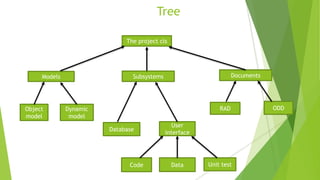
This document defines software configuration items and discusses how to identify them. It states that configuration items include any hardware, software, or documents related to a software project's development, such as code files, test drivers, design documents, manuals, and system configurations. Large projects can produce thousands of potential configuration items, so an entity naming scheme should be used to uniquely identify and relate items. Common configuration items include requirements, design documents, source code, test data, and support software. Once identified, configuration items are typically organized in a tree structure.