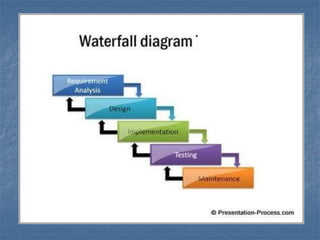
The document discusses the waterfall process model, including its history, definition, phases, advantages, disadvantages, and when it should be used. The waterfall model is a sequential software development process in which each phase must be completed before the next begins, with phases including requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. It is simple to understand but not suitable for complex or long-term projects where requirements may change.