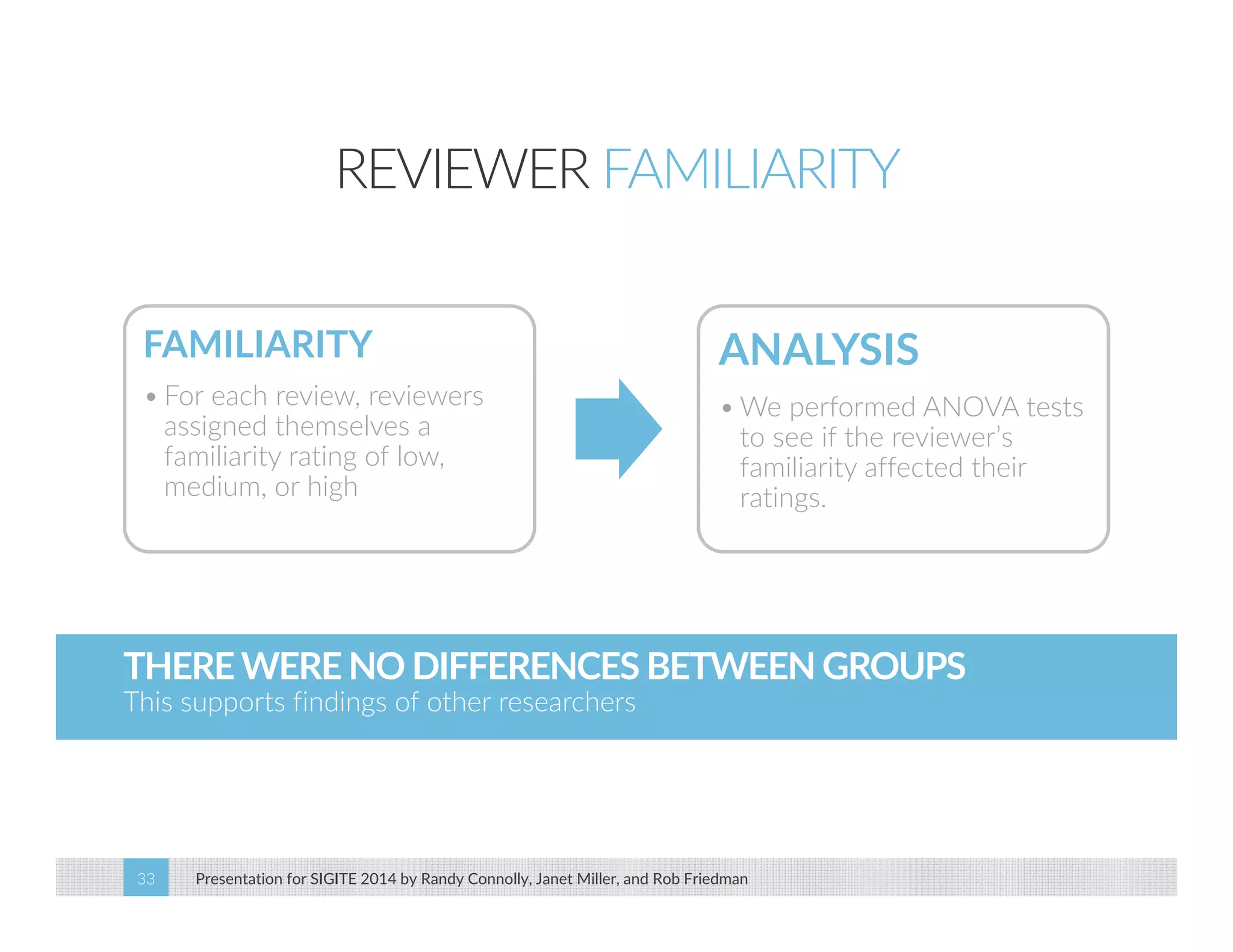
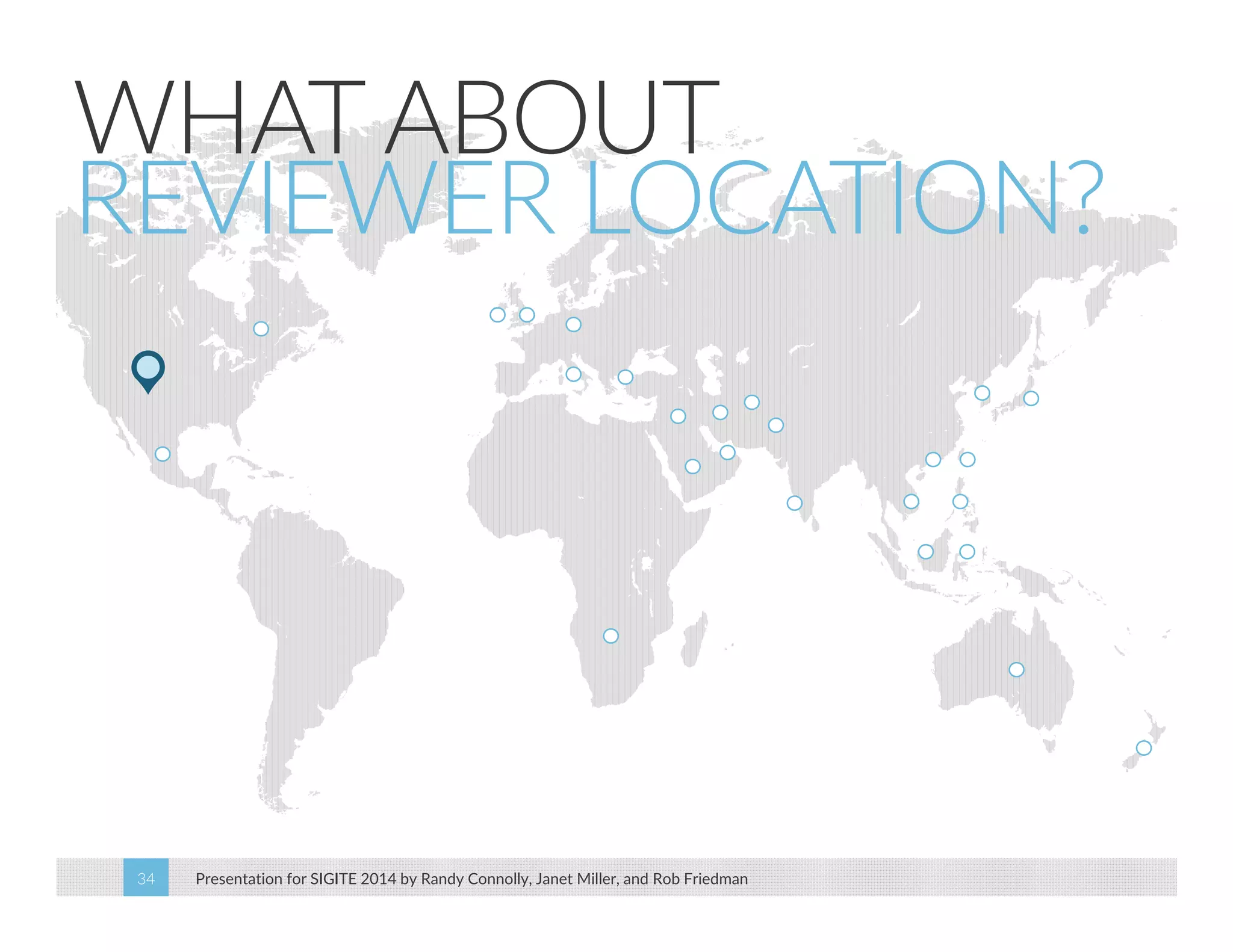
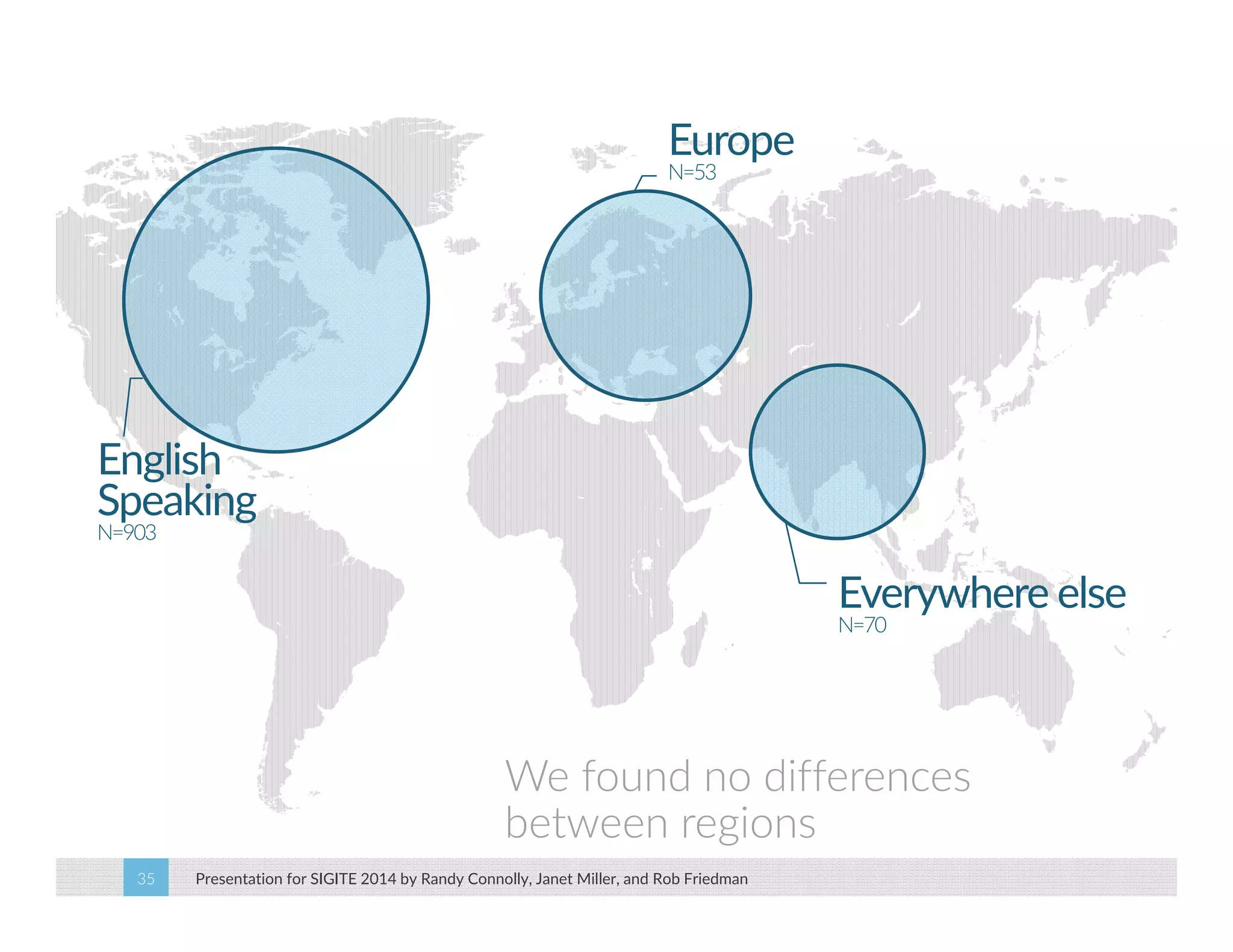
