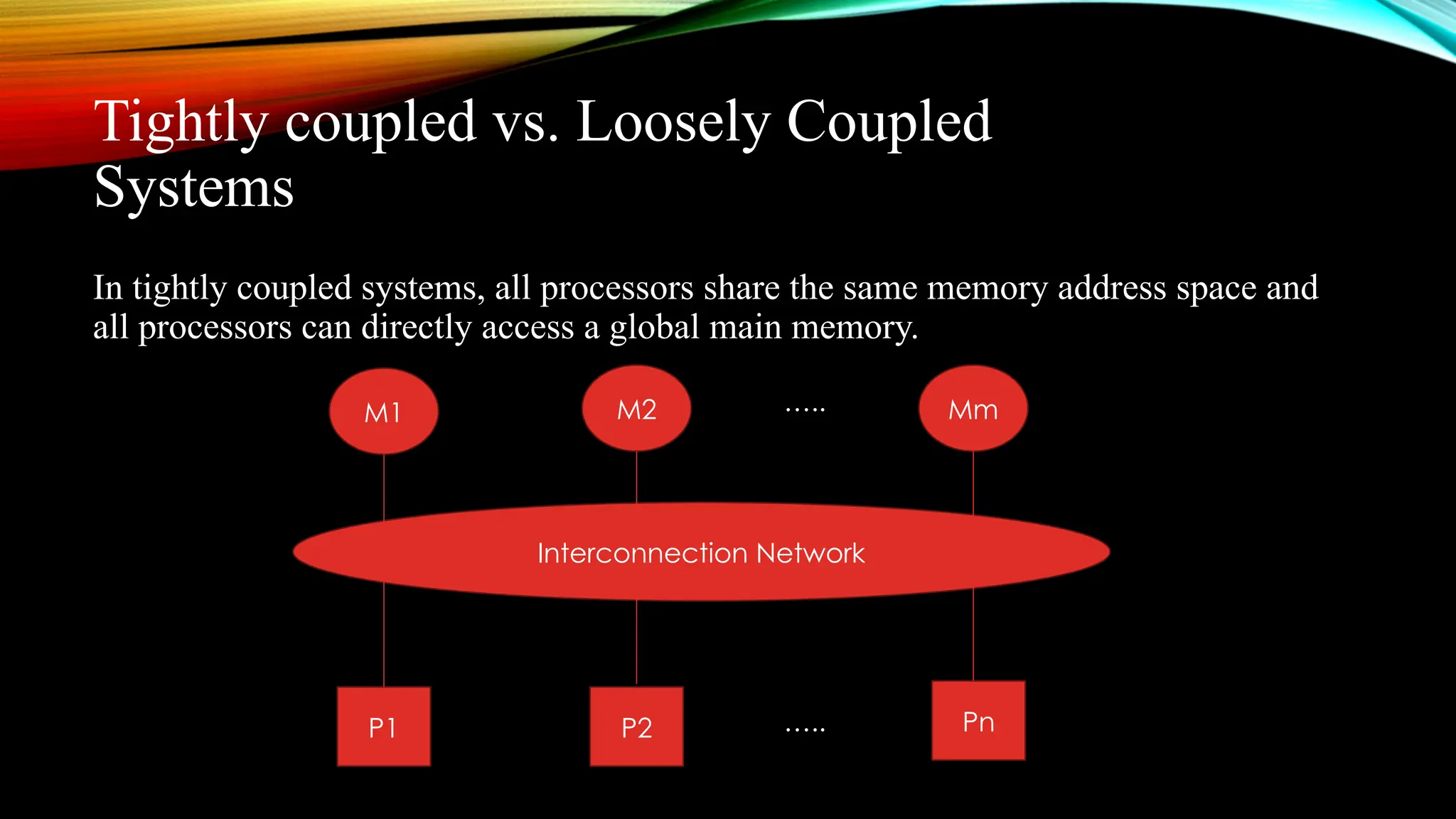
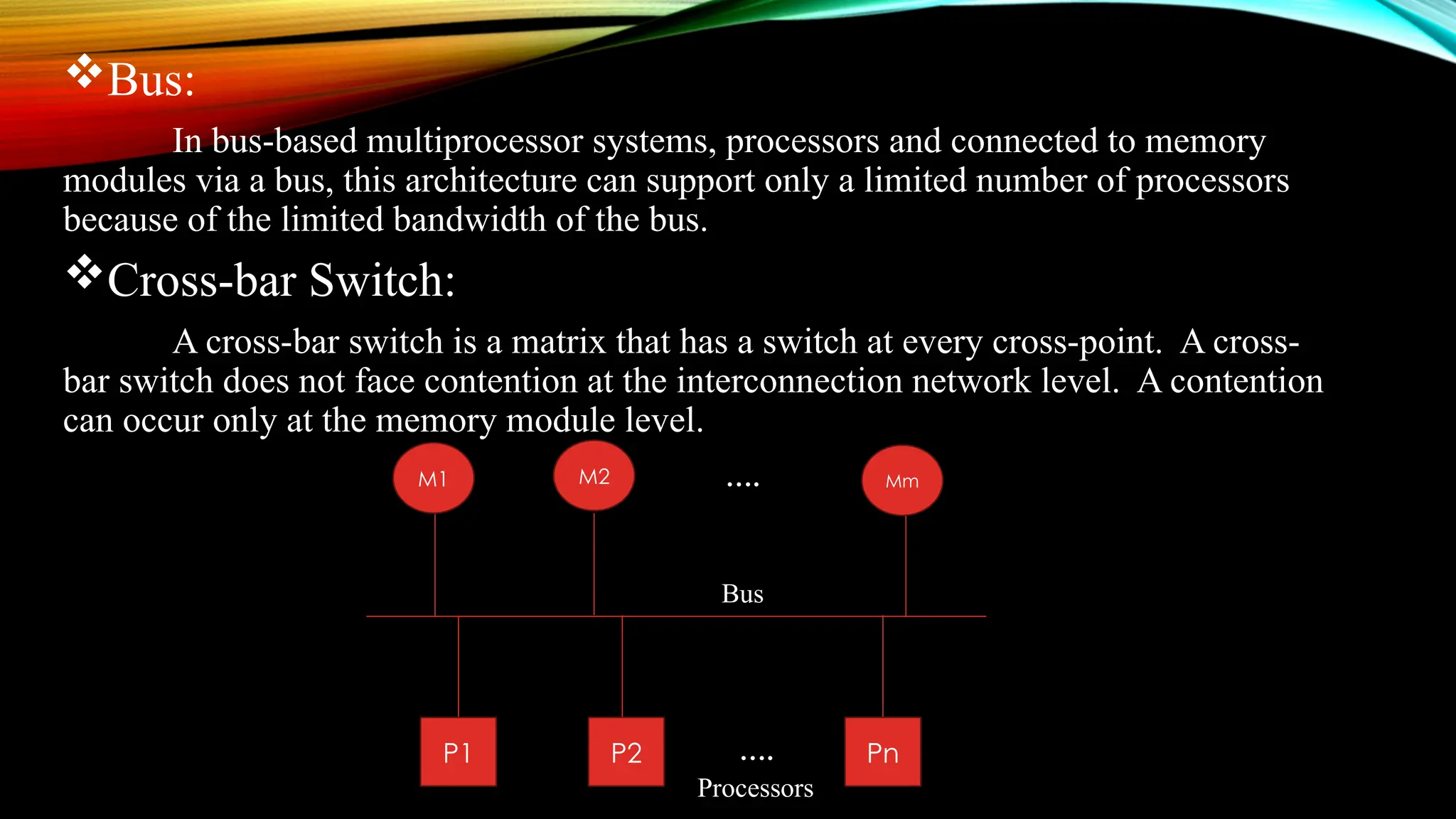
The document discusses multiprocessor system architectures, highlighting their role in enhancing computing power and speed through multiple shared processors. It contrasts different architectures, including UMA, NUMA, and NORMA, and explains the importance of interconnection networks for data transfer between processors and memory modules. Key motivations for adopting multiprocessor systems include improved performance and fault tolerance.