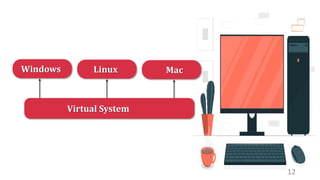
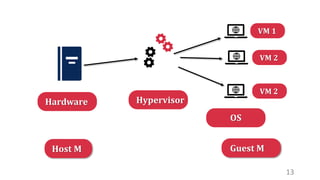
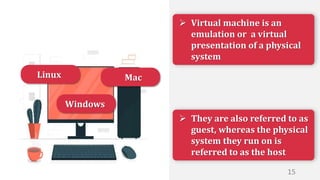
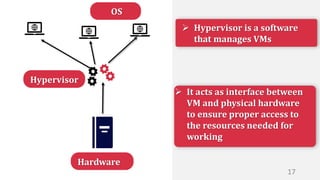
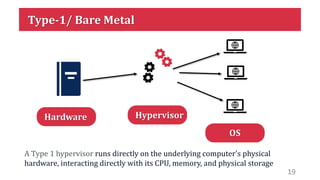
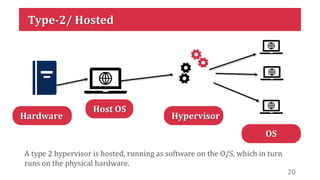
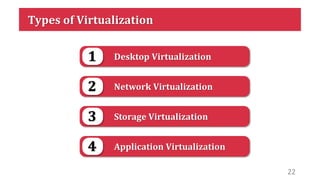
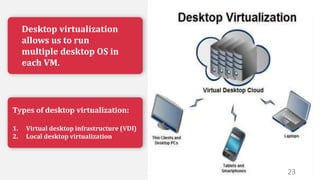
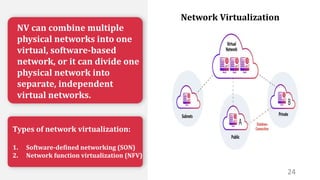
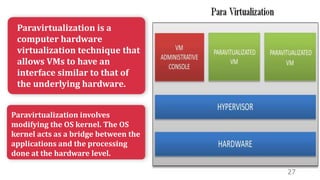
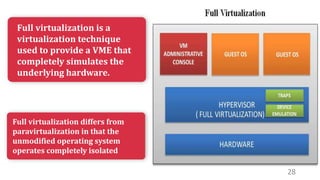
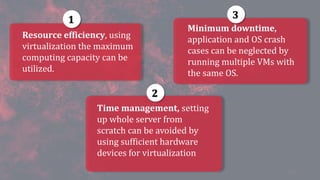
This document discusses virtualization and how it can help Hira, a software developer who needs to use different operating systems for his projects. Virtualization allows a single physical machine to run multiple virtual machines, each with its own operating system. This solves issues around managing multiple physical machines. The document defines key virtualization concepts like virtual machines, hypervisors, types of virtualization including desktop, network, storage and application virtualization. It also covers benefits of virtualization like improved resource efficiency, time management and reduced downtime.