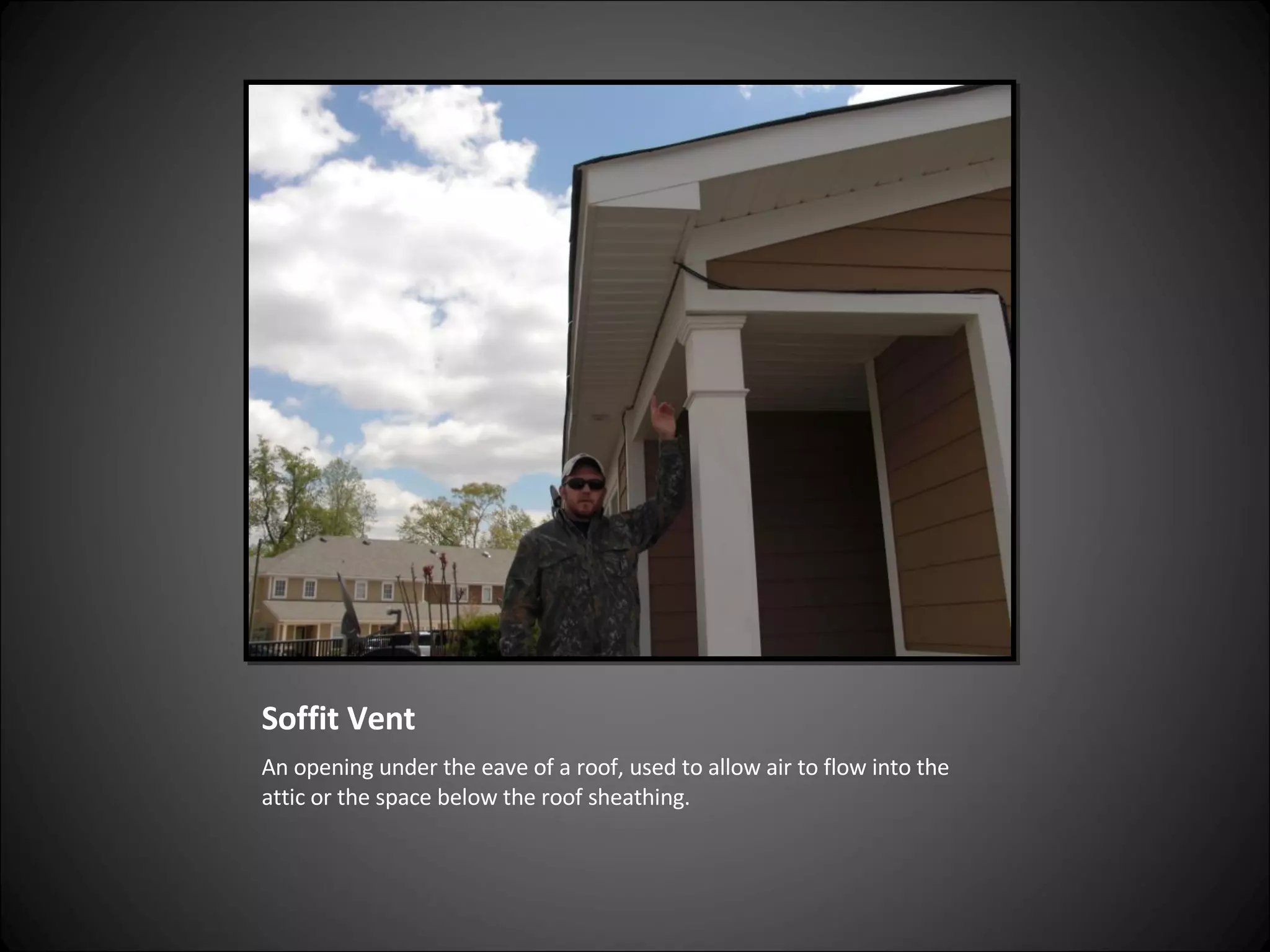
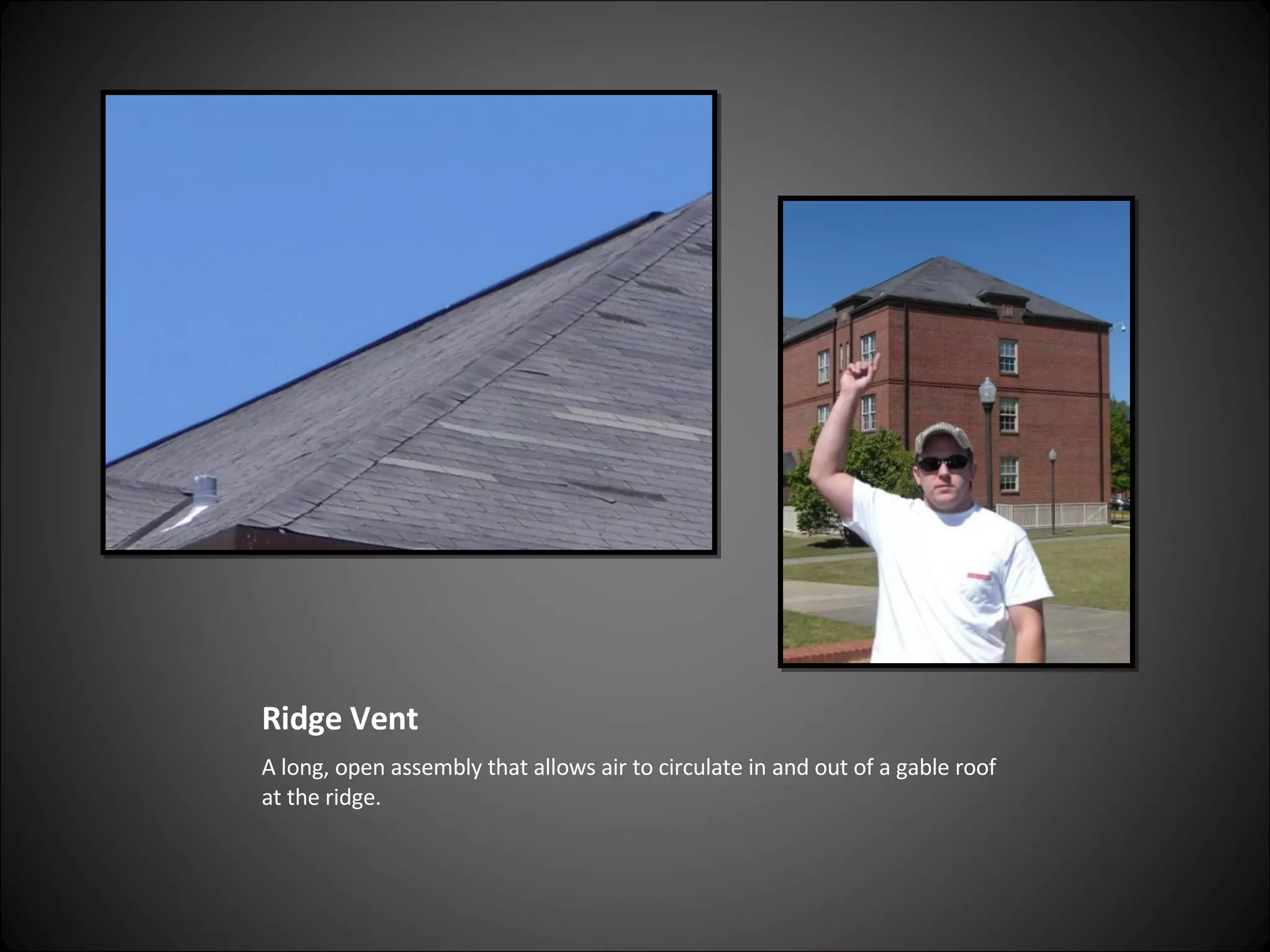
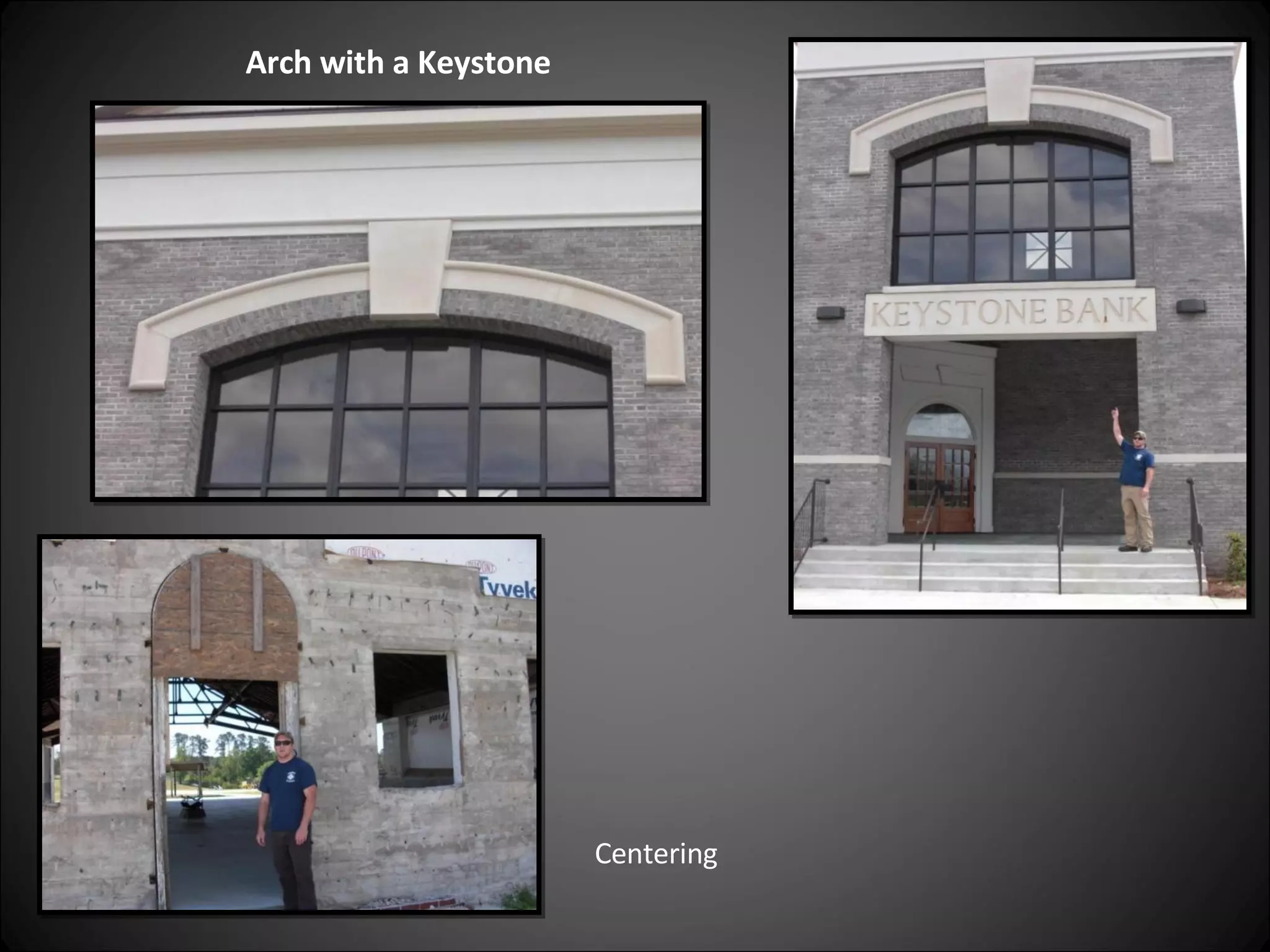
