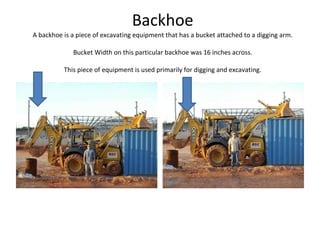
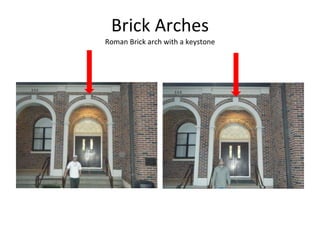
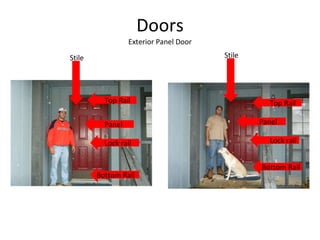
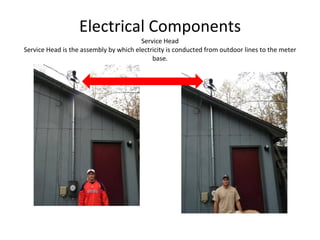
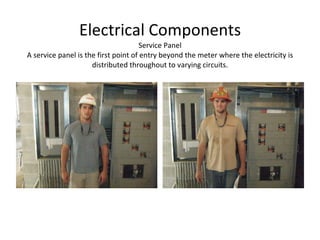
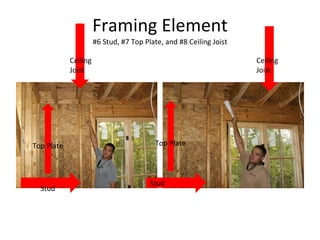
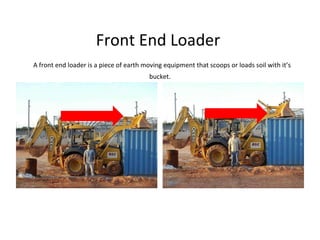
This document defines and describes various building materials and construction components. It includes definitions and photos of air barrier paper, attic ventilation components like ridge vents and soffit vents, construction equipment like backhoes and bulldozers, building cladding materials, concrete joints and masonry units, doors, electrical system components, framing elements, insulation materials, lintel, mortar joints, oriented strand board, plumbing fixtures, plywood, rebar, roof components like gutters and underlayment, roof shapes, siding materials, stone patterns, steep roof terms, vapor retarders, waterproofing, weep holes, welded wire fabric, and window types.