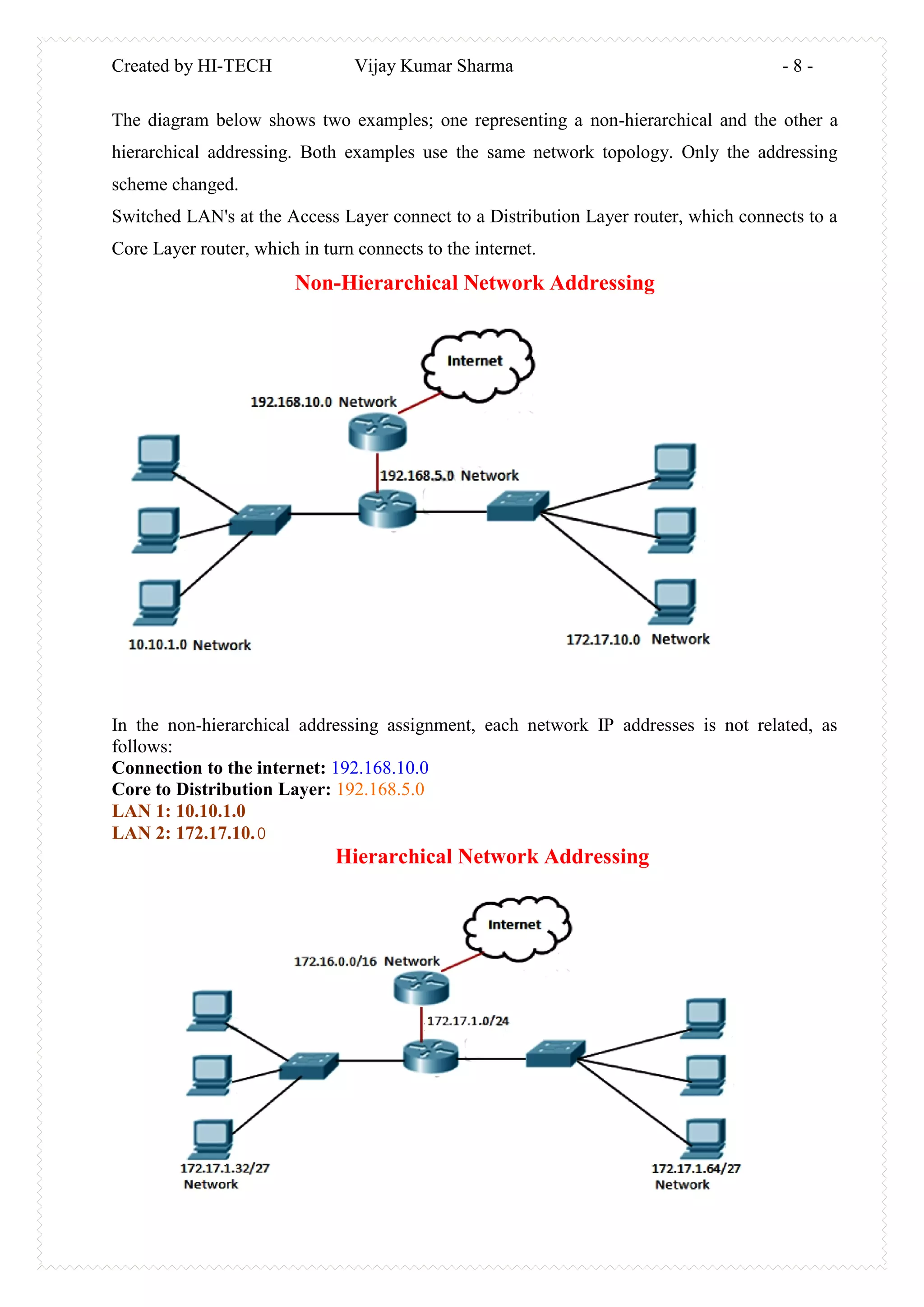
This document discusses Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM) and IP addressing. It begins with an overview of IP addressing fundamentals like IP address format and classes. It then explains that VLSM allows using different subnet masks for subnets of the same network, such as long masks for small subnets and short masks for large subnets. The rest of the document delves deeper into topics like hierarchical network design, subnetting, and implementing VLSM.