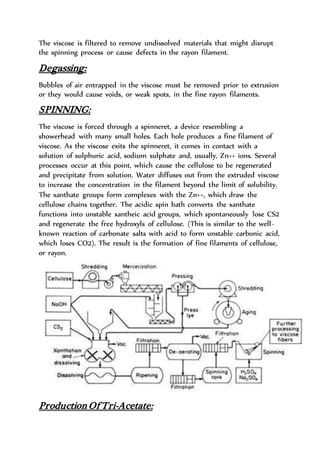
Acetate fiber is produced from cellulose through a chemical process involving esterification. The basic raw material is cotton which is treated with chemicals to form tri-acetate. Further treatment forms di-acetate or acetate. Viscose is produced through a multi-step process involving cellulose purification, treatment with caustic soda and carbon disulfide to form cellulose xanthate, which is then dissolved and spun through a spinneret into a chemical bath to regenerate the cellulose fiber. Tri-acetate is made through acetylation of cellulose with acetic acid and anhydride. Di-acetate is formed through hydrolysis of tri-acetate. Both have a variety of uses including app