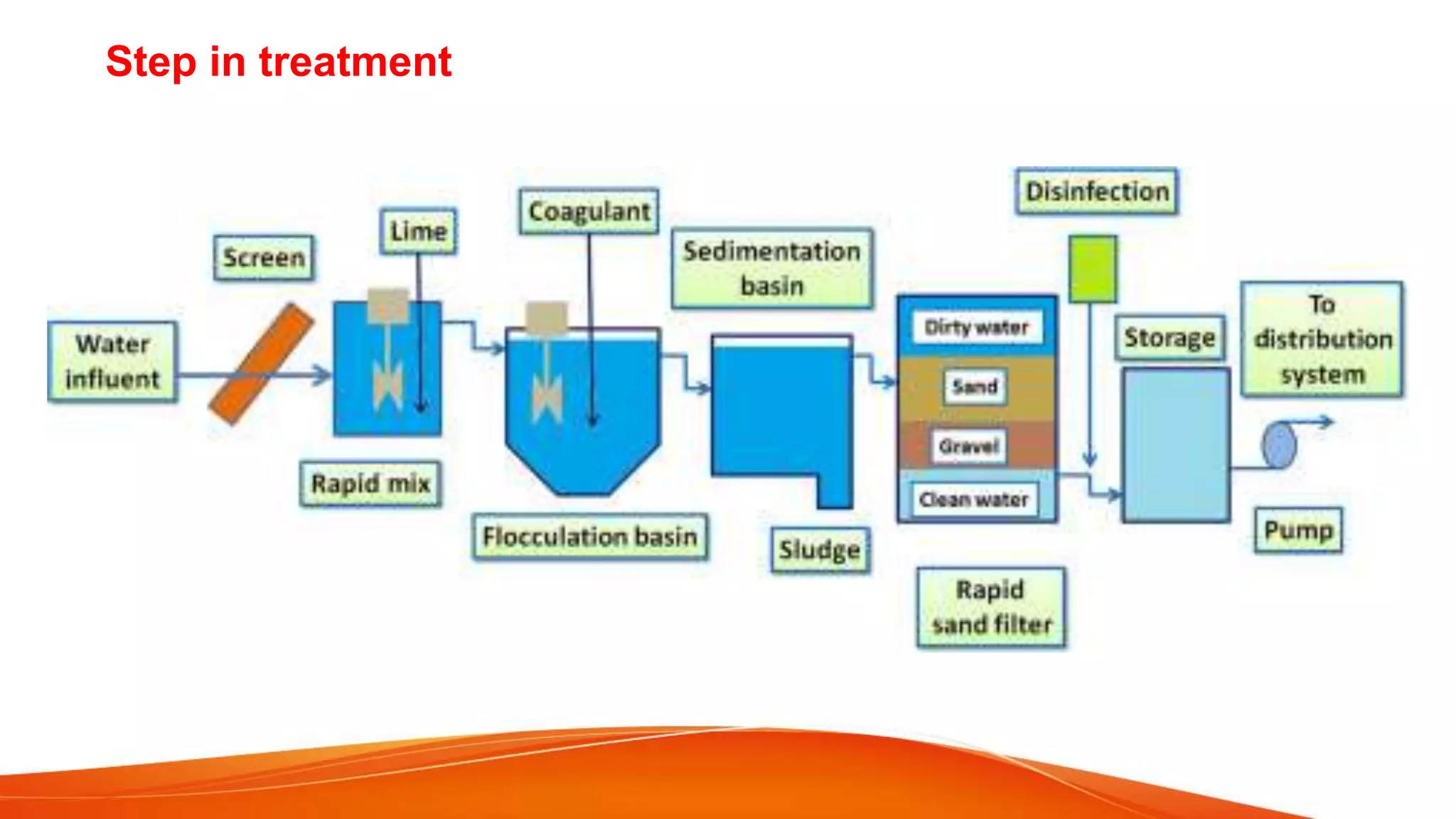
The document describes the process of drinking water treatment, which enhances water quality for various uses by removing contaminants through chemical, physical, and biological methods. Key processes include screening, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection, utilizing various chemicals to promote the clumping of particles and ensuring the removal of pathogens. Different types of filters and their respective methods are also detailed, highlighting the complexities and operational requirements of the treatment systems.