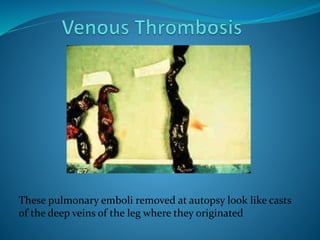
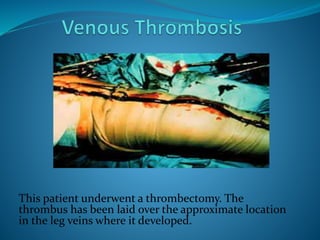
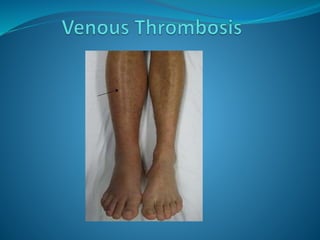
A venous thrombosis occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms inside a vein. Certain genetic factors like mutations in Factor V and prothrombin genes can increase the risk of thrombosis by making the blood more likely to clot. Environmental factors like taking oral contraceptives also increase risk. Deep vein thrombosis, which often originates in the legs, is the most common type of thrombosis and can lead to potentially fatal pulmonary embolisms if clots break off and travel to the lungs. Testing for genetic mutations is recommended for those with a personal or family history of thrombosis, recurrent clots, or clots in unusual areas.