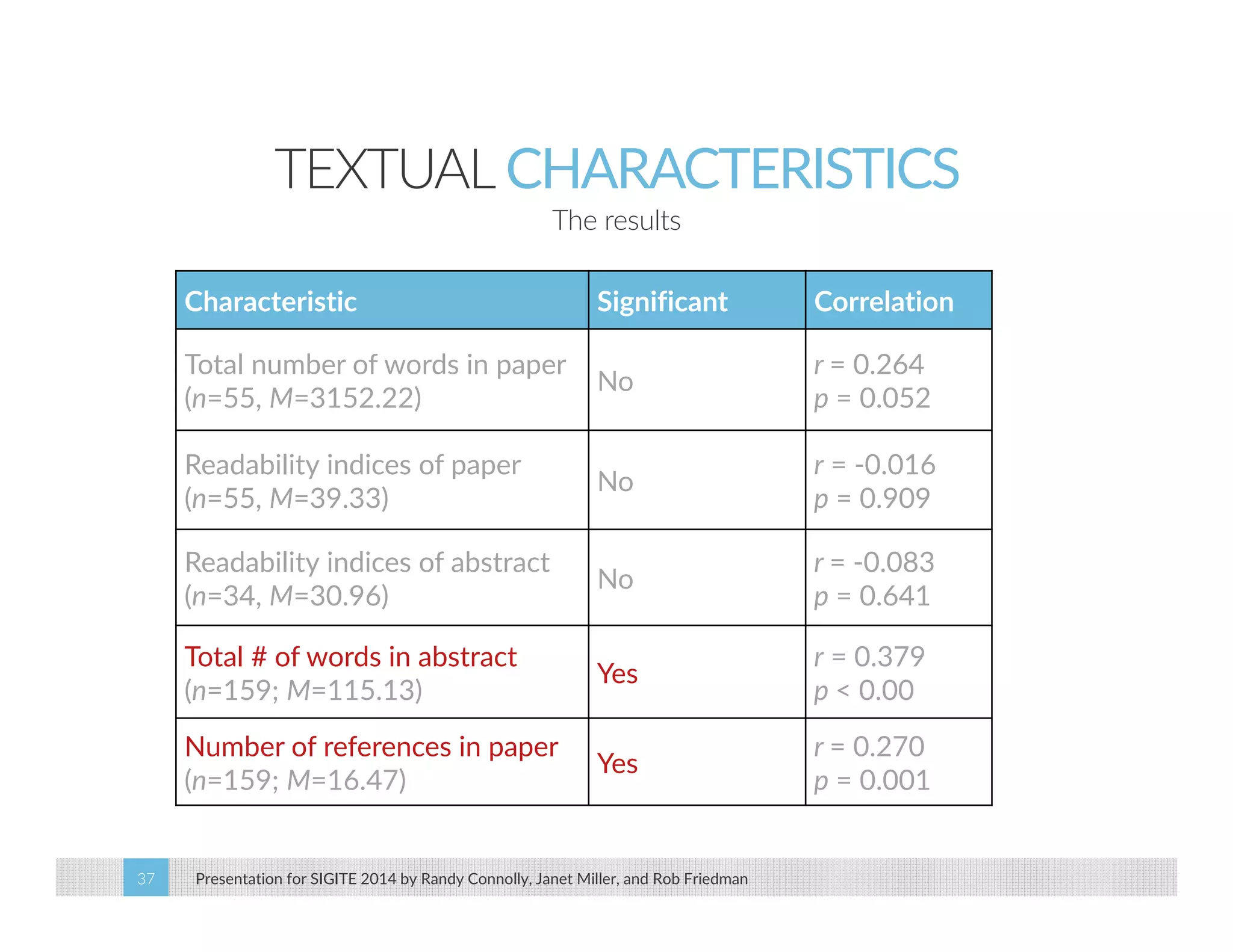
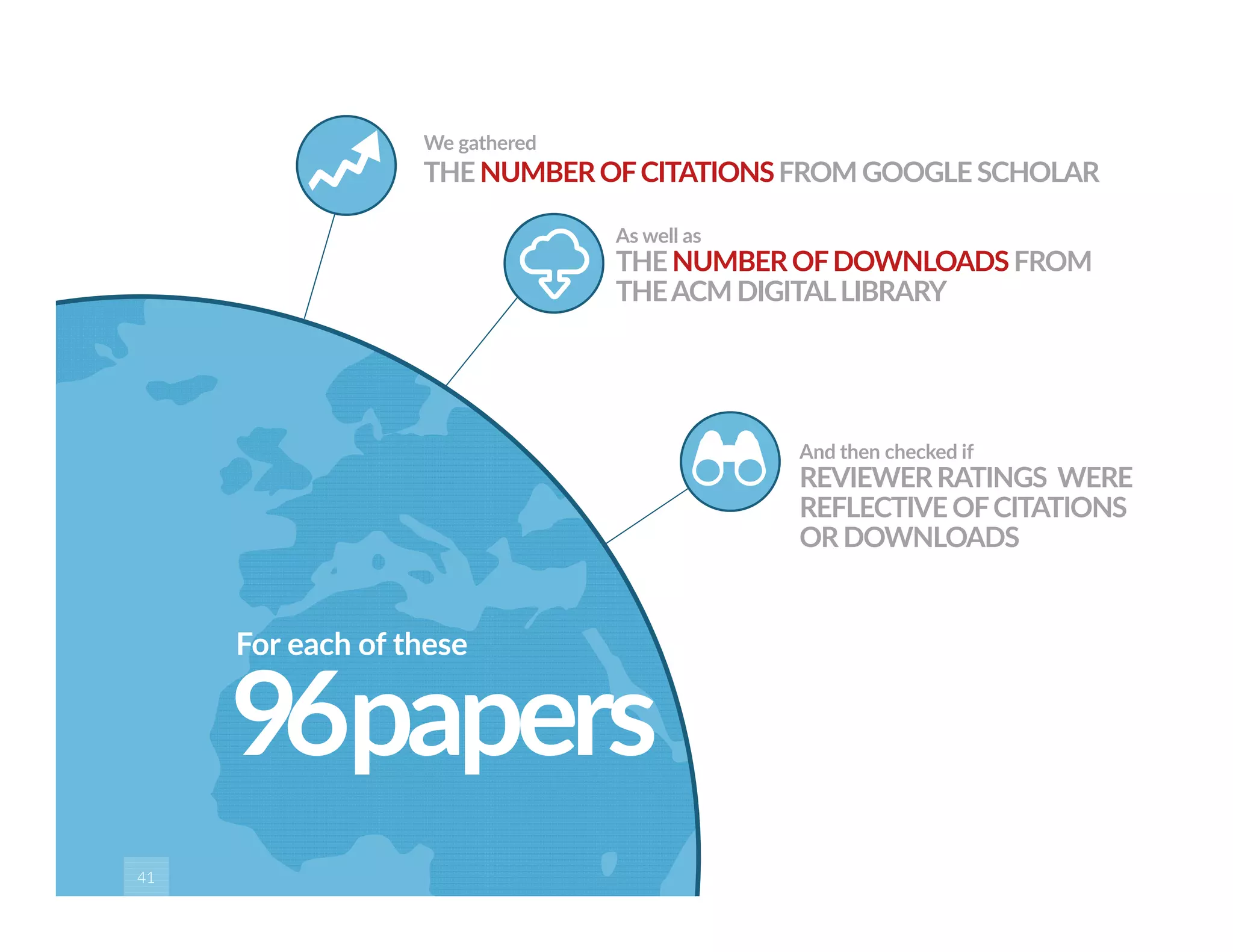
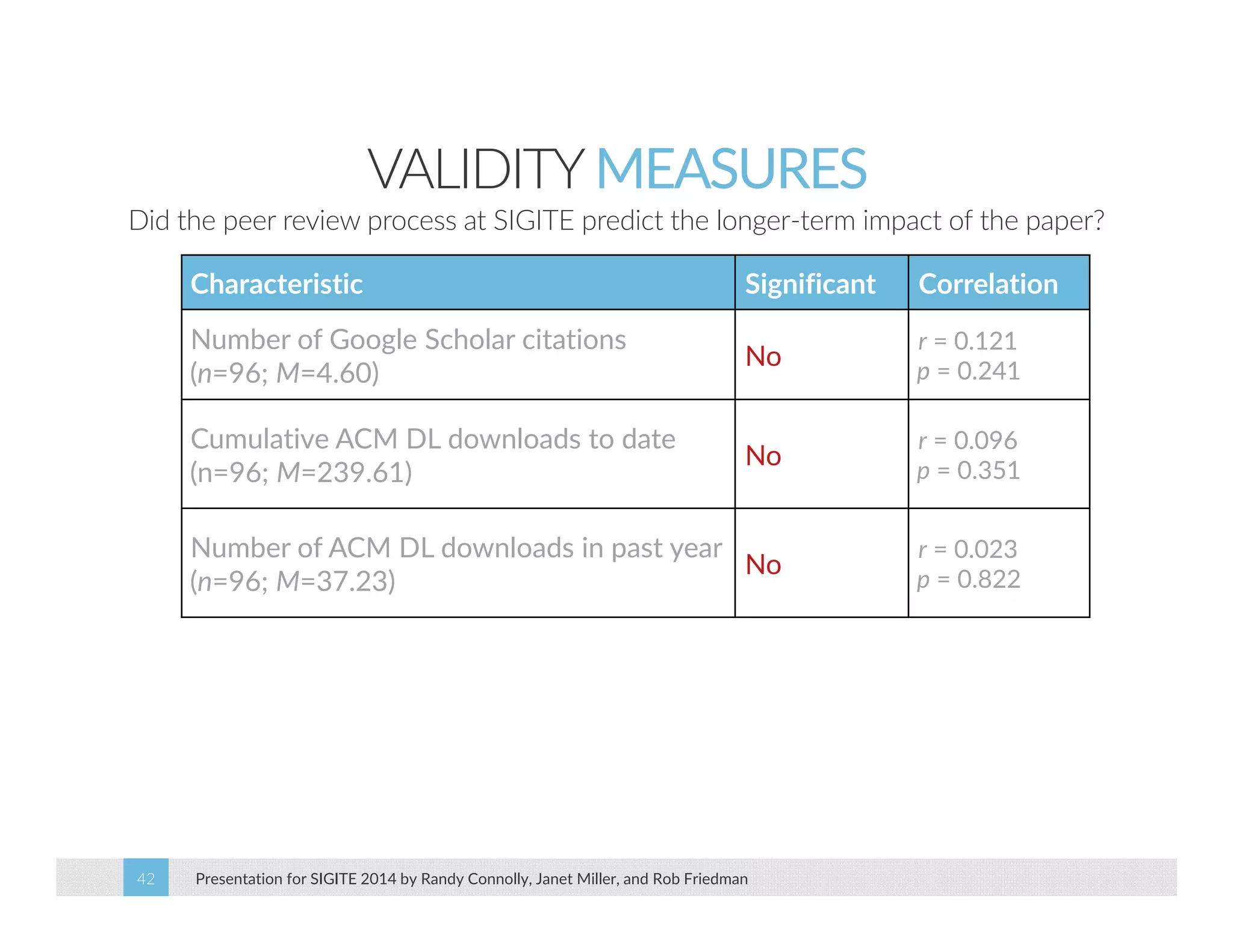
