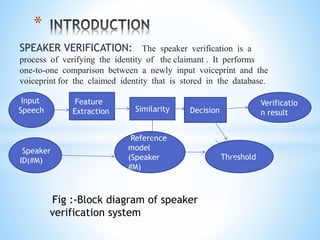
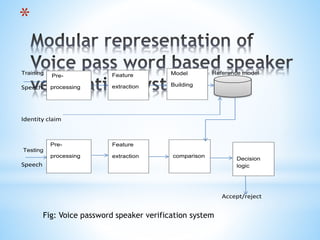
1) The document presents a literature review and proposal for a speaker verification system using voice passwords under guidance of Dr. G. Pradhan at NIT Patna.
2) The goals are to develop a text-independent speaker verification system that can perform well with short speech samples in limited data conditions by modeling speaker information and reducing phonetic variability.
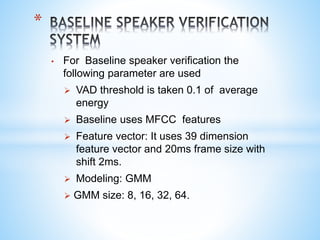
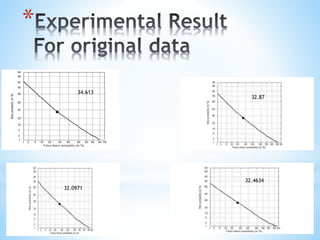
3) Baseline experiments use MFCC features with GMM modeling, achieving better performance with more Gaussian mixtures; future work will explore other features and modeling techniques to improve robustness to mismatches.






![*Literature
• Research in the field of speaker recognition was initially
carried out in 1950s in Bell laboratories using isolated digites
[1].
• In 2000 most of the research was describe the major elements
of Gaussian mixture model (GMM)-based speaker verification
system used successfully in several NIST Speaker Recognition
Evaluations(SREs).
• 1960-1990 most of the research was focused on extraction of
speaker specific information from the speech data, and
development of text dependent speaker verification system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt3-150624180230-lva1-app6891/85/DEVELOPMENT-OF-SPEAKER-VERIFICATION-UNDER-LIMITED-DATA-AND-CONDITION-10-320.jpg)