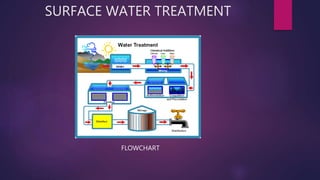
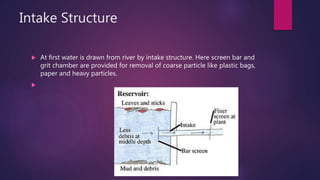
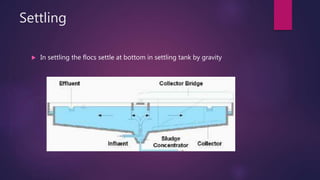
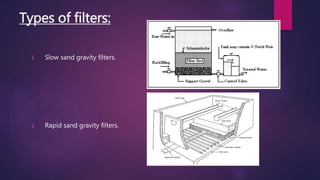
Surface water treatment involves several steps: (1) intake of water from rivers through screens and grit chambers, (2) addition of chemicals like chlorine, lime, and alum through rapid mixing, (3) coagulation through slow mixing to form and densify flocs, (4) settling of flocs in tanks, (5) filtration through granular materials to remove particles, and (6) disinfection through chlorination to remove pathogens before distribution. Proper treatment is essential to make surface water potable and safe for human consumption.