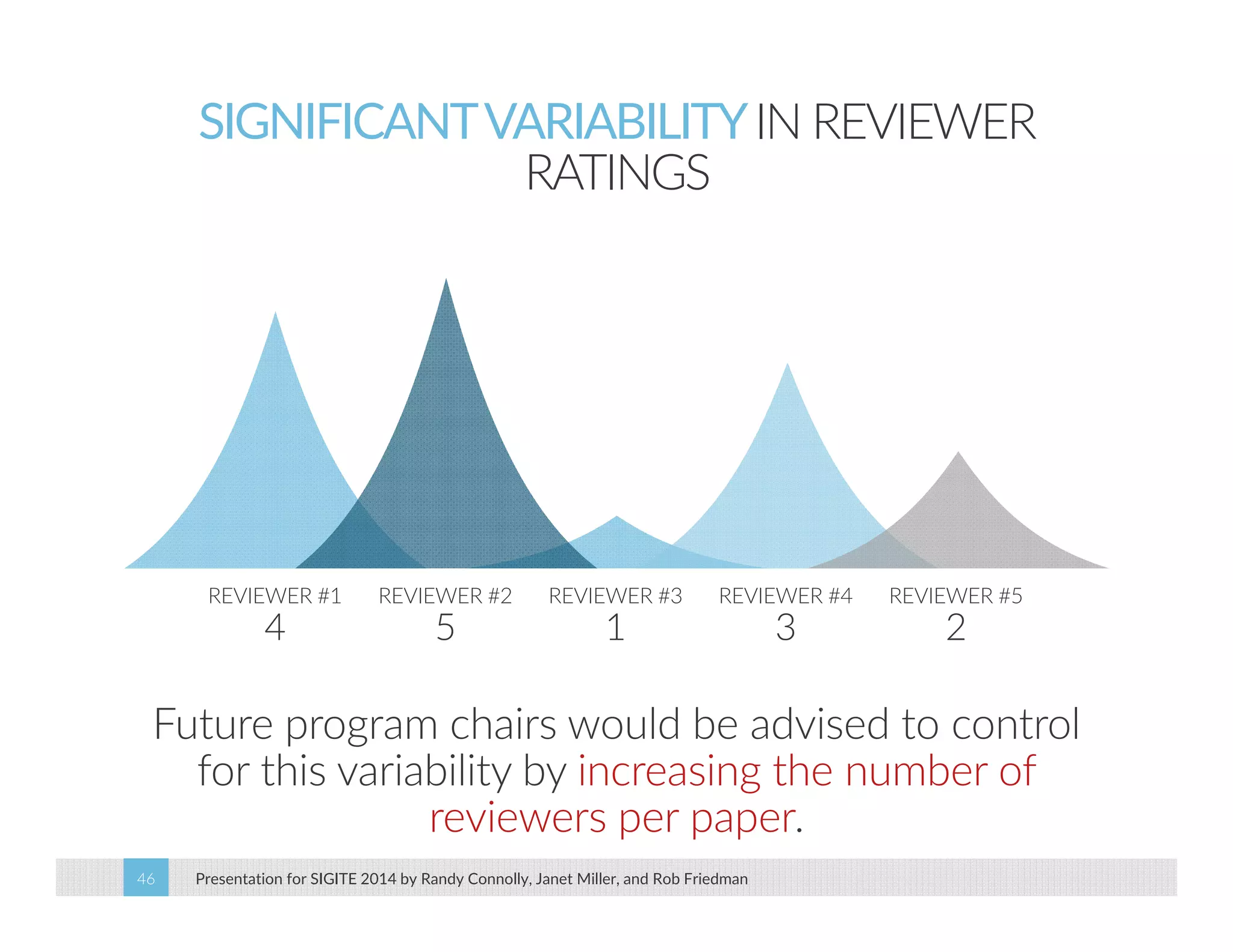
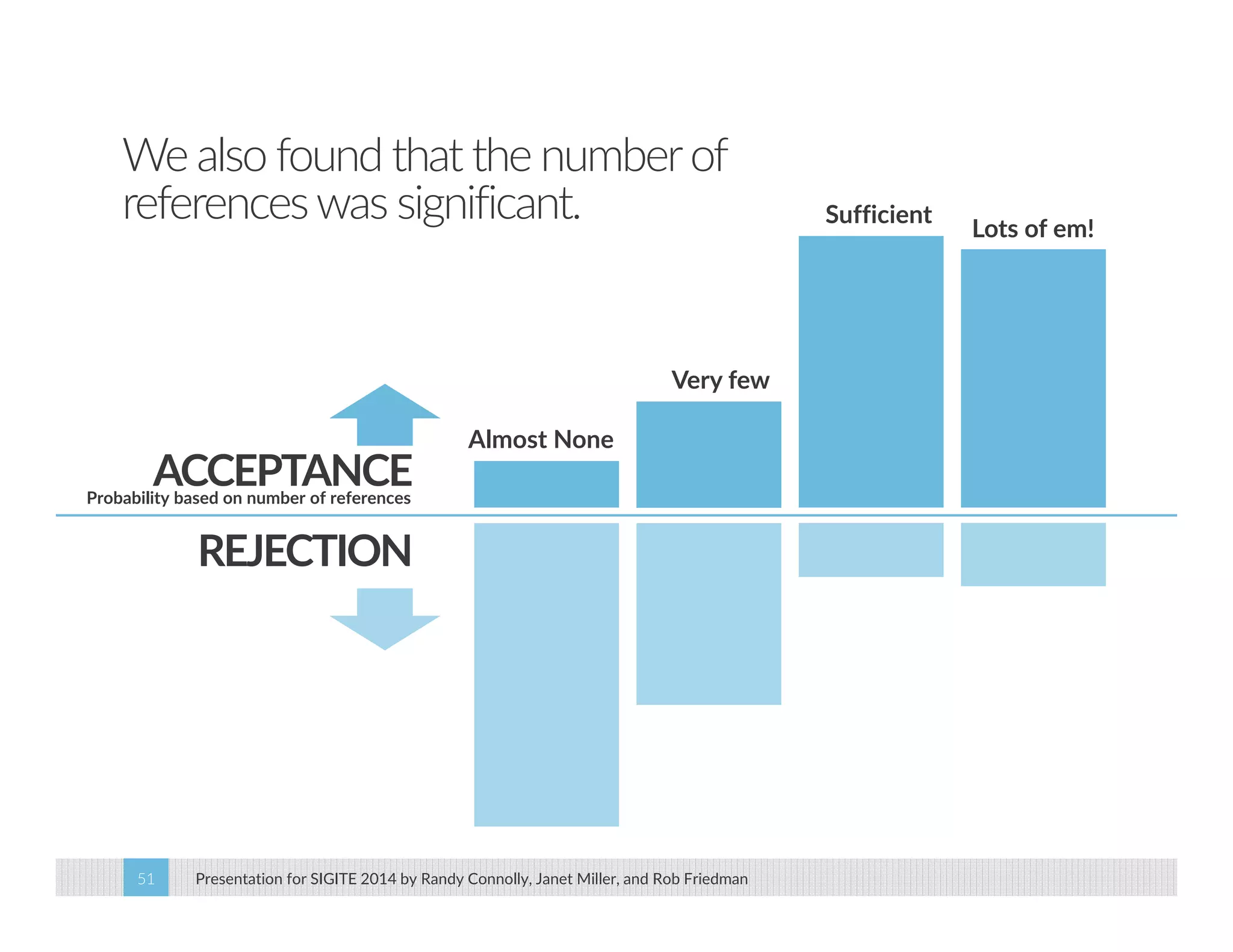
