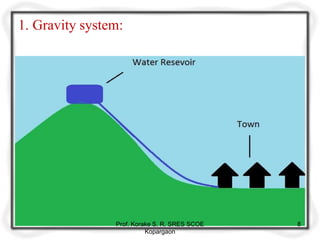
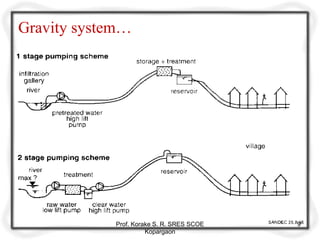
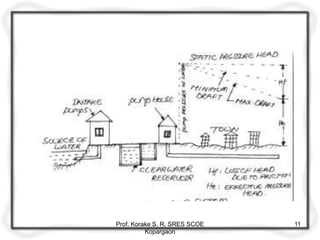
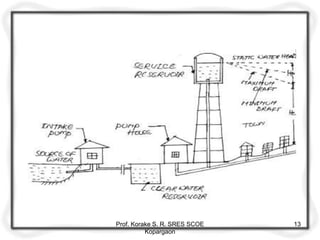
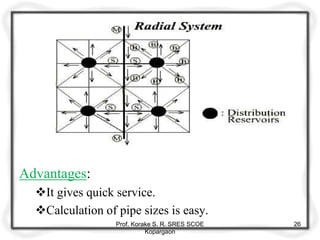
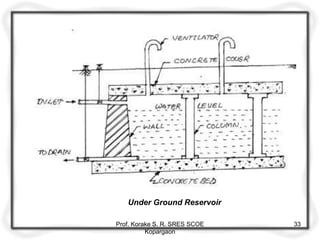
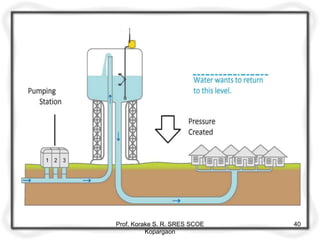
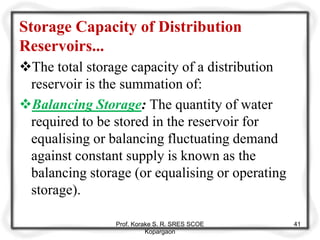
The document provides an overview of water distribution systems, detailing the layout, methods, and storage capacities necessary for effective water supply to consumers. It discusses various distribution methods such as gravity, pumping, and combined systems, along with the requirements for a good distribution system, types of reservoirs, and recommendations for minimum pipe sizes. Additionally, it covers the storage capacities needed for regular supply, emergencies, and fire safety.