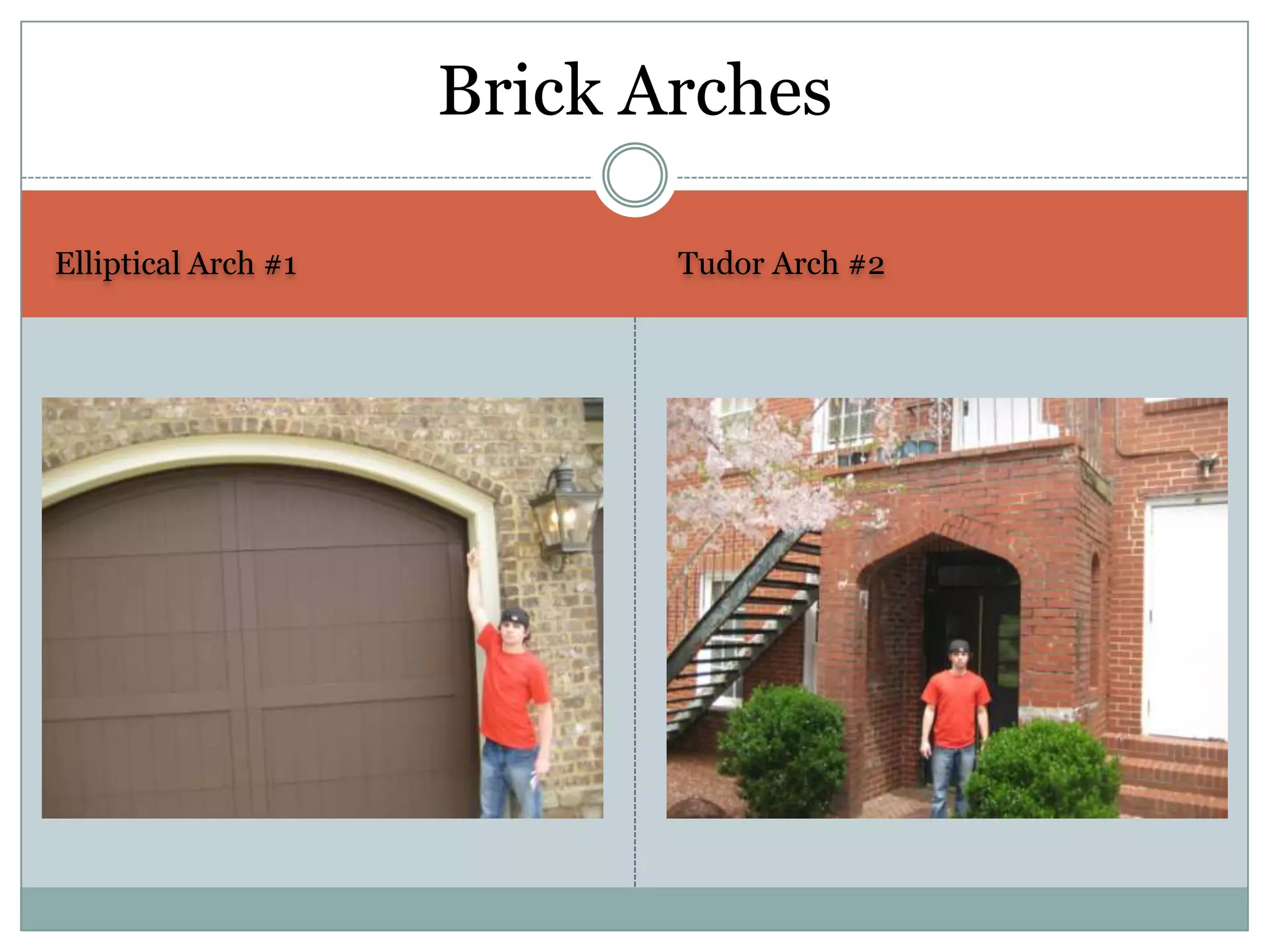
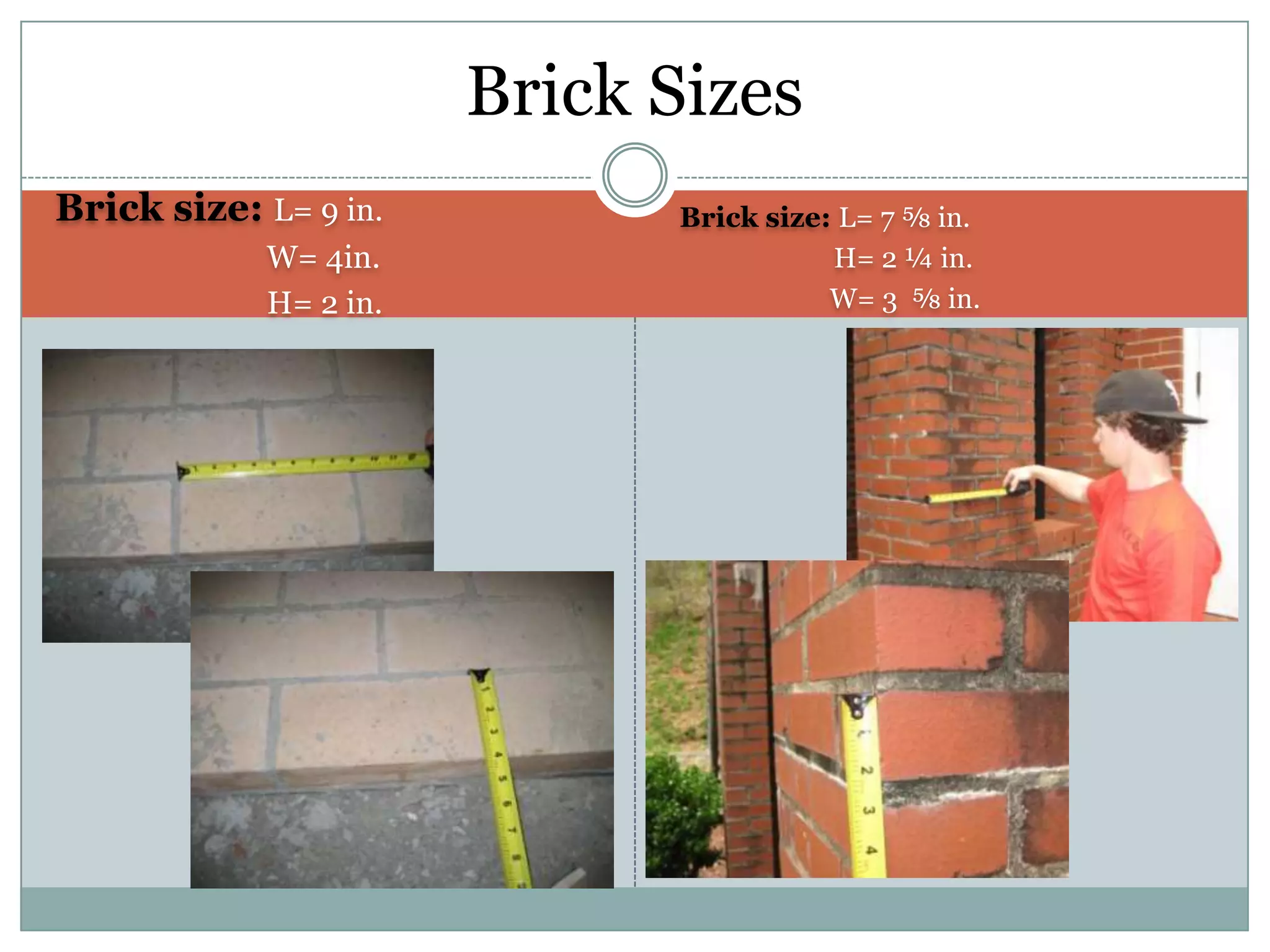
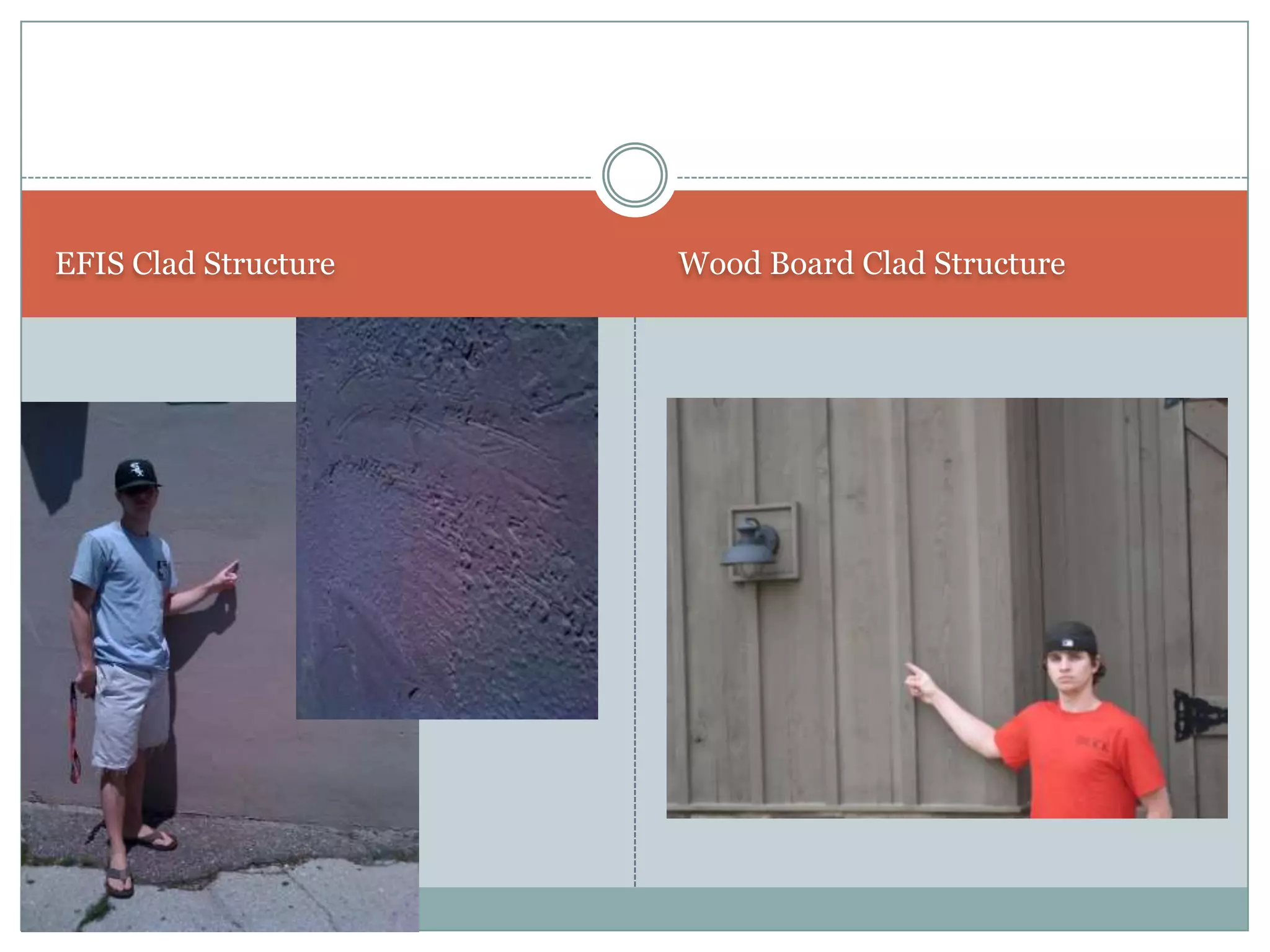
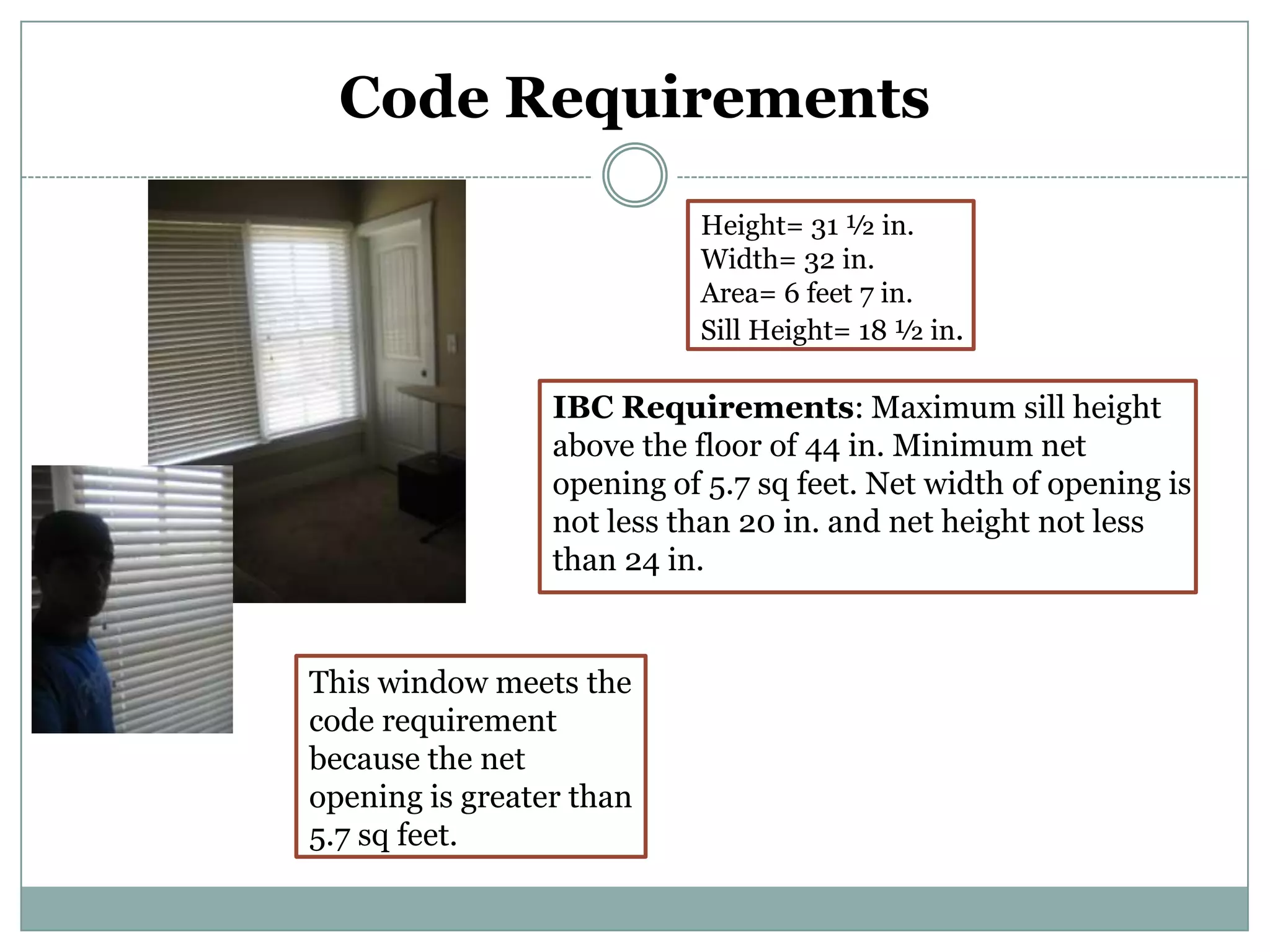
