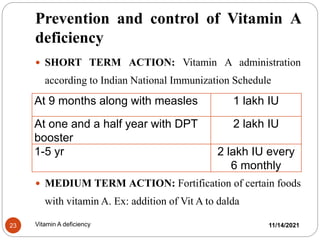
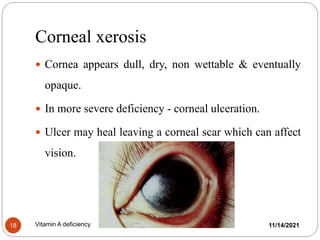
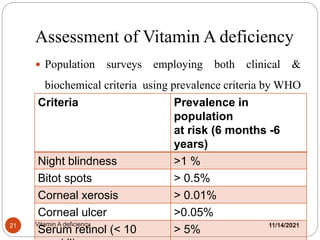
The document outlines the significance of vitamin A, its functions, sources, and the clinical manifestations of its deficiency. It emphasizes the health impacts, including night blindness and xerophthalmia, and discusses treatment strategies and preventive measures. Additionally, it provides recommended dietary allowances and assessment criteria for populations at risk.
















![Treatment of Vitamin A deficiency
Two doses of 2 lakh I.U of vitamin A are given 4
weeks apart according to the NPCB.
However, WHO recommends another dose that should
be given on 2nd day after the first dose [so totally 3
doses are given]
11/14/2021
22 Vitamin A deficiency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vitaminadeficiency-211114144807/85/Vitamin-A-deficiency-22-320.jpg)