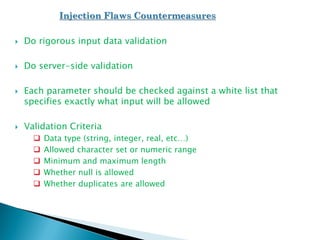
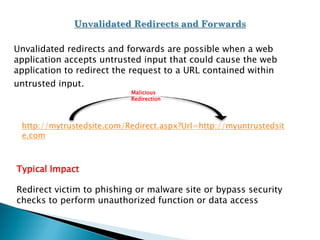
The document discusses the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) and the top 10 web application vulnerabilities according to OWASP. These include injection flaws, broken authentication, cross-site scripting, insecure direct object references, security misconfiguration, sensitive data exposure, missing access controls, cross-site request forgery, use of vulnerable components, and unvalidated redirects/forwards. It provides details on each vulnerability and recommendations for countermeasures.