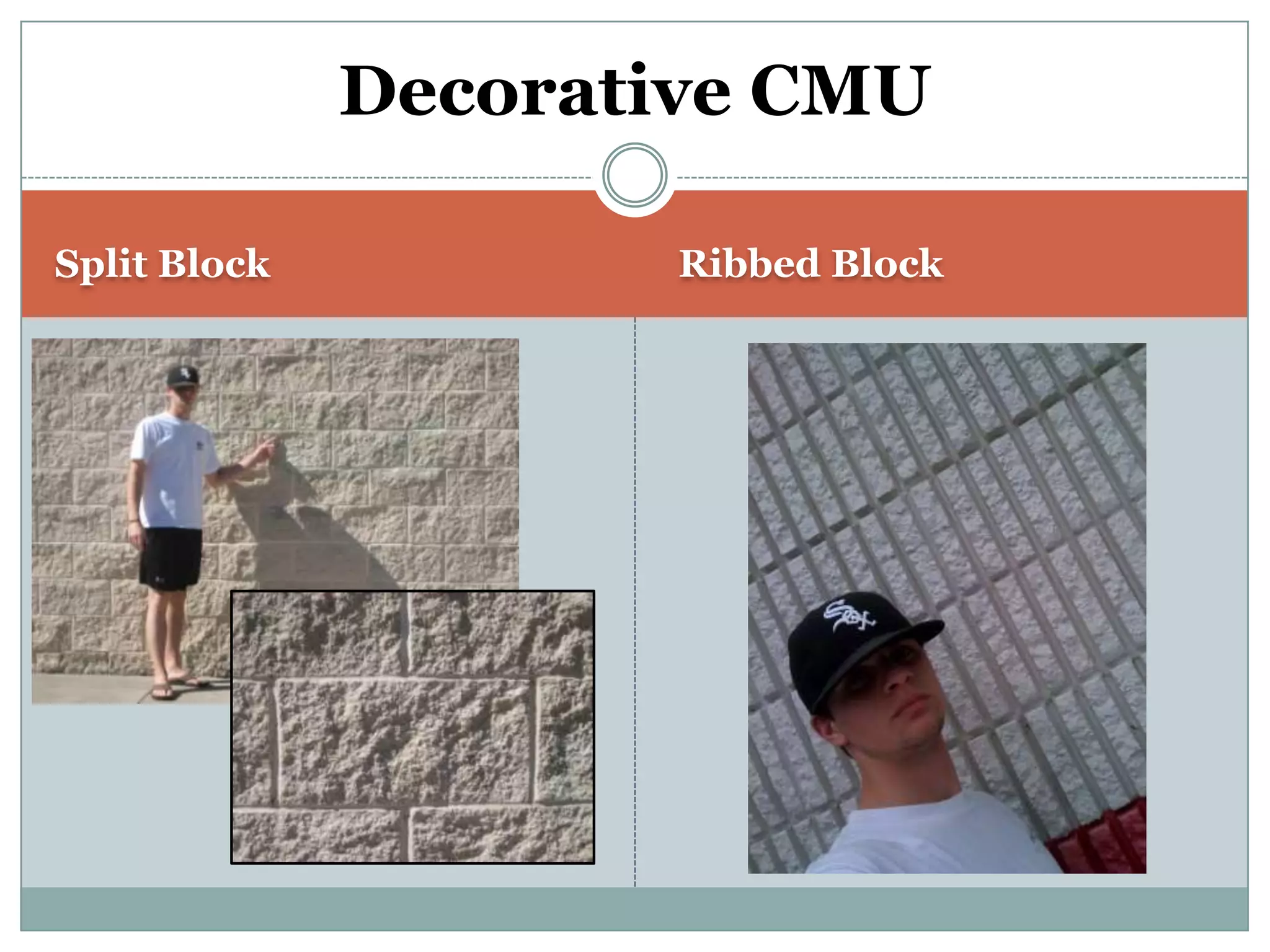
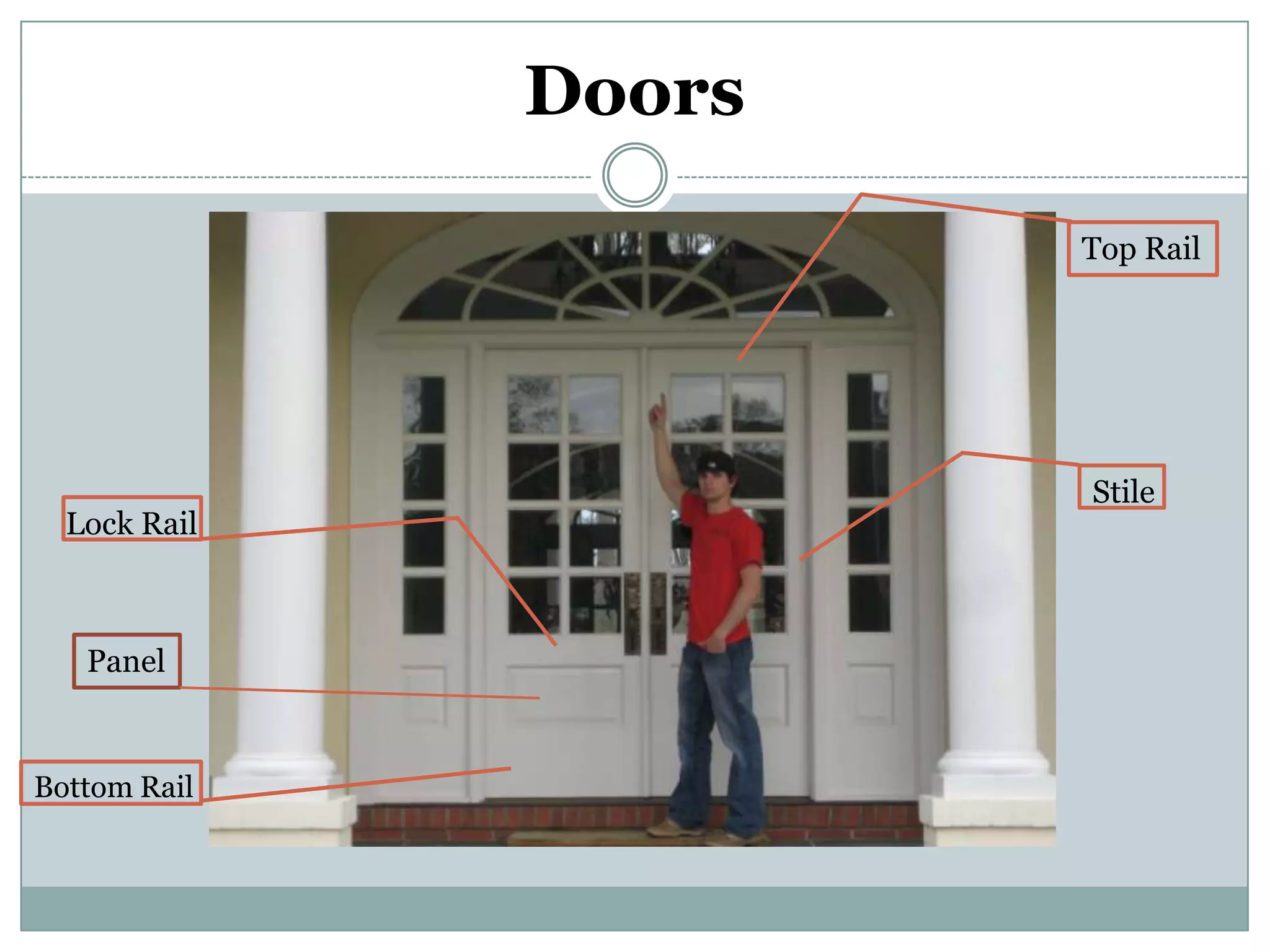
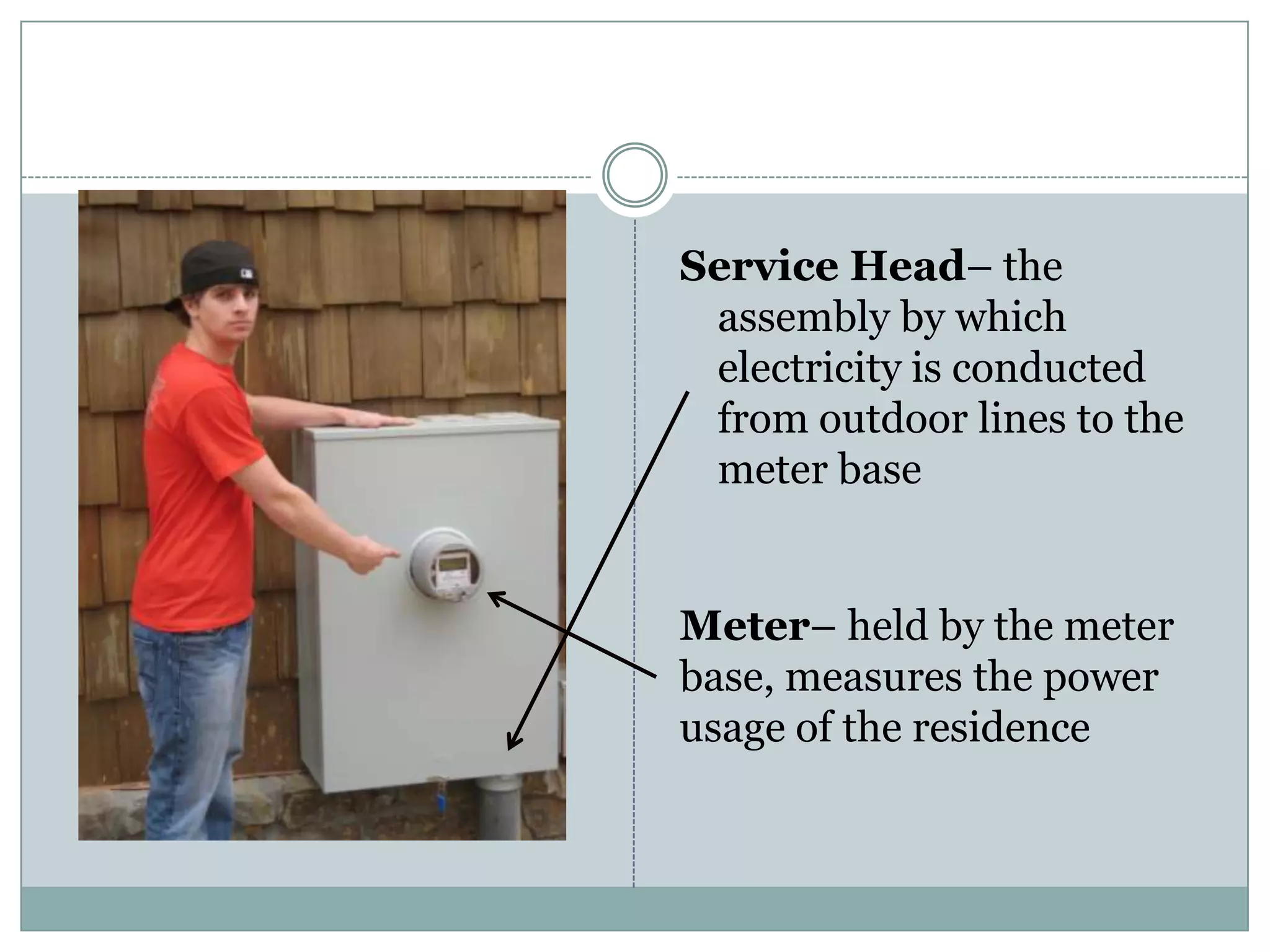
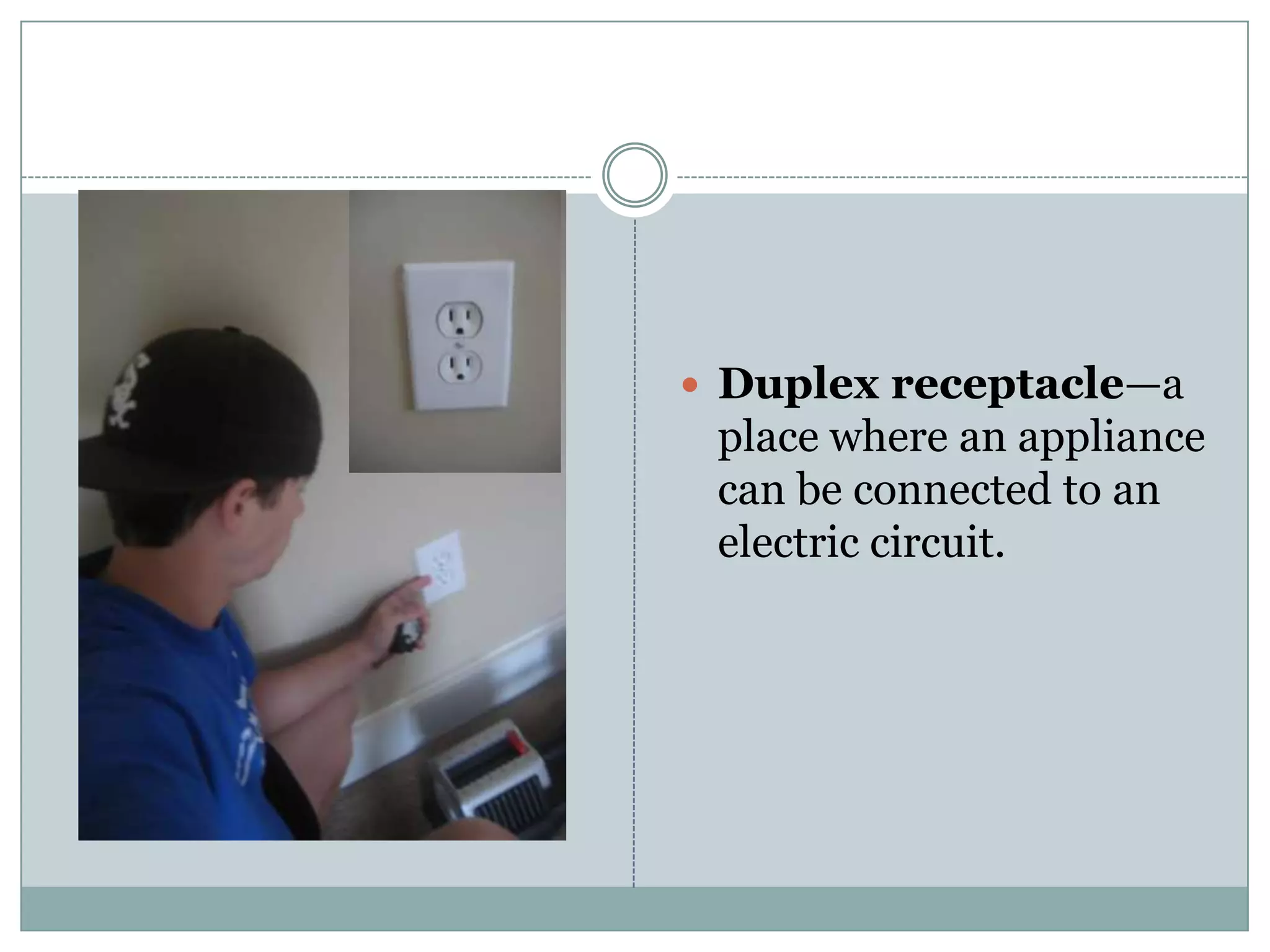