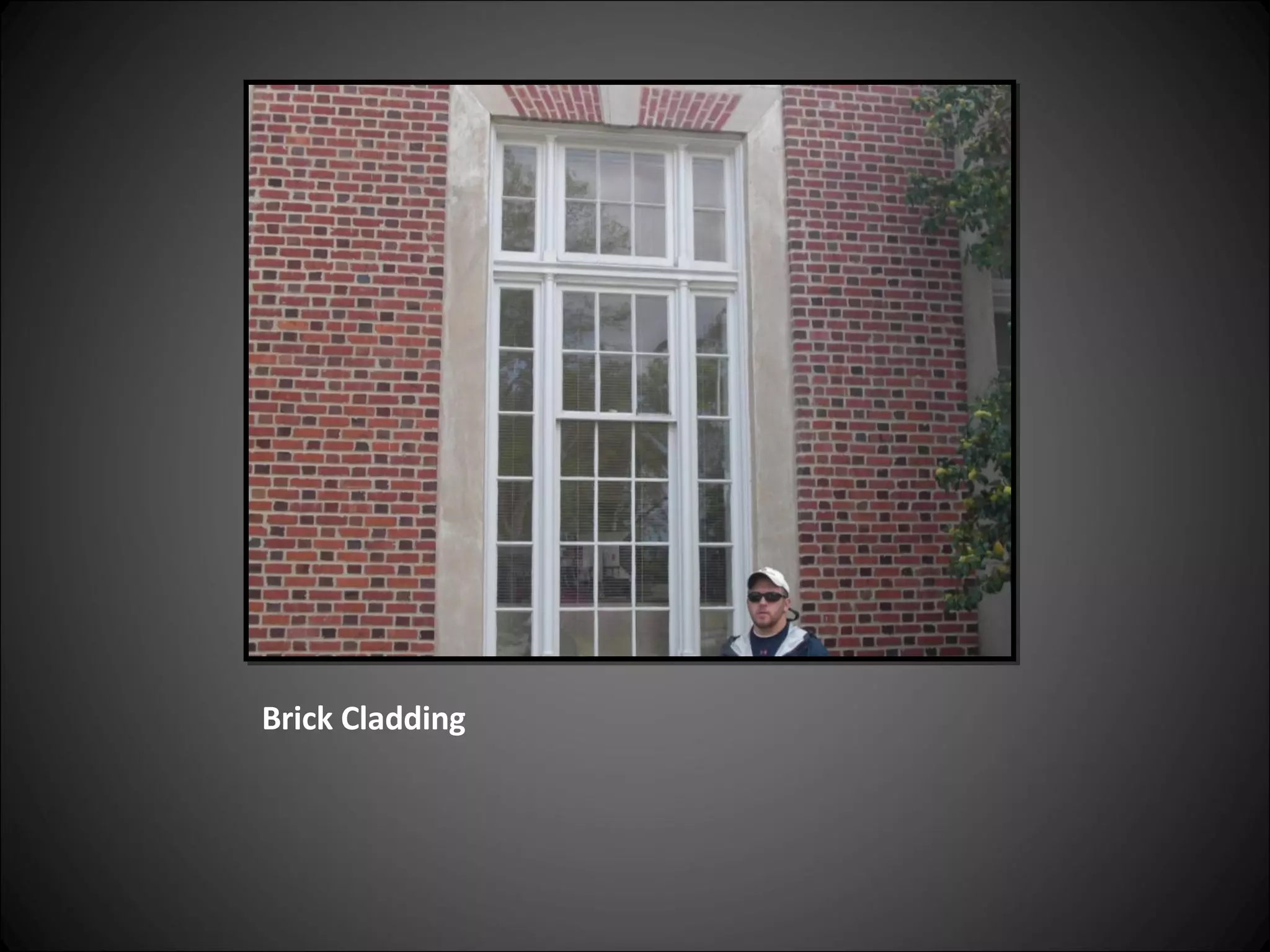
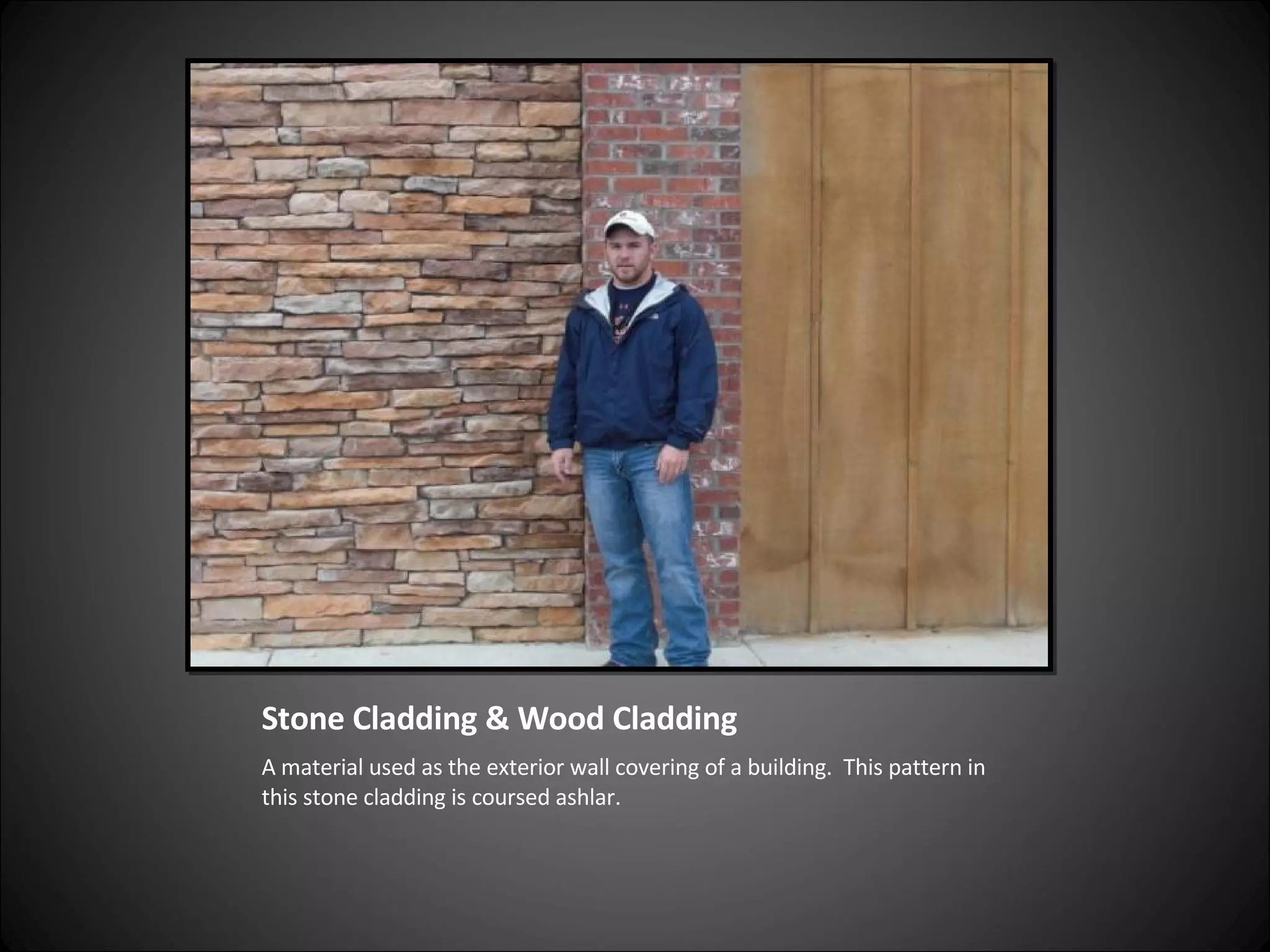
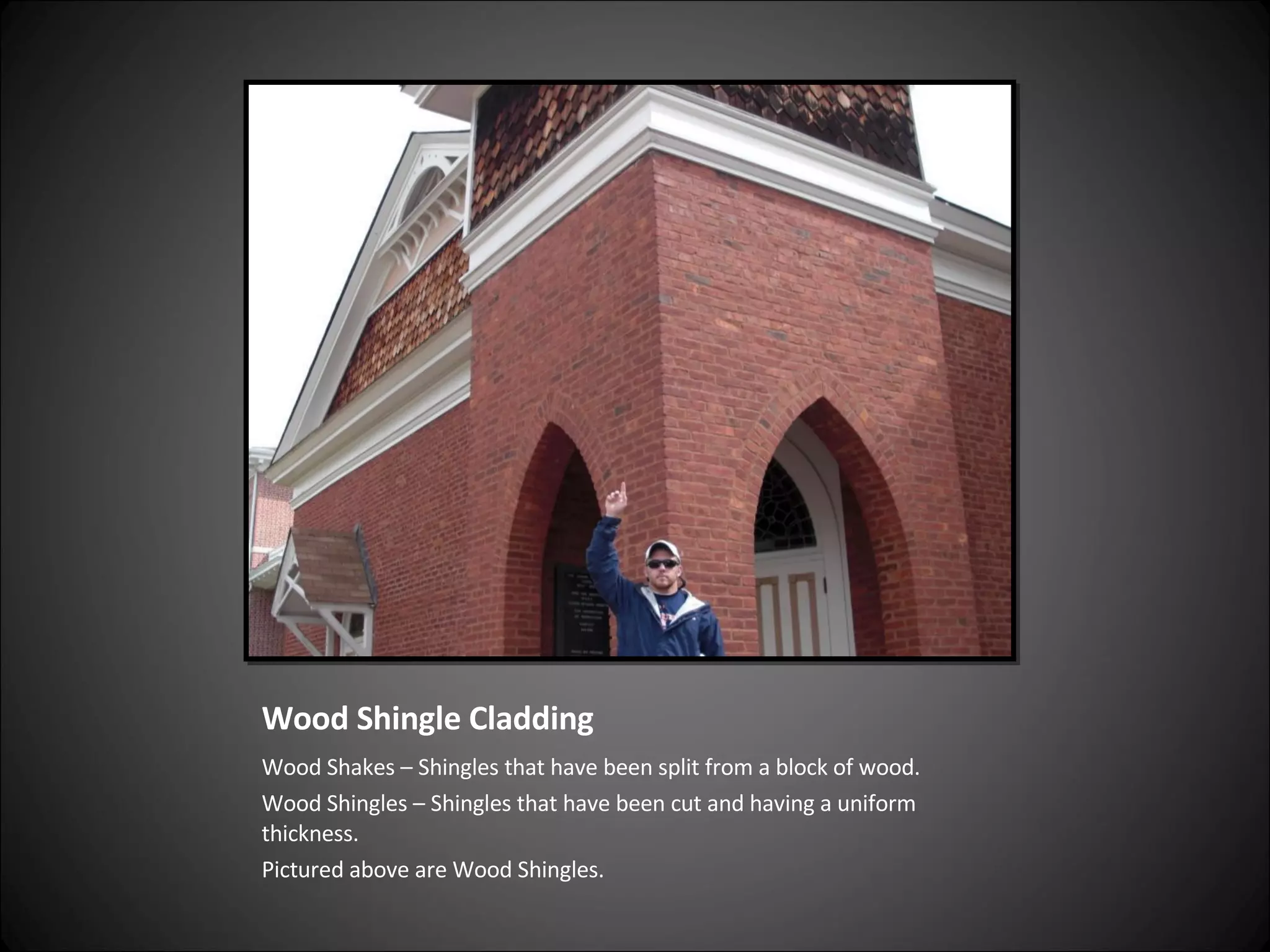
