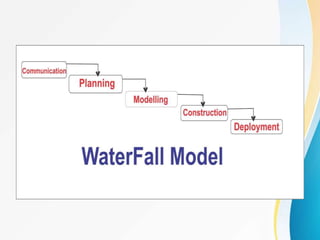
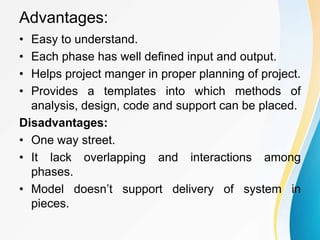
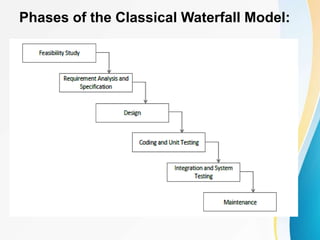
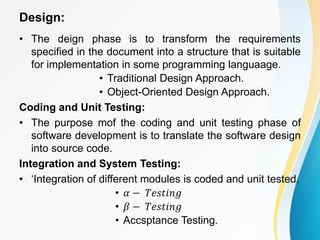
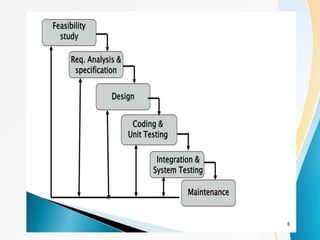
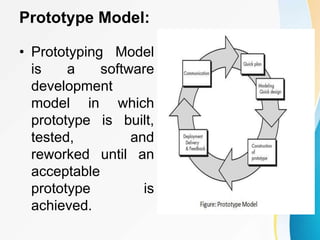
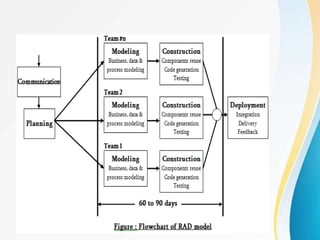
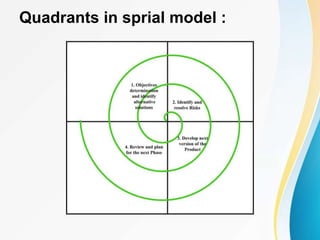
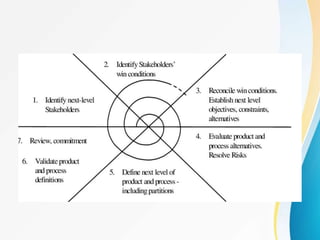
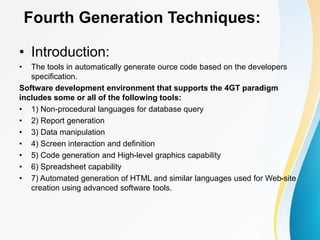
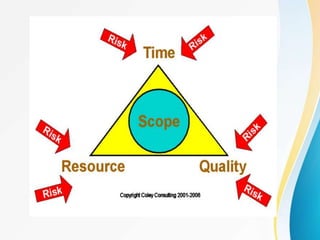
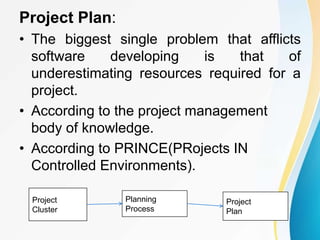
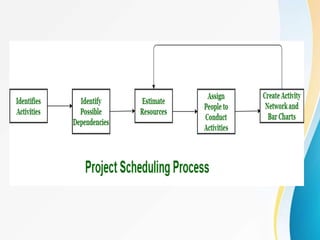
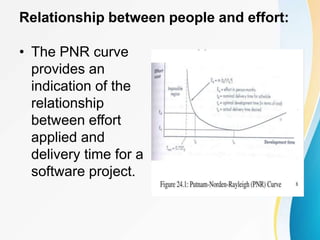
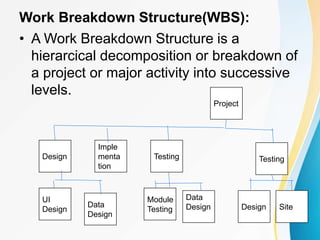
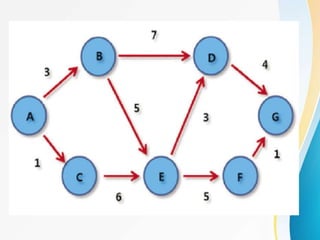
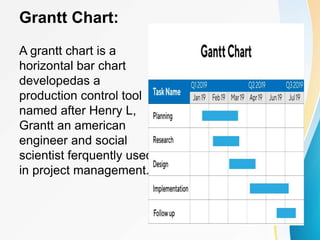
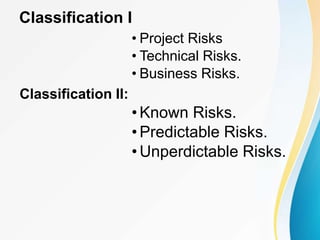
This document outlines the topics covered in five units of a Software Engineering course. Unit I introduces software engineering paradigms like waterfall and spiral models. Unit II covers software design concepts like abstraction and modularity. Unit III discusses software testing and maintenance. Unit IV covers software metrics and quality assurance. Unit V focuses on software configuration management. Key concepts covered include software development lifecycles, risk analysis, requirements engineering, and project planning techniques.