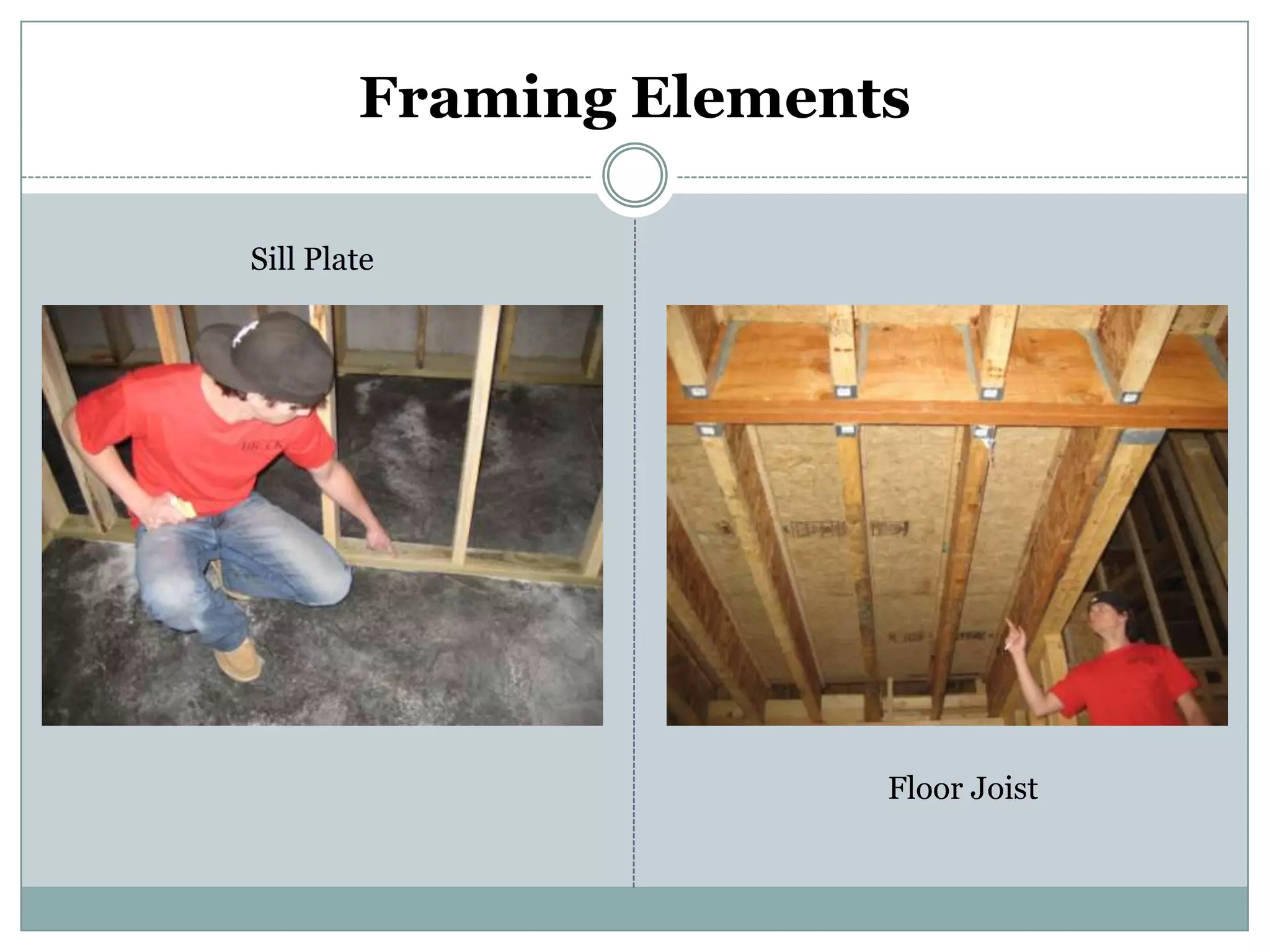
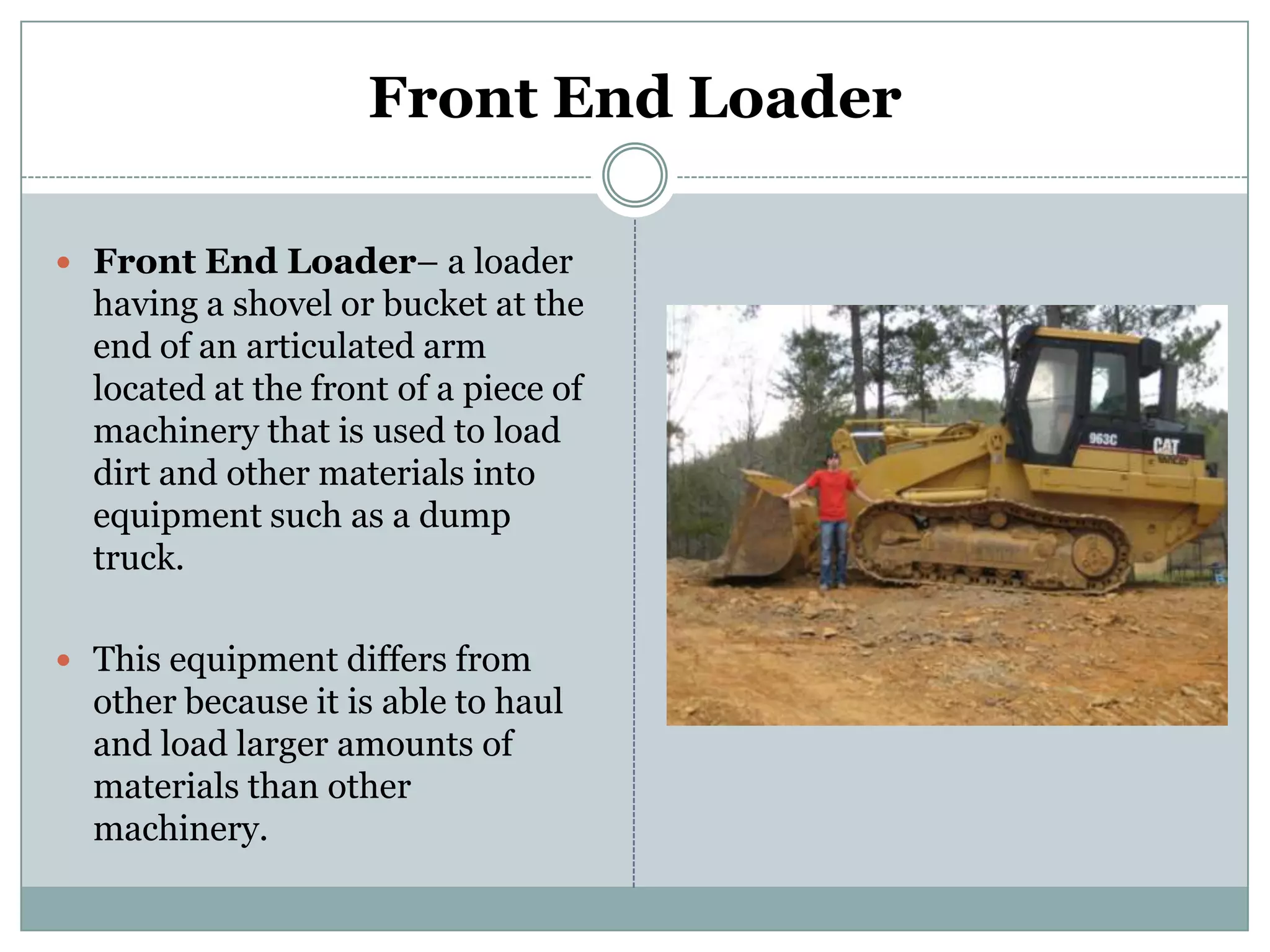
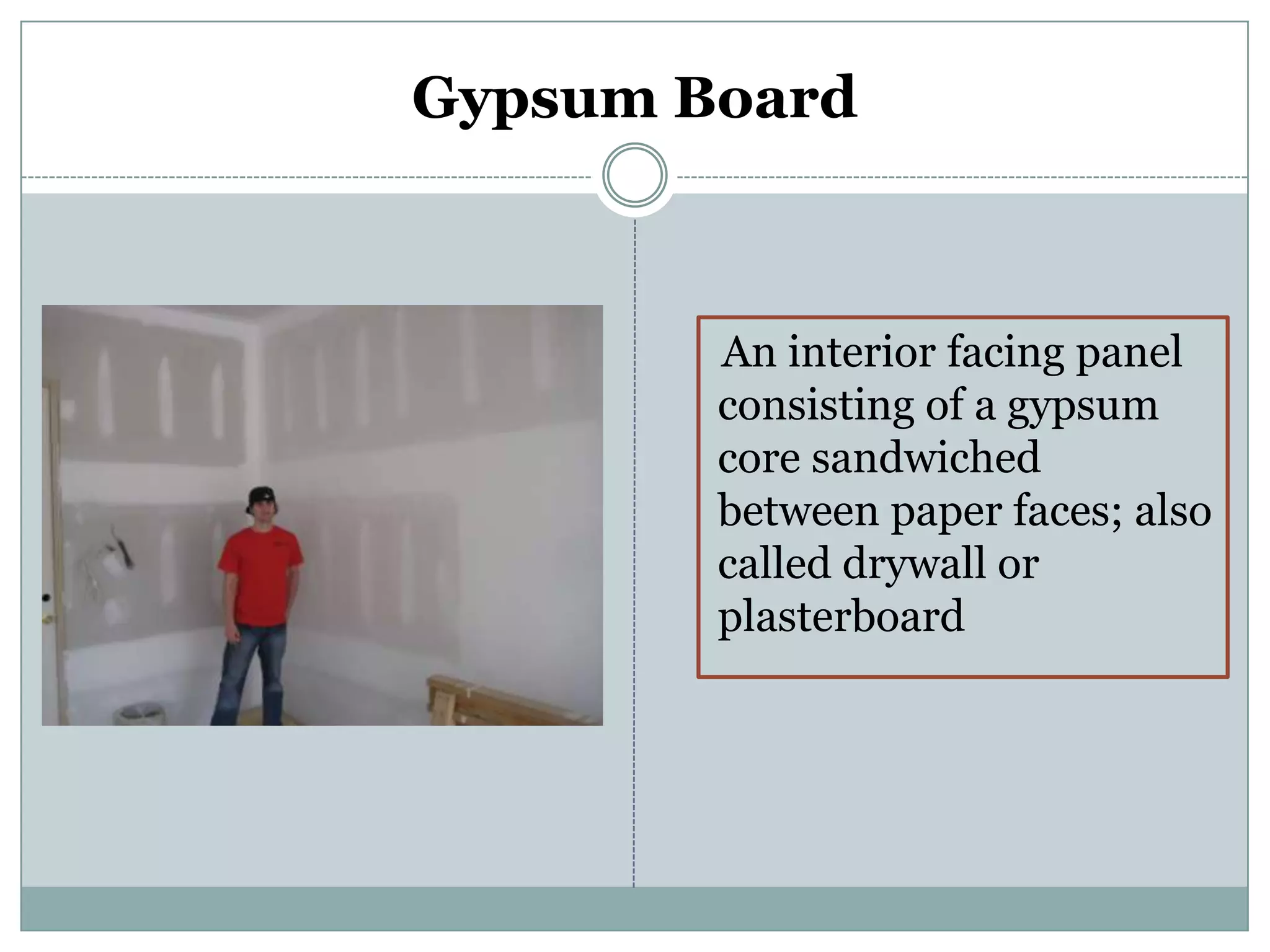
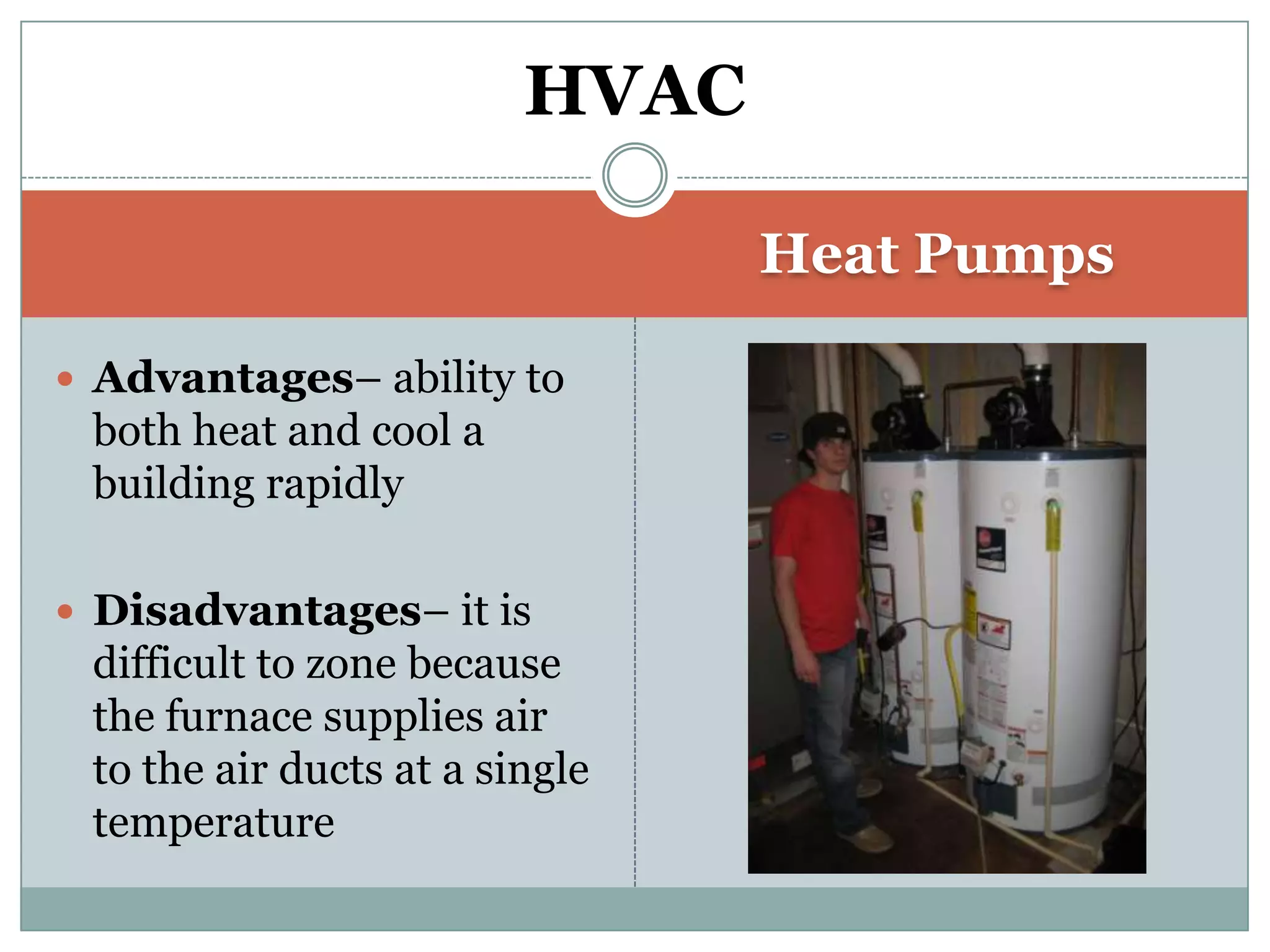
