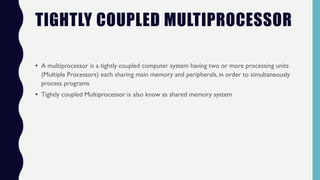
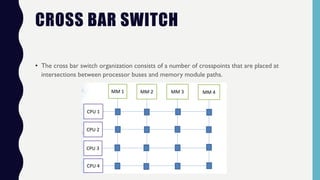
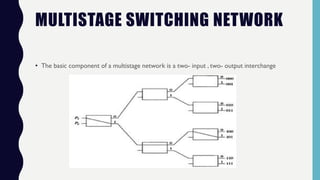
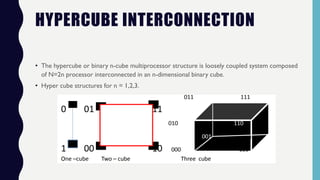
This document discusses multiprocessor systems. It begins by defining a multiprocessor as an interconnection of two or more CPUs, memory, and I/O equipment. Multiprocessors are classified as either tightly coupled or loosely coupled based on how their memory is organized. Tightly coupled multiprocessors have shared memory across CPUs while loosely coupled multiprocessors have distributed memory. The document then covers various interconnection structures used in multiprocessors like bus, memory, switch networks, and hypercubes. It concludes by discussing advantages of multiprocessing like improved performance, reliability, and throughput.