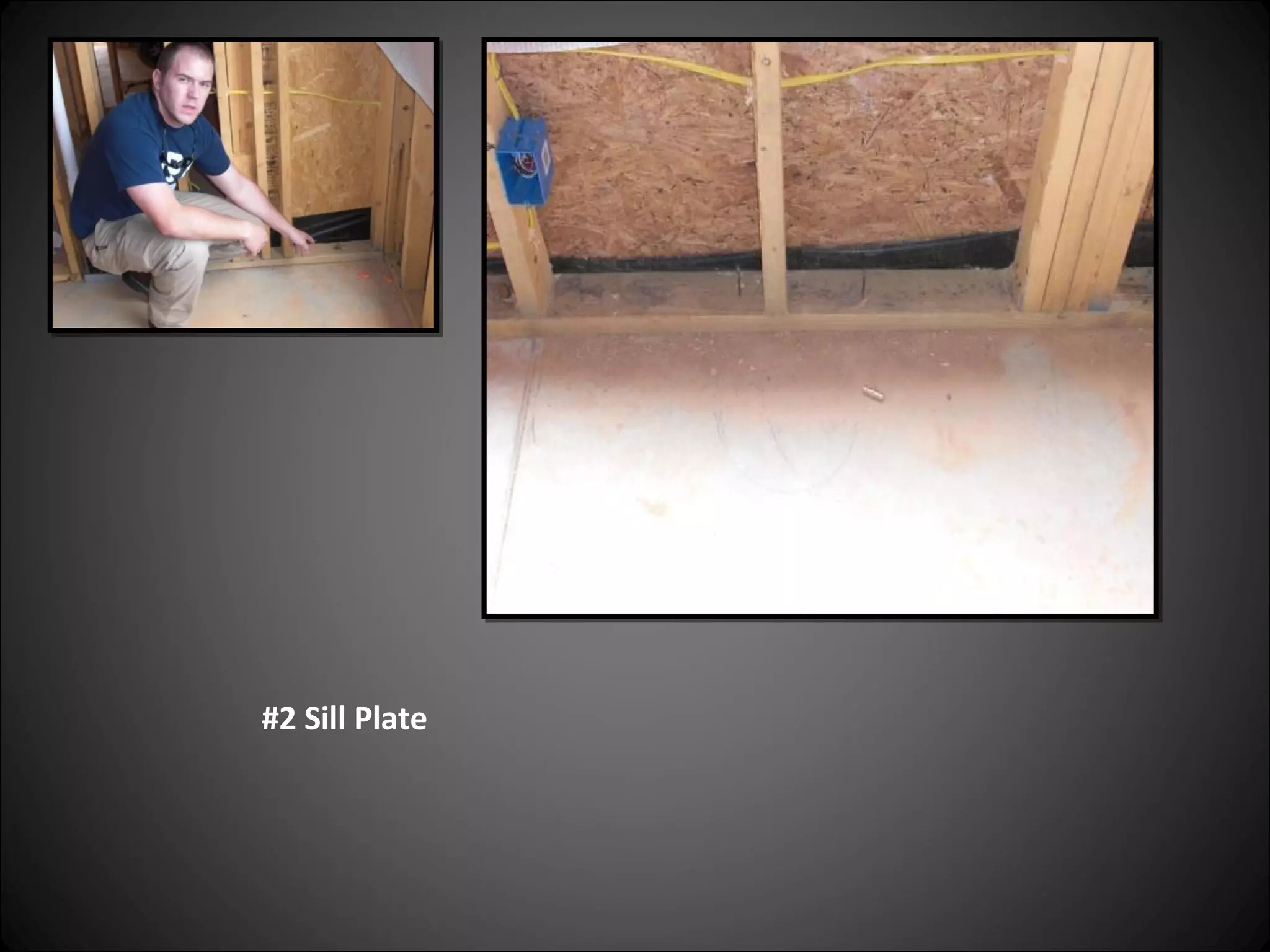
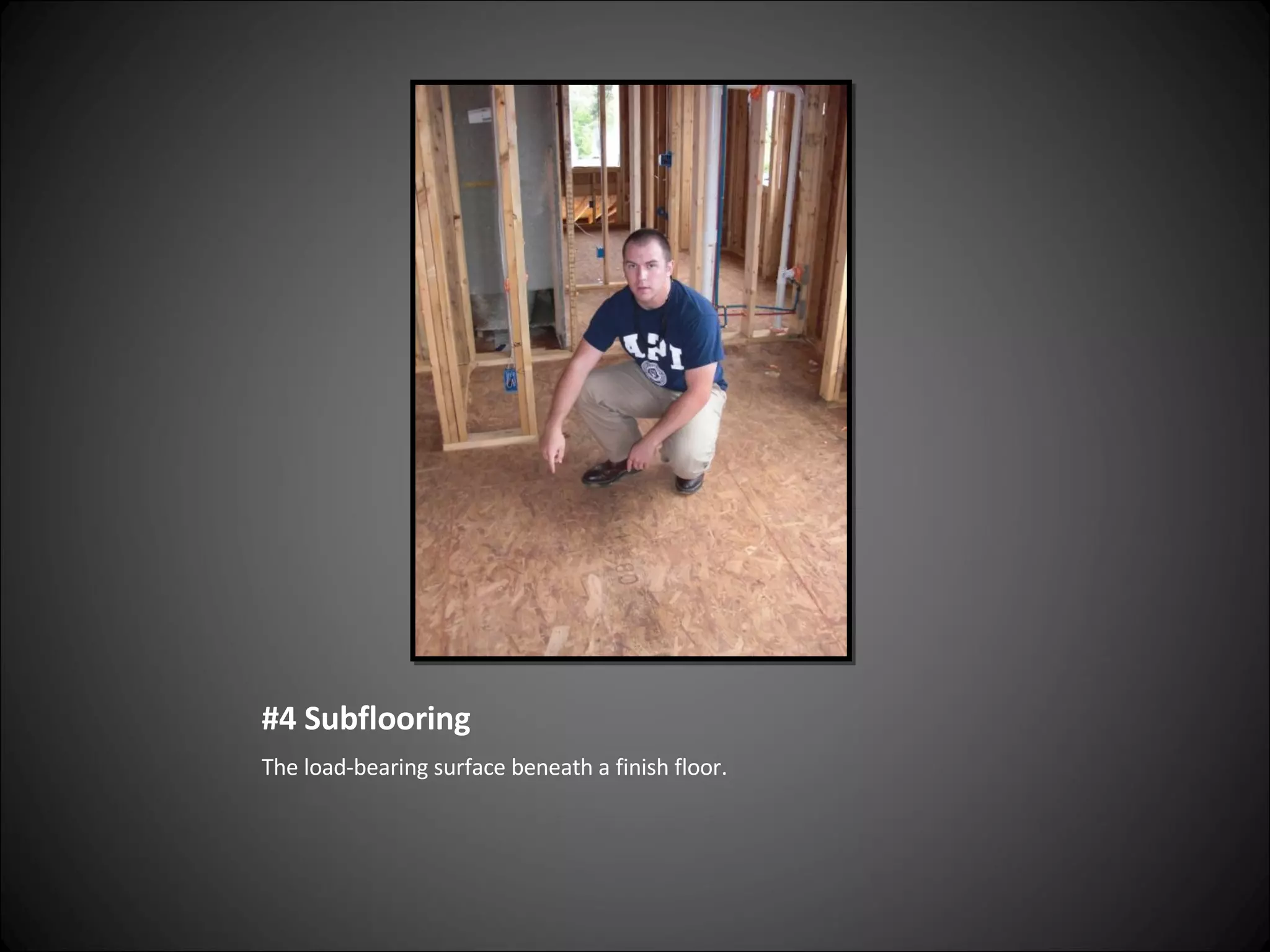
