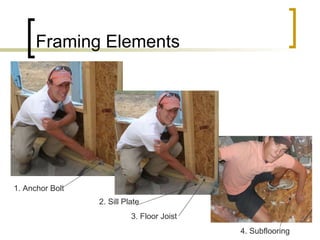
The document provides an overview of various construction and building elements including air barrier paper, ventilation systems, heavy machinery, and materials used in framing, plumbing, and insulation. It outlines code requirements for structural components, describes the functions and specifications of various tools and materials, and discusses methods for water management in building design. Additionally, it mentions specific types of roofs, windows, and waterproofing techniques to enhance the durability and functionality of structures.