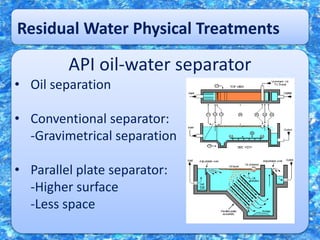
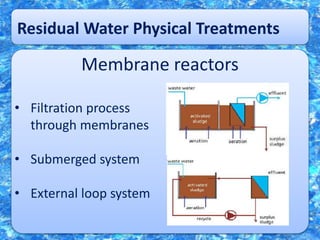
Water is essential for life but limited on Earth. It is important to recycle and purify water to ensure a sustainable supply for human use. Various physical, chemical, and biological processes can be used to purify water through processes like filtration, sedimentation, chlorination, and the use of lagoons and reactors to break down organic pollutants using microorganisms. Proper treatment is needed to remove contaminants and pathogens to provide safe drinking water.