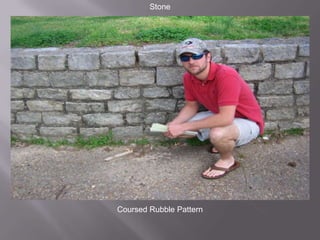
This document defines and describes various construction terms related to building components and materials. It provides brief definitions for over 100 terms, including types of roofing materials and shapes, framing elements, windows, doors, masonry, plumbing, electrical, insulation, and more. Each term is concisely defined in a sentence or two to provide the essential information about its use or purpose.