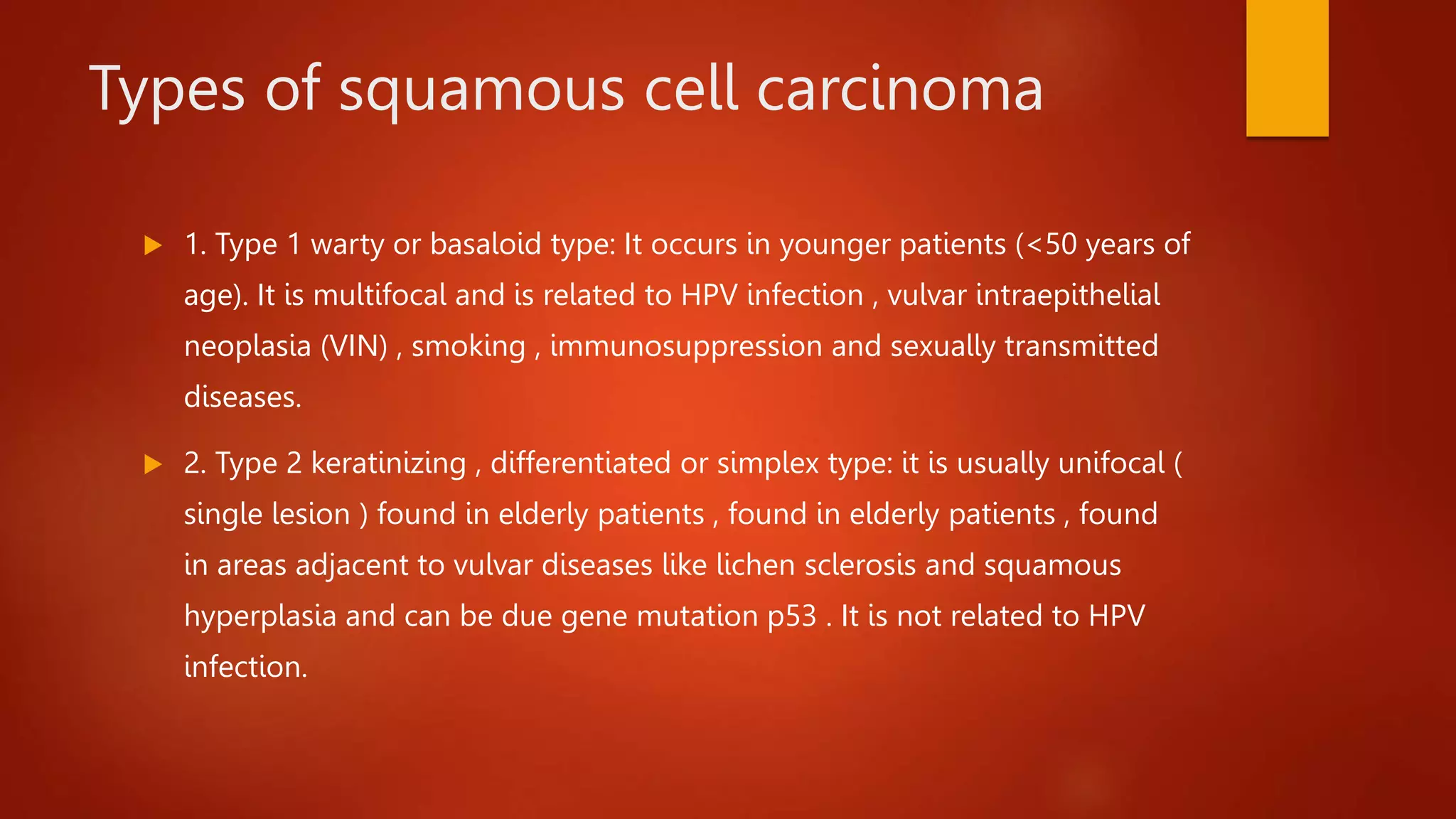
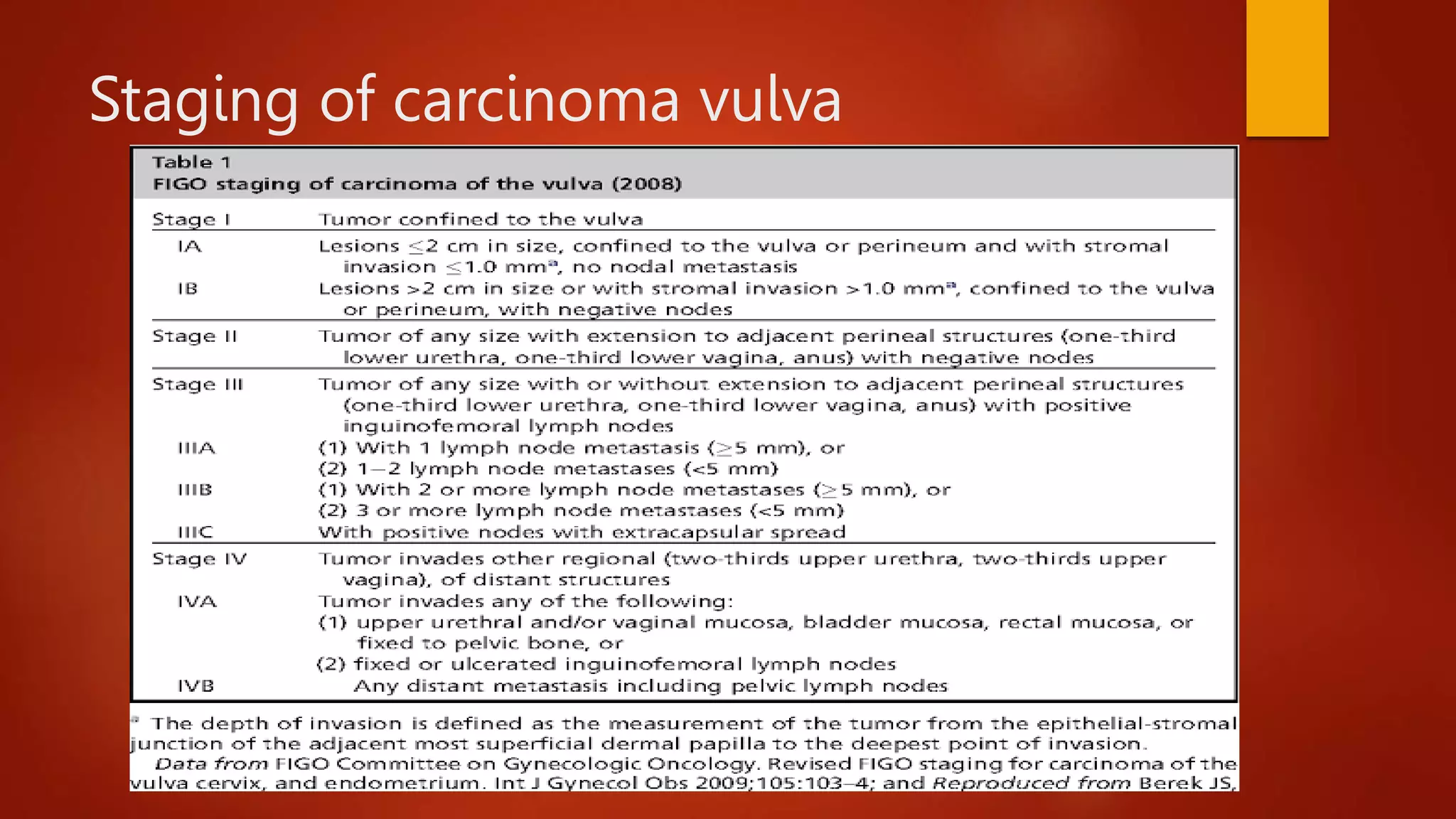
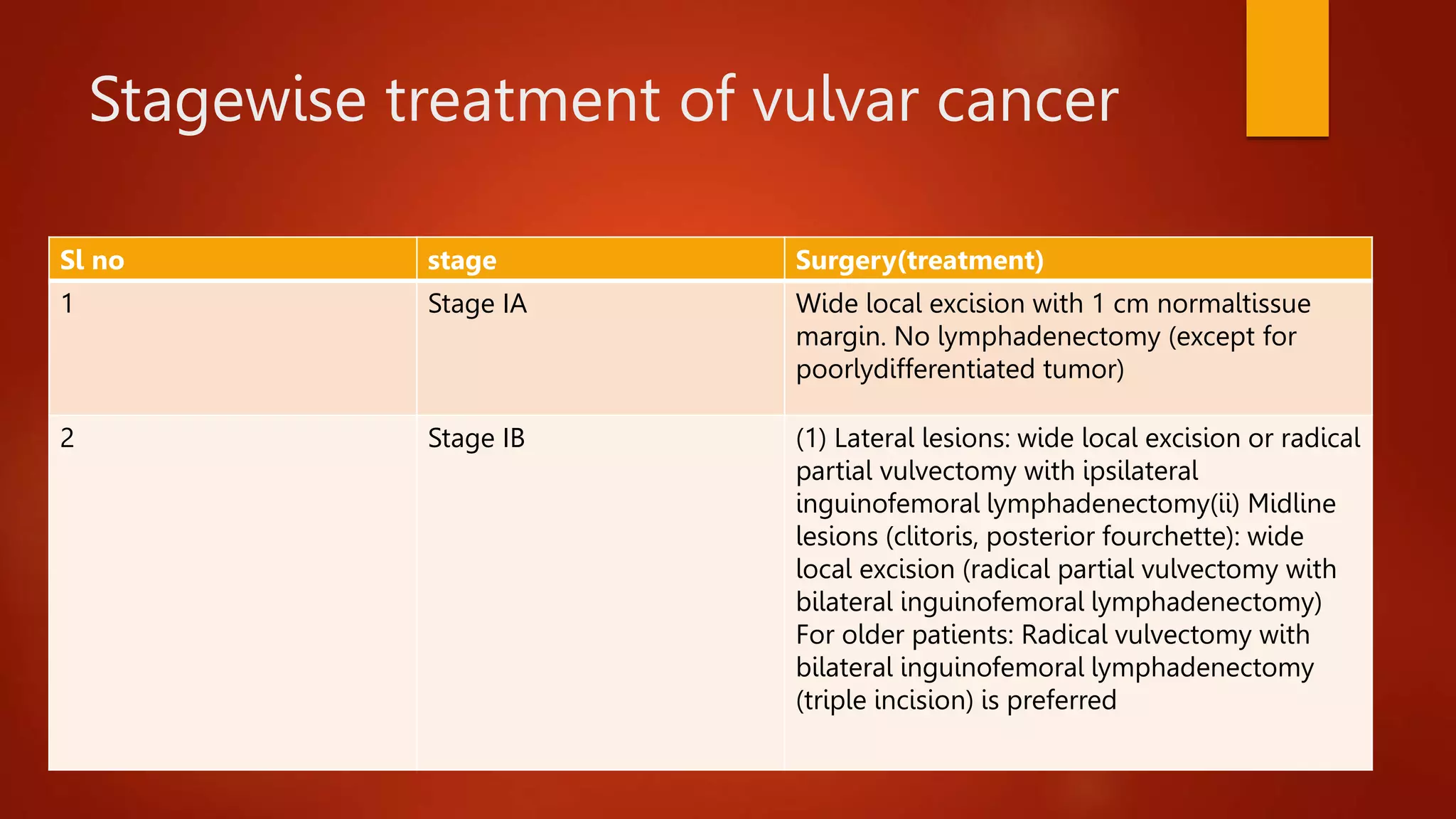
Vulvar cancer is an uncommon gynecological cancer that mainly affects elderly women. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type, comprising 92% of cases. Lymphatic drainage occurs to ipsilateral lymph nodes but some areas can drain to bilateral nodes, facilitating spread. Diagnosis is by biopsy and treatment involves wide local excision or radical vulvectomy with lymph node dissection. Prognosis depends on stage, with 5-year survival rates of 90% for stage I but only 11% for stage IVB.