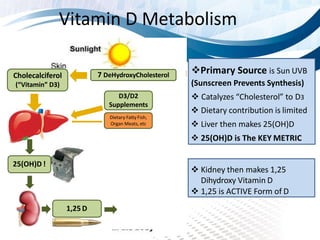
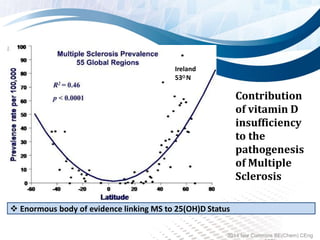
Vitamin D has increasingly been recognized for its importance beyond bone health. It may help prevent over 100 disorders ranging from cancer to diabetes to depression. Many people have deficient or insufficient vitamin D levels. While sunlight is the best source, factors like sunscreen use, age, and skin pigmentation can reduce natural vitamin D production. Supplementation is often recommended. Vitamin D is involved in processes throughout the body like immune function, cell growth, neuromuscular and immune functioning. Low levels are linked to higher risk of diseases like cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions like multiple sclerosis. Testing levels and supplementing to reach optimal levels may provide significant health benefits.