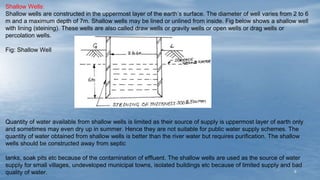
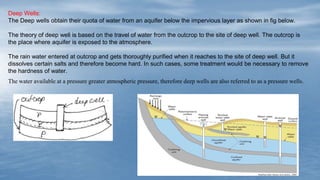
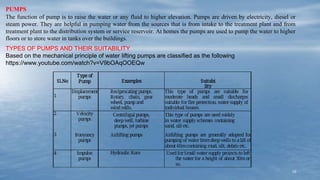
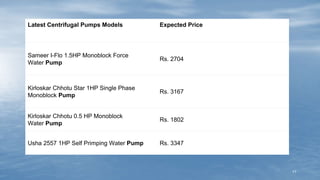
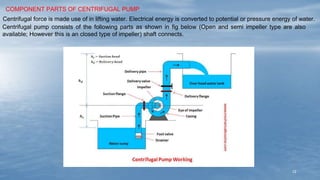
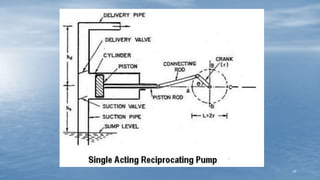
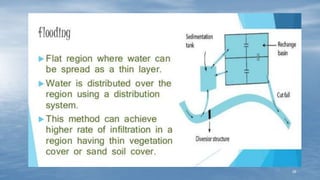
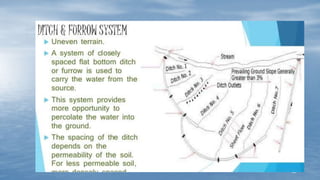
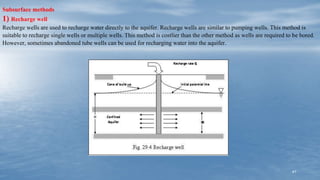
The document discusses various methods of groundwater development including wells, tube wells, artesian wells, and dug wells. It provides details on the construction and functioning of shallow wells, deep wells, tube wells, and artesian wells. The document also discusses different types of pumps used for extracting groundwater including centrifugal pumps and reciprocating pumps. It compares the working and components of centrifugal and reciprocating pumps. Finally, the document talks about various techniques for artificial groundwater recharge including percolation tanks, flooding, contour bunds, and recharge wells.