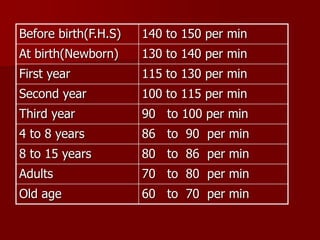
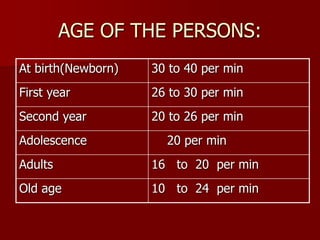
Vital signs include temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure. They are called "vital" because they are regulated by vital organs and reveal changes in body function. Monitoring vital signs allows detection of changes in a patient's condition from treatment or illness and can provide diagnostic information. Normal ranges are provided for adults, with rates varying by age. Factors like emotions, activity level, and medications can cause variations. Regular monitoring of vital signs is important for assessing patient health and treatment effectiveness.