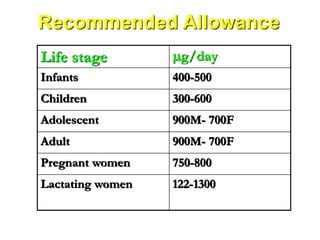
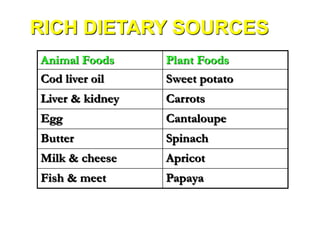
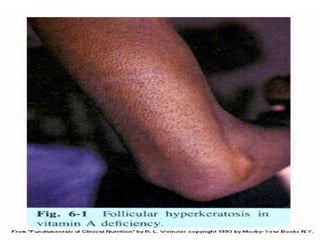
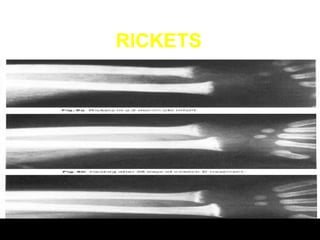
Vitamin deficiencies can cause several disorders. There are 13 known vitamins classified as either fat-soluble or water-soluble. Vitamin A deficiency can lead to night blindness and immune problems, while vitamin D deficiency results in rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Both vitamins are important for growth, immunity, and calcium absorption. Maintaining adequate levels through diet and sunlight exposure is important to prevent deficiency disorders.