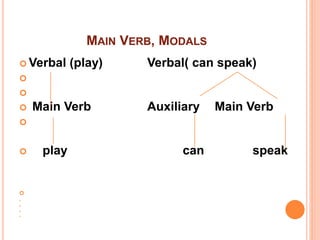
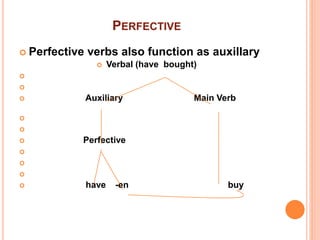
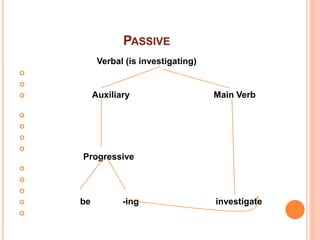
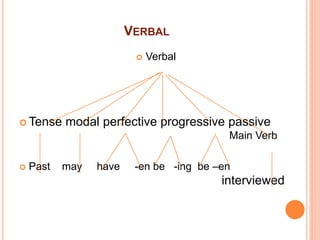
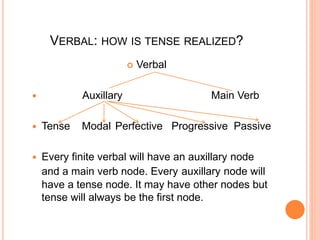
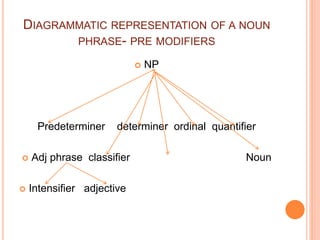
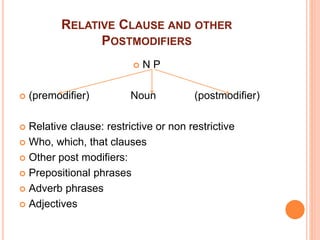
This document discusses English grammar concepts including verbal, noun phrases, and relationals. It defines a verbal as a functional element that includes the main verb and any auxiliary or helping verbs. Auxillary verbs function as operators and can change a sentence to a question if placed in initial position. The document also discusses how tense, modals, perfective, progressive, and passive verbs are realized in a verbal. Additionally, it examines the noun phrase, defining it as a group of words with a noun as the head, and explores the different constituents that can make up a noun phrase, including premodifiers and postmodifiers.