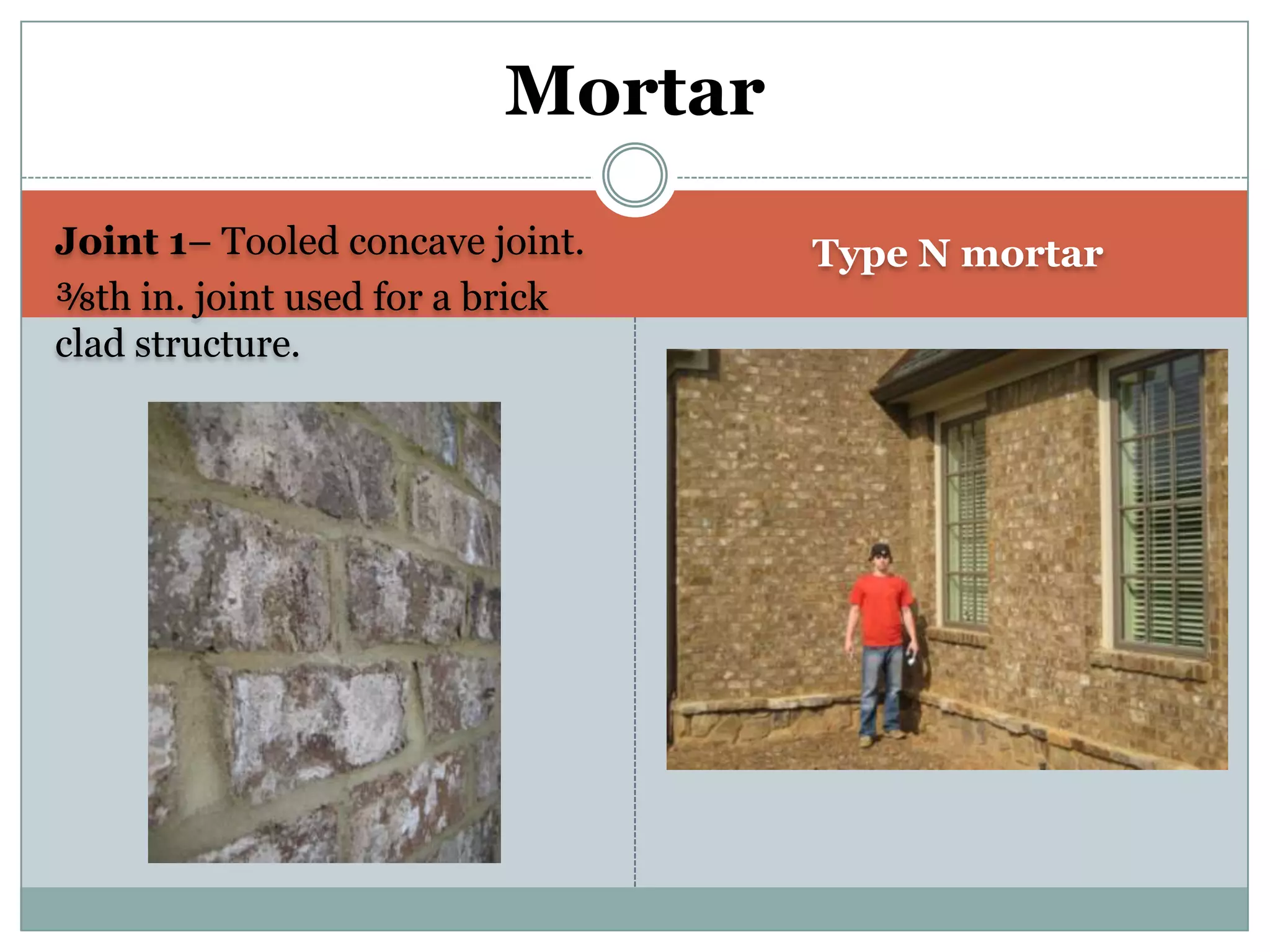
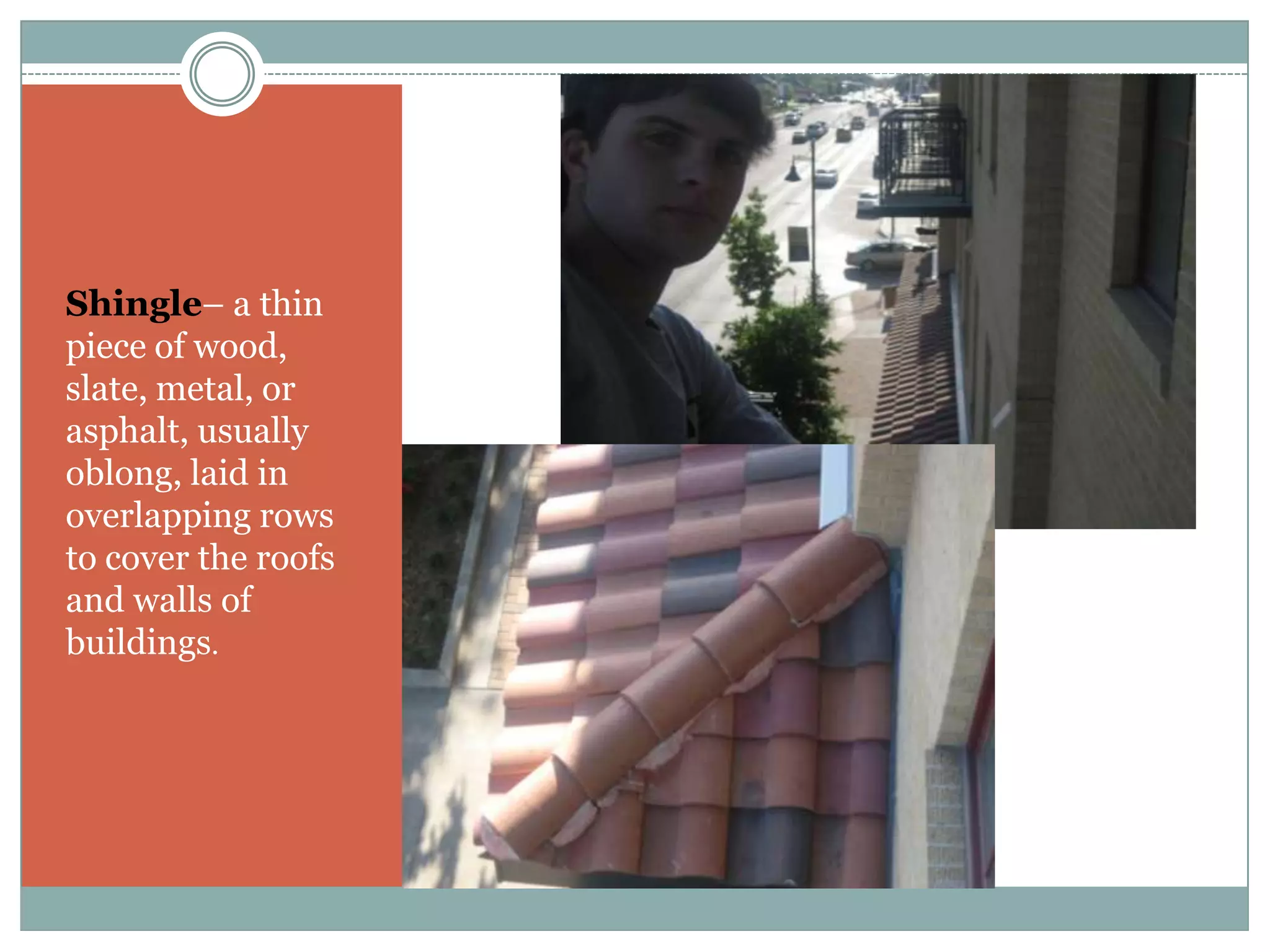
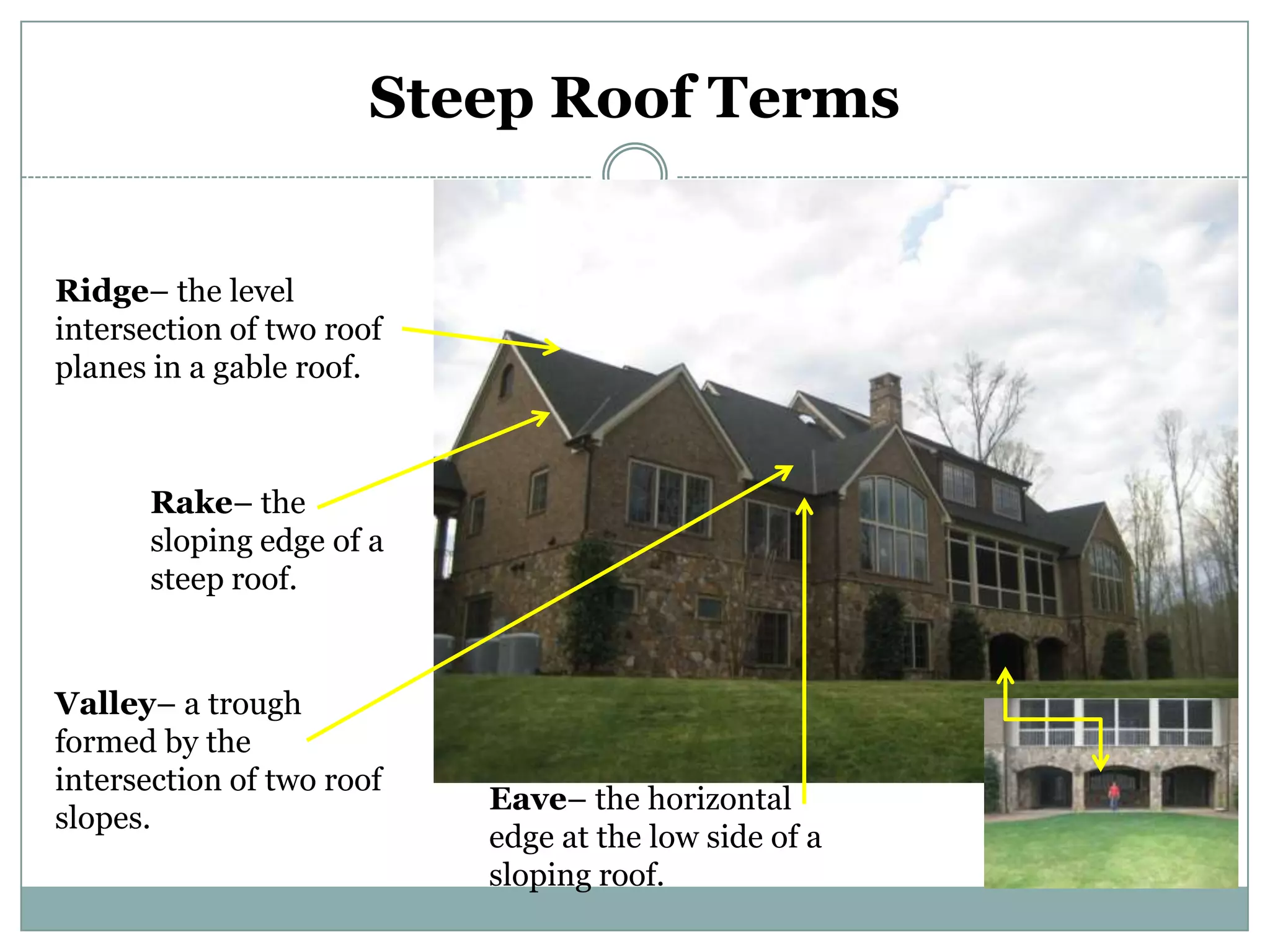
This document provides definitions and descriptions of various construction terms. It includes explanations of materials and components used in building structures like houses. Some terms that are defined include air barrier, attic ventilation, backhoe, batter boards, brick bonds, brick sizes, bulldozer, cladding types, concrete joints, doors, electrical components, framing elements, gypsum board, heat pumps, insulation types, joints in masonry, lintel, mortar, oriented strand board, plumbing components, plywood manufacturing process, radiant barrier, rebar, roof drainage, roofing underlayment, roof shapes, siding materials, stone patterns, vapor retarder, waterproofing, weep holes, welded wire