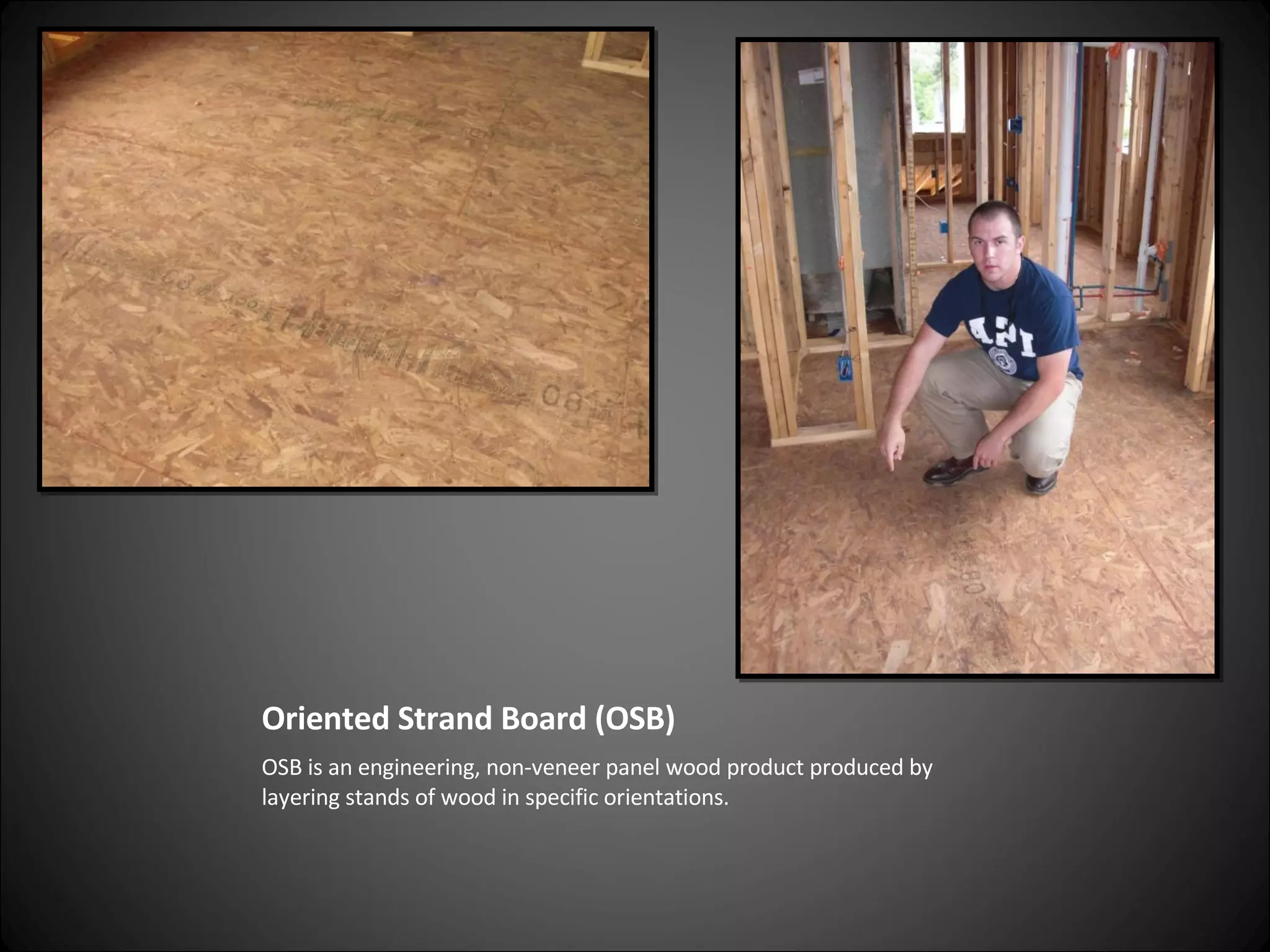
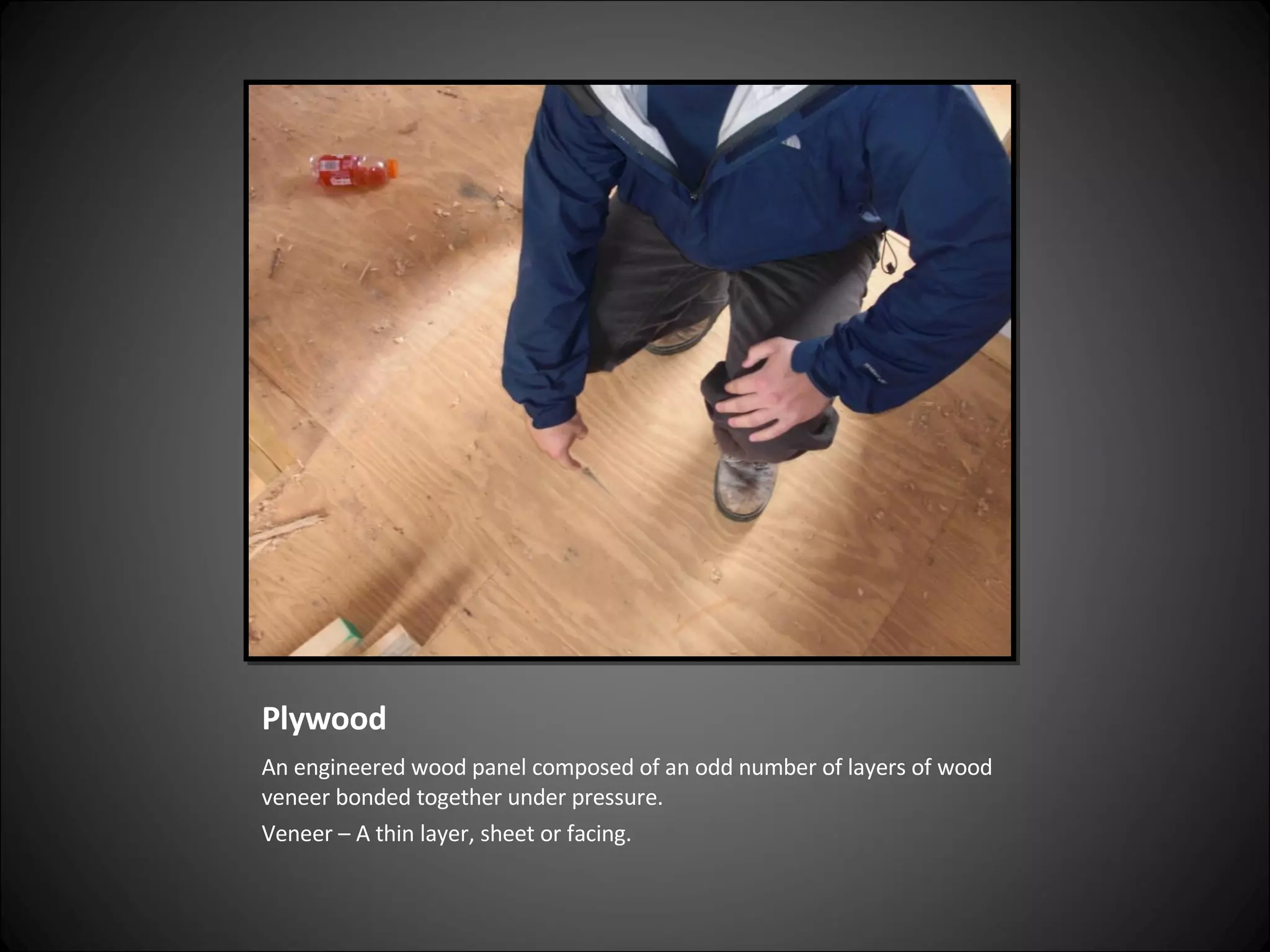
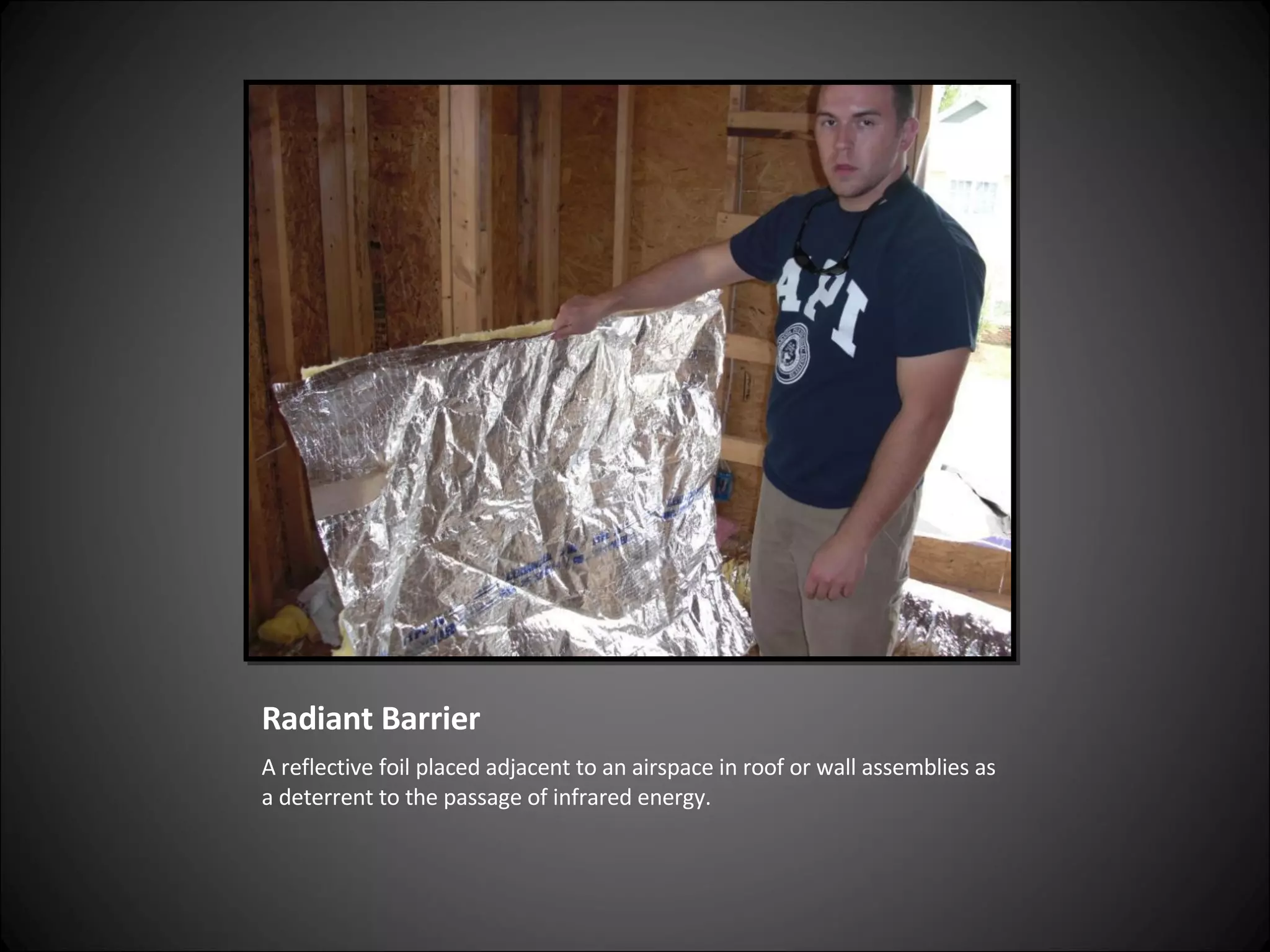
