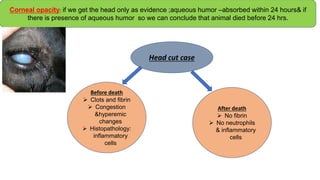
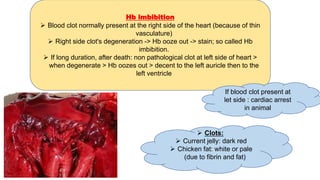
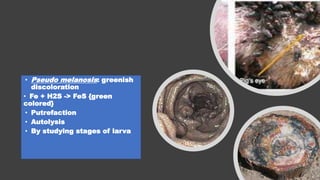
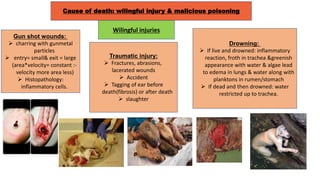
The document outlines procedures for conducting veterolegal necropsies, including evidence collection and proper documentation requirements. It covers various aspects of cause of death assessment, such as rigor mortis and pathological changes in injuries, as well as types of malicious injuries and their forensic implications. The document emphasizes the importance of obtaining proper requests from law enforcement and wildlife departments for handling cases involving livestock and wildlife.