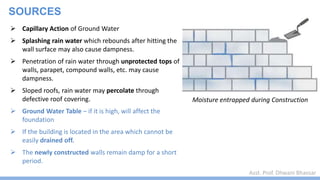
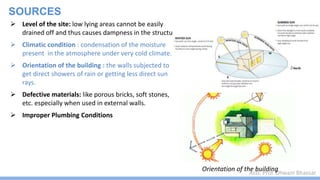
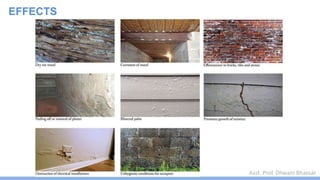
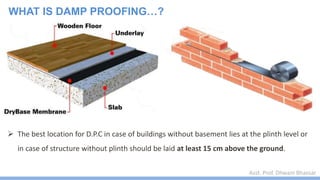
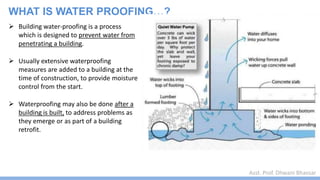
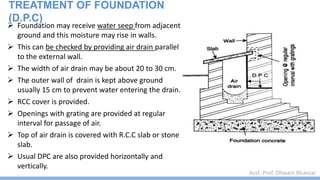
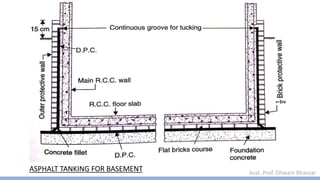
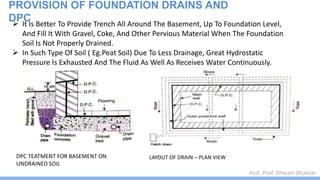
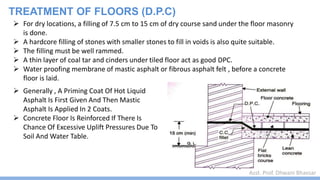
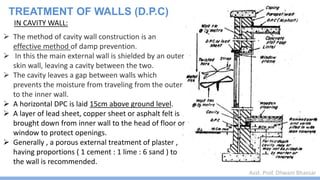
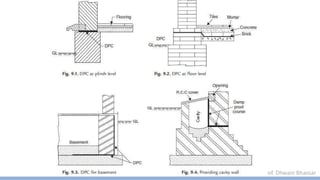
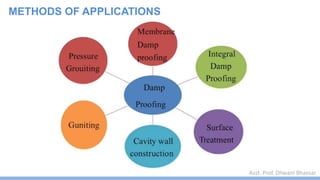
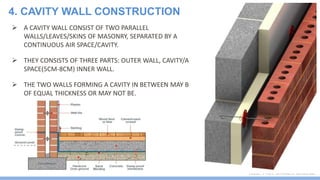
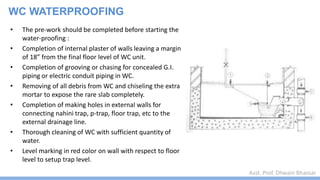
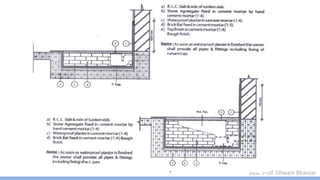
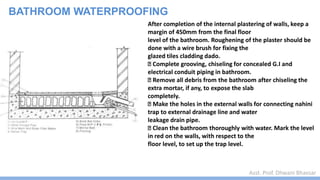
This document discusses damp proofing and water proofing methods for buildings. It defines dampness as moisture in the air or on surfaces and identifies various sources like capillary action, rain penetration, and trapped moisture during construction. Damp proofing is used to slow water passage into foundations, walls and floors, while water proofing completely prevents absorption and is used for areas like bathrooms. Common materials used include bitumen, asphalt felt, concrete and mortar applied as coatings or horizontal barriers. The effects of dampness and treatments for areas like foundations, basements, floors and walls are described.