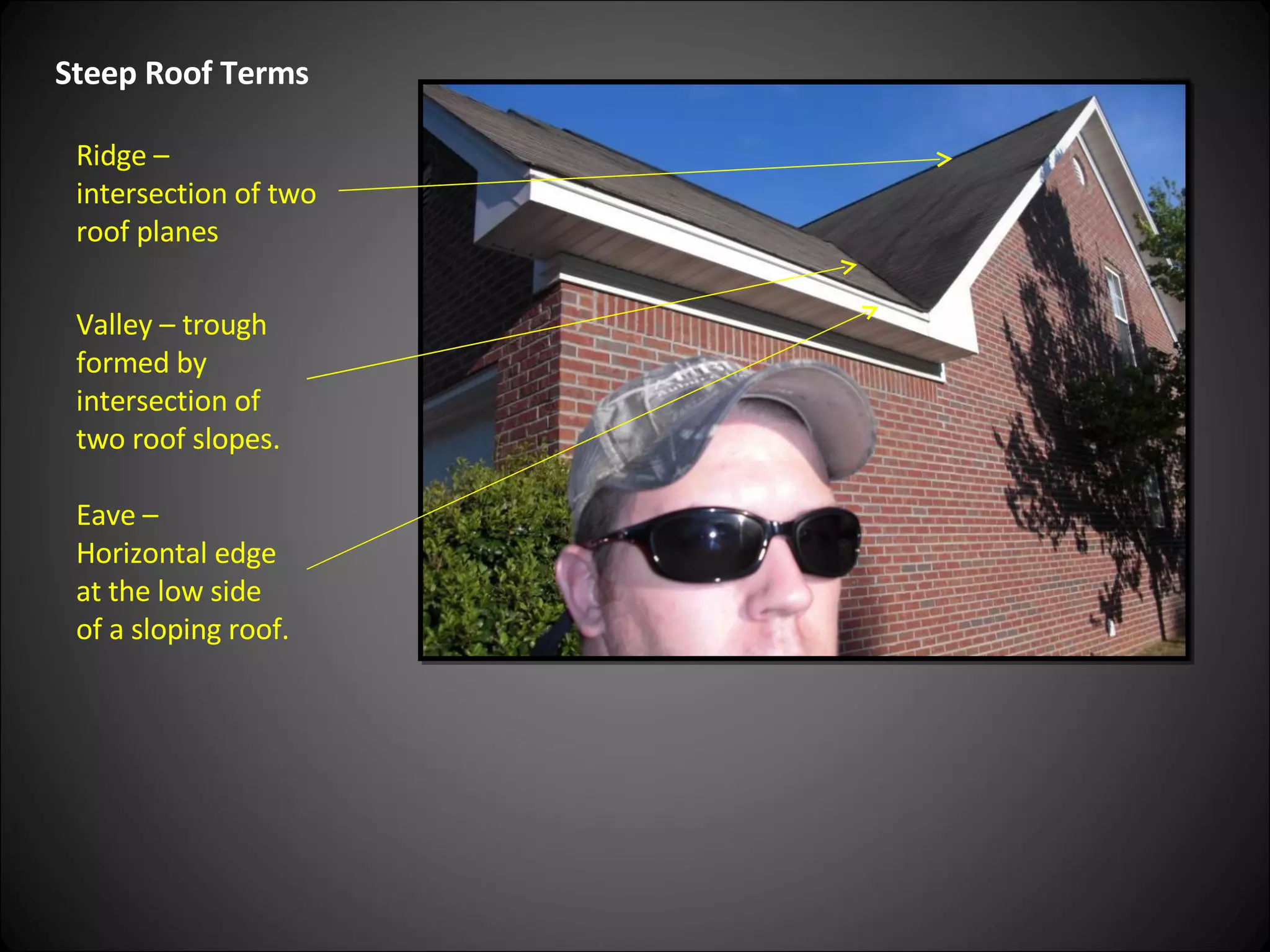
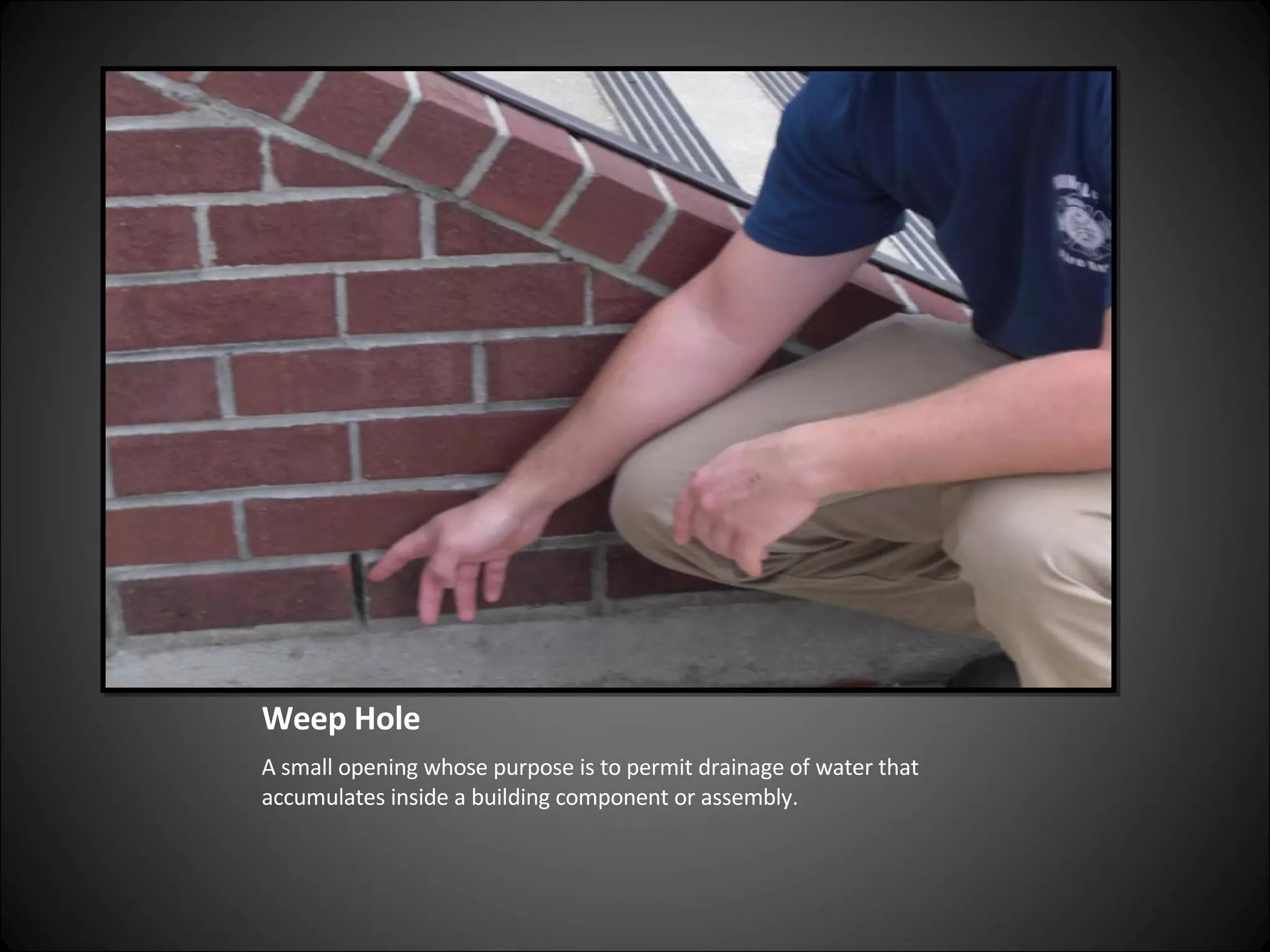
This document provides definitions and descriptions of various construction terms related to building materials, components, and systems. It includes explanations of different types of vents, claddings, concrete joints, bricks, doors, roofs, foundations, framing members, insulation, plumbing fixtures, and more. Diagrams and photos accompany many of the entries to illustrate key details.