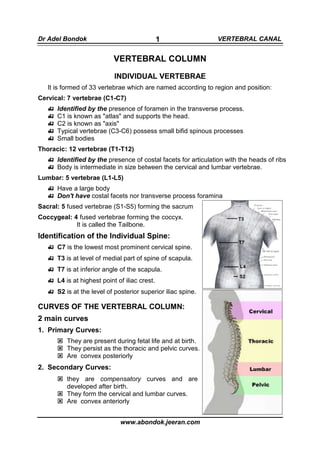
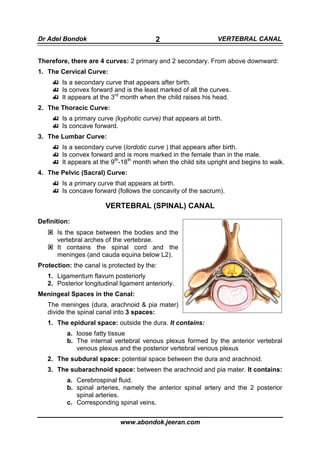
This document discusses the anatomy of the vertebral column and spinal canal. It describes the individual vertebrae, curves of the vertebral column, structures within the vertebral canal including the meningeal spaces, abnormalities, blood supply, the intervertebral disc, and changes that occur with aging. Key points include there being 33 vertebrae grouped into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal sections, and the presence of primary and secondary curves forming the cervical, thoracic, lumbar and pelvic curves. The vertebral canal contains the spinal cord and meninges, and is protected anteriorly and posteriorly. The intervertebral disc acts as a shock absorber and its structure and function changes