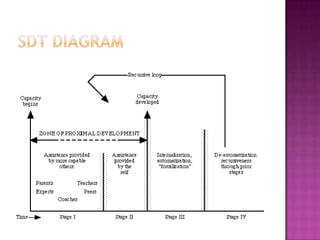
The Social Development Theory argues that social interaction precedes development and causes cognitive development. It was developed by Lev Vygotsky, who believed that learning occurs in the Zone of Proximal Development, which is the distance between what a learner can do independently and with guidance. In the Zone of Proximal Development, a More Knowledgeable Other, such as a teacher, helps guide the learner's development. According to the theory, teachers should first have students work collaboratively in groups when learning new concepts before doing independent work to reinforce the ideas on their own.