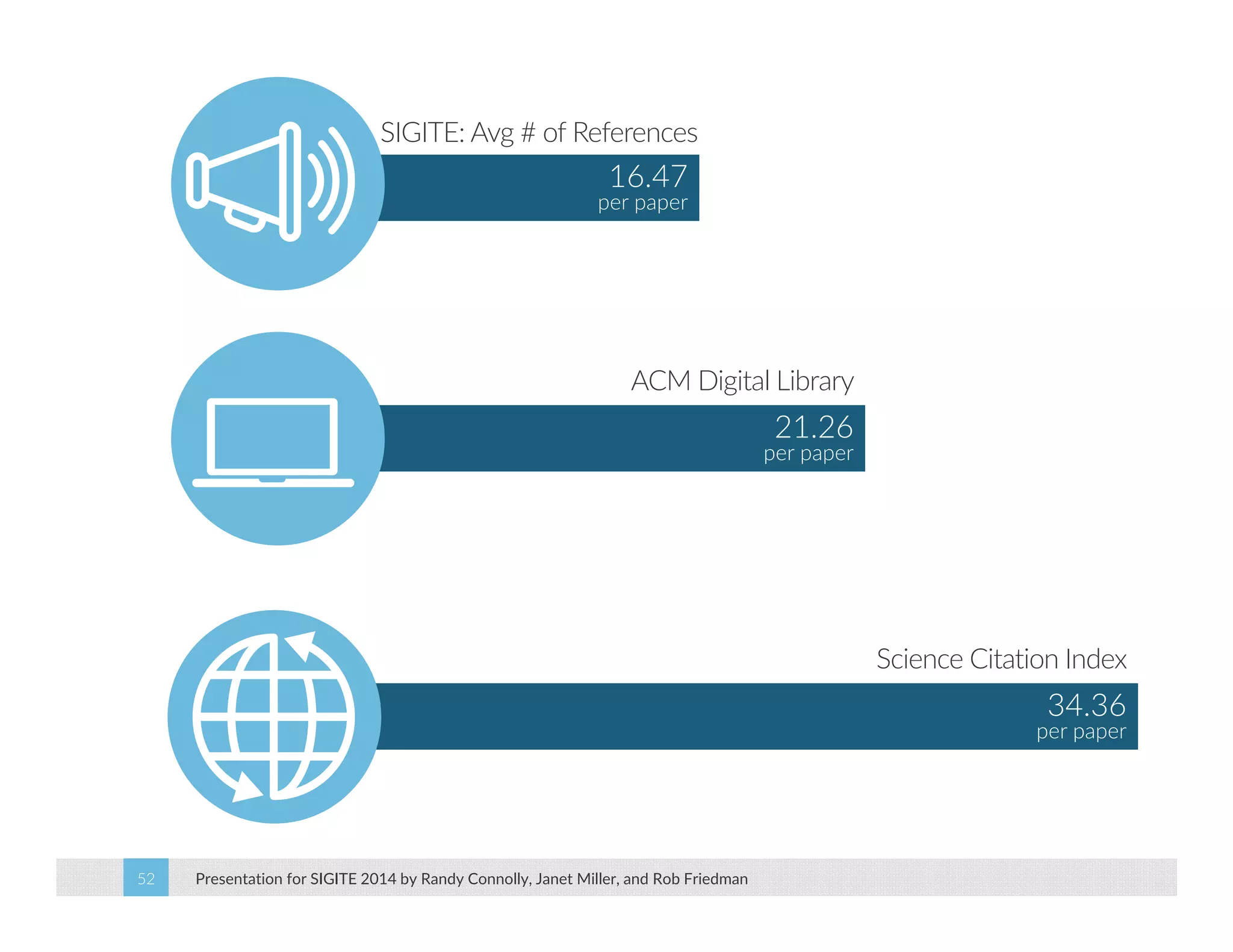
This paper analyzes submission data from the SIGITE conference (2007-2012) to explore factors influencing reviewer ratings and the reliability of the peer review process. It finds a significant variability in reviewer ratings, with characteristics like the number of references and the length of abstracts affecting evaluations, while educational impact metrics like citations had no strong correlation with reviewer ratings. The study calls for future program chairs to increase the number of reviewers per paper to enhance reliability.