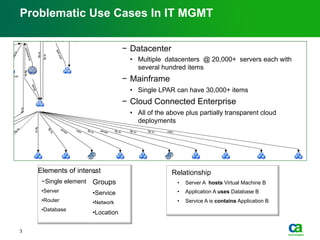
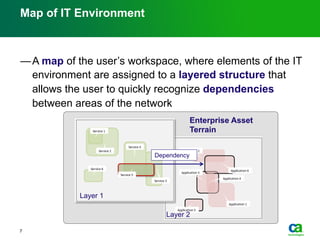
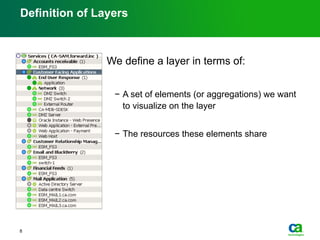
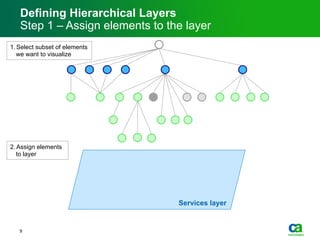
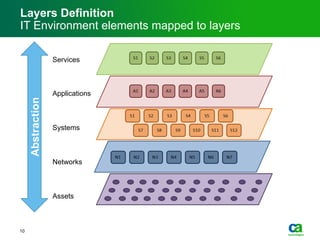
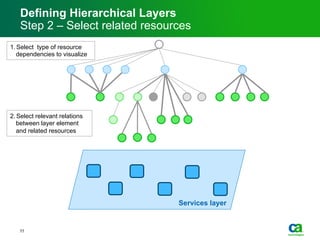
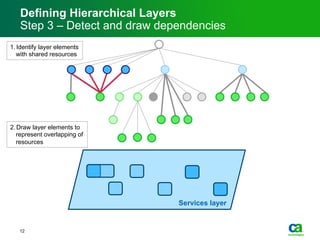
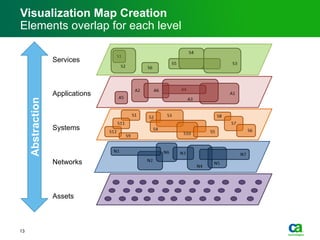
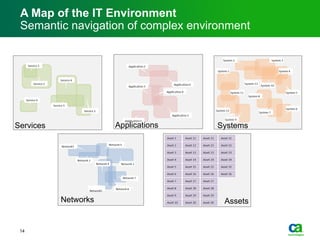
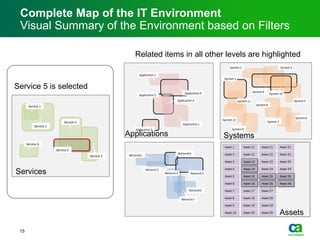
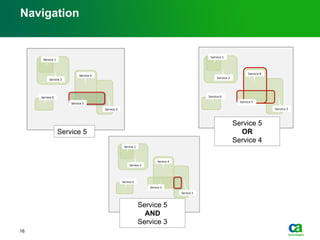
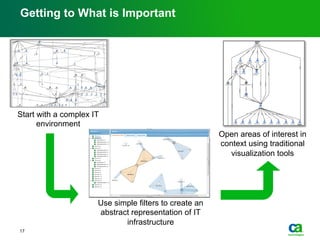
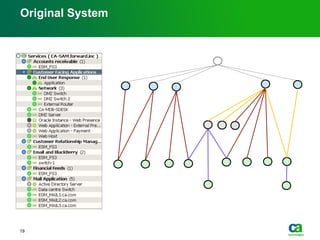
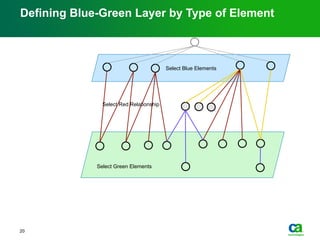
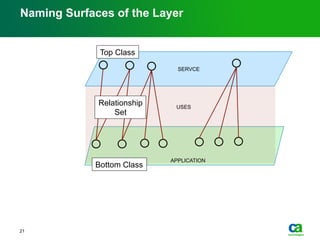
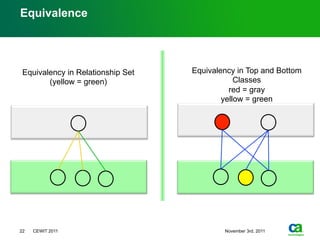
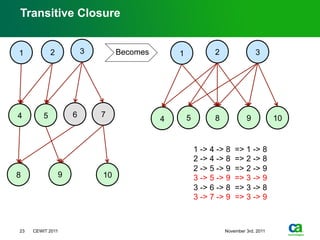
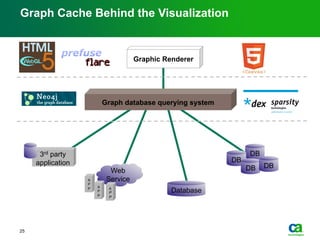
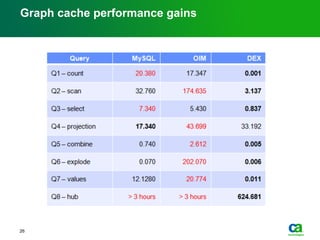
The document discusses the challenges of big data visualization in IT management, emphasizing the increasing complexity of data and the need for new techniques to represent it effectively. It proposes a layered hierarchical visualization approach that simplifies complex environments by allowing users to recognize dependencies more easily. The approach includes semantic zooming and layered overviews to create a clearer map of the IT environment.