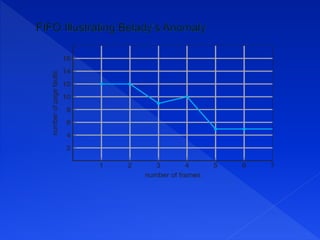
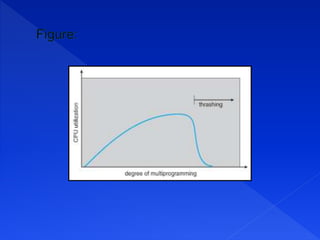
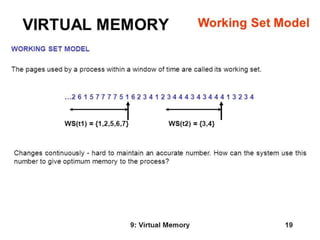
Virtual memory allows processes to execute using both physical RAM and disk storage. When a process references a page not in RAM, demand paging brings that page into a free frame from disk. Page replacement completes the separation of logical and physical memory, allowing a larger virtual memory in a smaller physical RAM. Common page replacement algorithms include FIFO, LRU, and LFU.