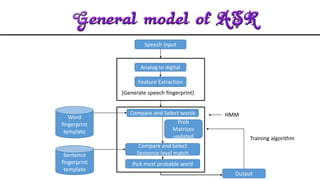
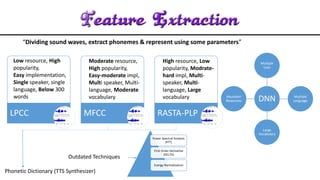
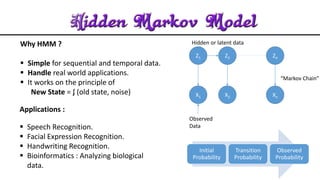
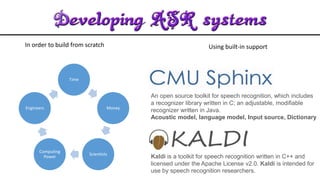
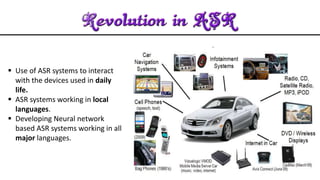
The document discusses acoustic speech recognition techniques. It provides an introduction and historical survey, then describes the general model of ASR which involves feature extraction and hidden Markov models. It notes the development of early systems in the 1950s-1980s and more recent neural network approaches. The document advocates for expanding ASR systems to support local languages to improve human-machine interaction and information access for more people.