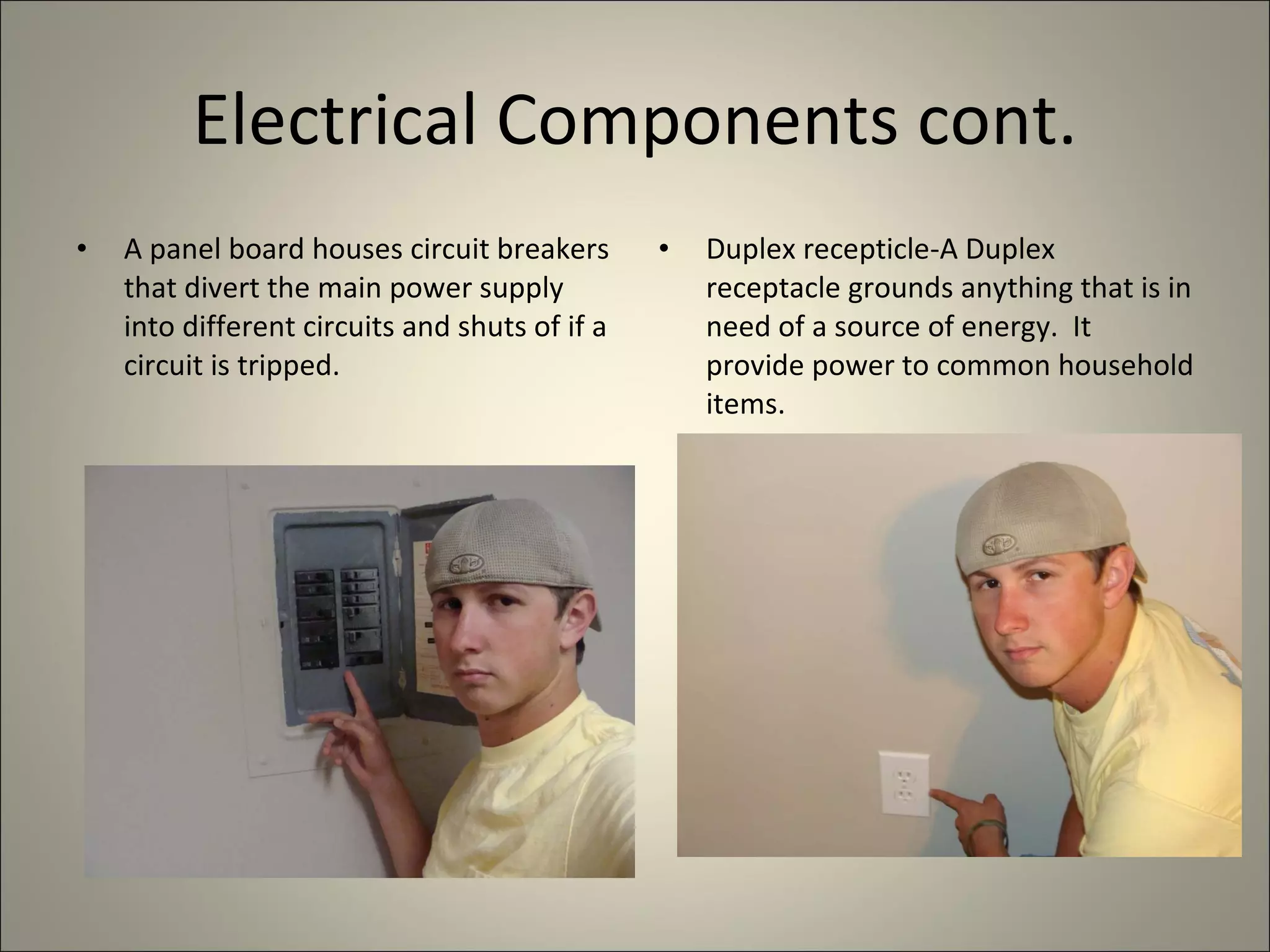
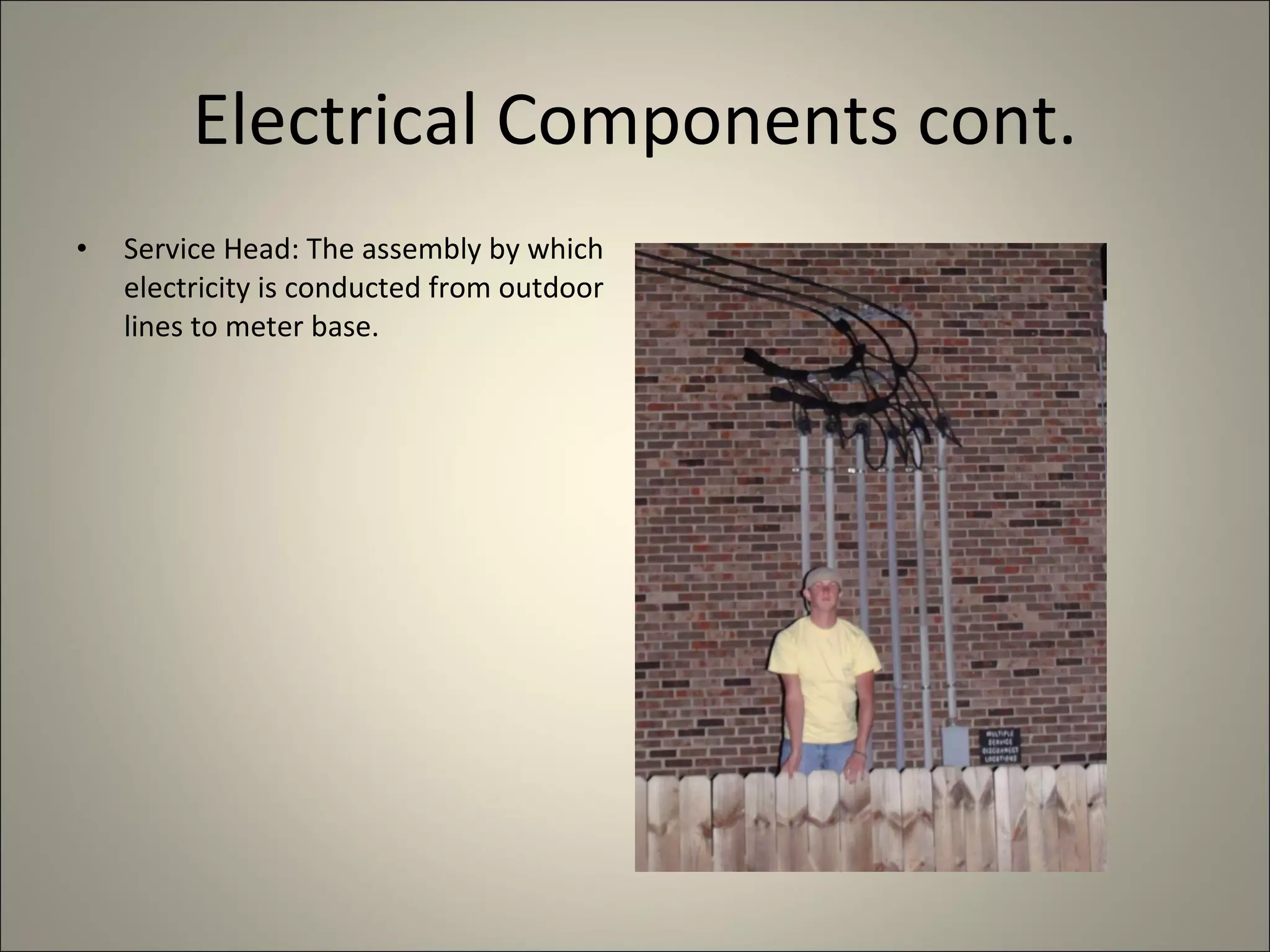
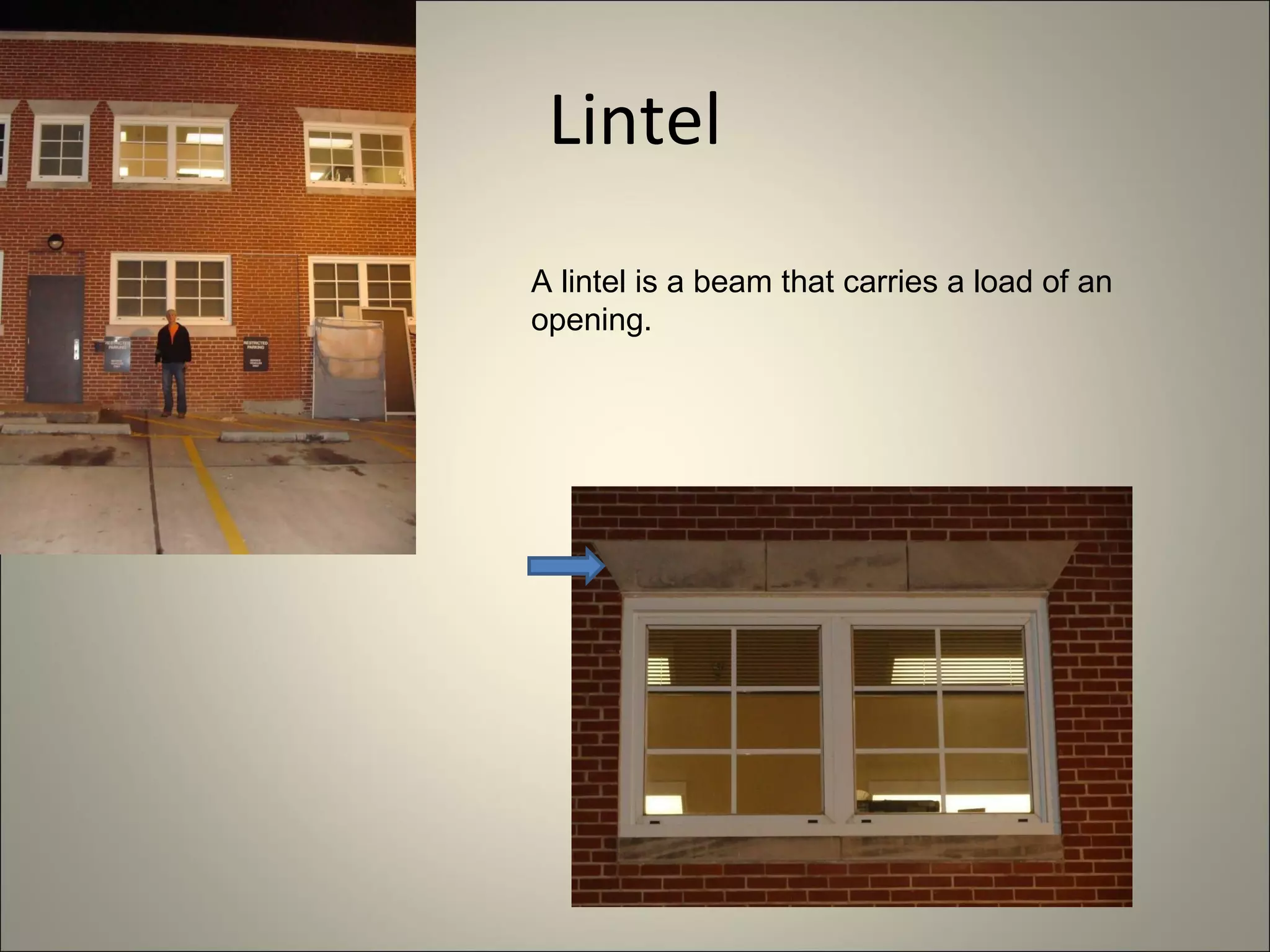
This document defines and describes various construction materials and components. It provides definitions and descriptions of items like air barrier paper, attic ventilation materials, backhoes, batter boards, brick bonds, concrete joints, framing elements, insulation materials, mortar joints, rebar, roof drainage components, siding materials, vapor retarders, waterproofing, windows, and more - with accompanying diagrams and photos. The document acts as a visual dictionary to concisely define and illustrate essential construction terms and products.