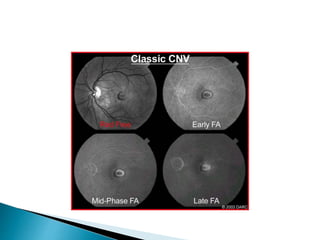
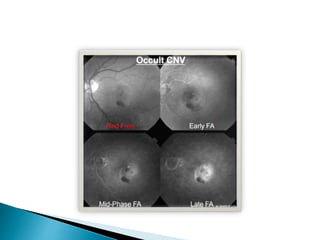
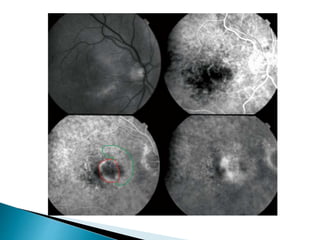
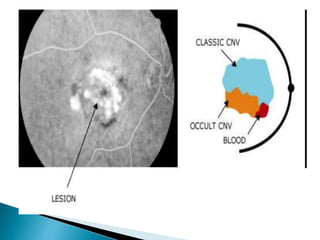
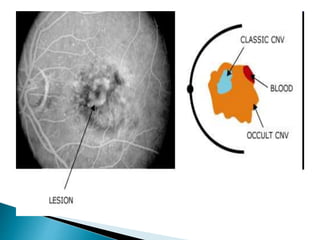
This document discusses characteristics, types, diagnosis, and treatment of choroidal neovascularization (CNV). It describes signs of CNV seen on examination including vision changes, scotomas, and drusen. Types of CNV identified on fluorescein angiography include classic, occult, and retinal angiomatosis proliferans. Treatment options discussed include anti-VEGF drugs like ranibizumab and aflibercept, as well as emerging therapies. Complications and differential diagnoses are also outlined.