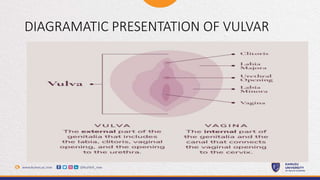
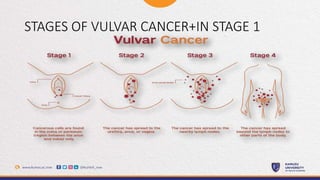
This document provides information about vulvar cancer, including its description, risk factors, signs and symptoms, prevention, treatment, and terminal care. It aims to educate participants on vulvar cancer by describing what it is, how it can be prevented through lifestyle changes and vaccination, how it presents, and the treatment and palliative options depending on the stage of cancer. The focus is on providing a comprehensive overview of vulvar cancer to improve understanding.