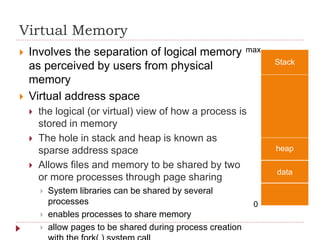
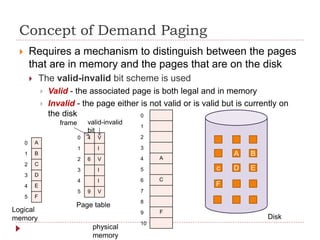
Virtual memory allows processes to execute without being completely loaded into physical memory. It abstracts memory into a large, uniform array that allows processes to easily share files and memory. With virtual memory, programs are no longer constrained by the amount of physical memory and more programs can run simultaneously with less I/O. Pages are loaded into memory on demand via demand paging to avoid loading unused pages. When a page fault occurs for an invalid page, it is paged into memory if valid. Common page replacement algorithms are FIFO, Optimal, and LRU which replace pages based on time since last use to make space for new pages on faults.