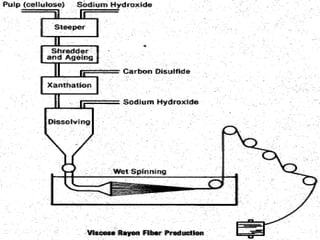
This presentation by Md. Yousuf Hossain discusses the production of viscose rayon. Viscose rayon is a regenerated cellulosic fiber produced from cellulose. The production process involves steeping pulp in sodium hydroxide, pressing, shredding, aging, xanthation, dissolving, ripening, filtering, spinning and drawing. Key steps include converting cellulose to cellulose xanthate and dissolving it to create a viscose solution that is spun into filaments and drawn. Viscose rayon is used in apparel and hygienic products due to its absorbency and thermal stability.