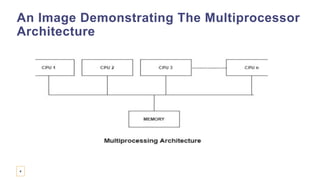
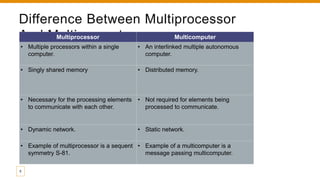
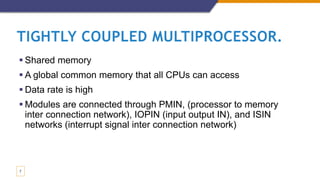
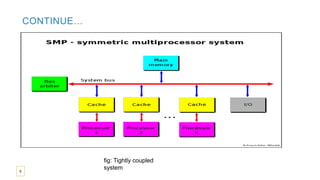
The document provides an overview of multiprocessor and multicomputer systems, detailing their definitions, classifications, advantages, and disadvantages. It distinguishes between tightly coupled multiprocessors, which share memory and have high data rates, and loosely coupled multiprocessors, which utilize distributed memory and have lower data rates. Additionally, it highlights the communication needs, costs, and applications of each system type.