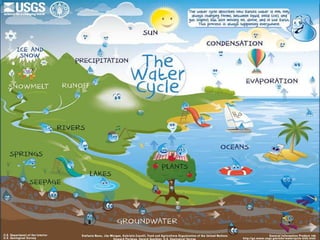
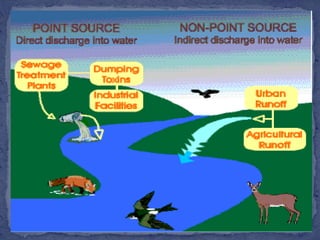
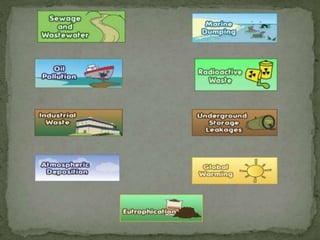
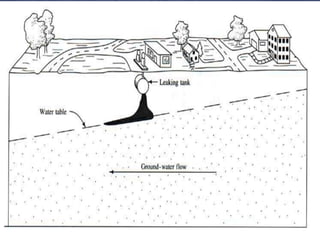
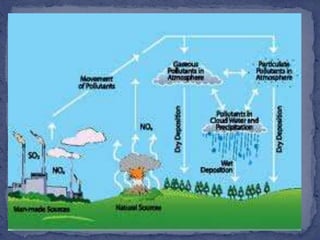
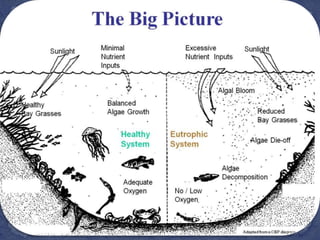
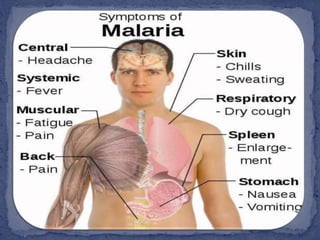
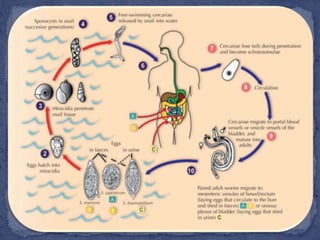
Water covers most of the Earth's surface and is essential for life. While the majority is found in oceans, water pollution from various sources contaminates other bodies of water used by humans and other species. There are two main types of water pollution - point source from identifiable pipes or drains, and non-point source from diffuse runoff. Common causes include untreated sewage, industrial chemicals, acid rain, oil spills, and agricultural runoff. Water pollution harms aquatic plants and organisms and poses health risks to humans such as diarrhea, hepatitis and cholera. Solutions involve cleaning up pollution, preventing new sources, using filtration and bacteria to break down contaminants, and educating people on the issue.