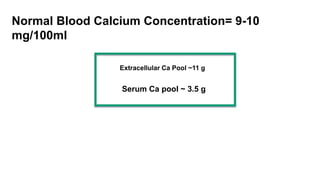
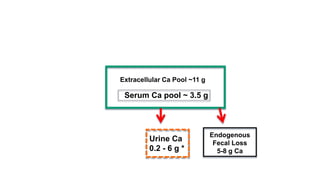
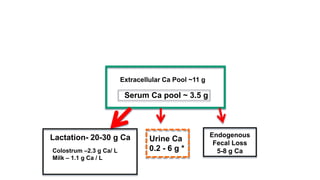
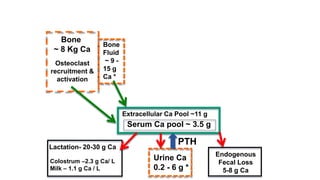
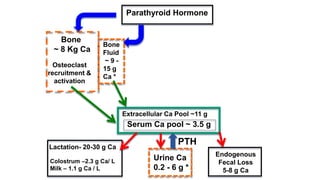
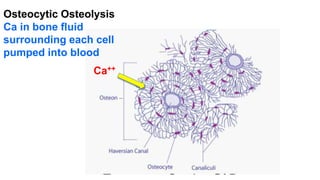
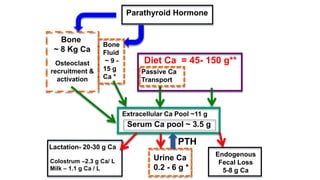
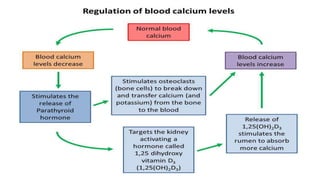
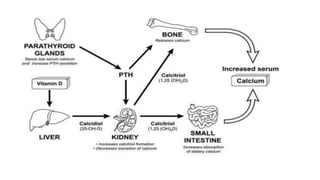
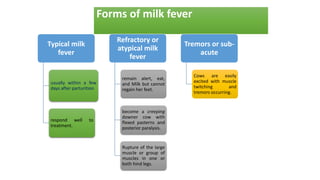
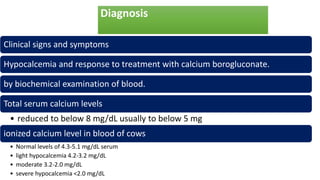
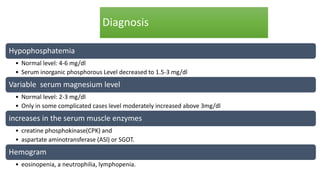
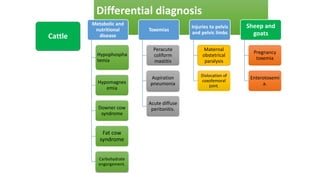
Parturient Paresis, also known as milk fever or hypocalcemia, is a metabolic disease that occurs in dairy cows within 12-72 hours of giving birth. It is characterized by low calcium levels in the blood (hypocalcemia) which causes general muscle weakness, paralysis, collapse and recumbence. The disease occurs due to a sudden increase in calcium demand for milk production at calving that the cow cannot meet due to impaired calcium mobilization from bones and intestines. Successful treatment involves rapid intravenous calcium supplementation to restore calcium levels while prevention focuses on dietary modifications pre-calving to optimize calcium metabolism and mobilization.