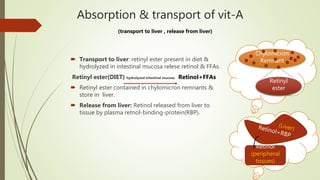
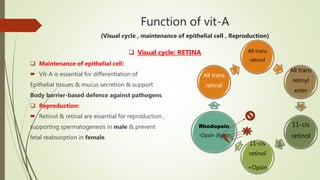
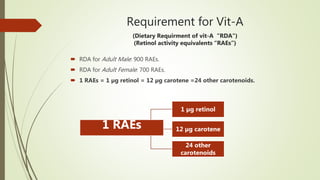
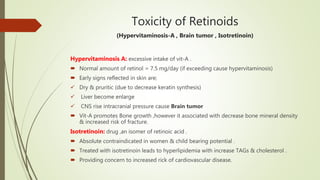
This document discusses vitamin A, including its structures, functions, sources, requirements, and clinical uses. It notes that vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that includes retinol and provitamin A carotenoids. It is essential for vision, reproduction, growth, and epithelial tissue maintenance. The document outlines the absorption and transport of vitamin A in the body as well as its mechanisms of action on gene expression. It also covers vitamin A functions in visual cycles, epithelial cells, and reproduction, along with its sources, requirements, deficiency symptoms, and uses to treat conditions like acne and psoriasis. Risks of excessive intake like hypervitaminosis A and potential side effects of isotretinoin are