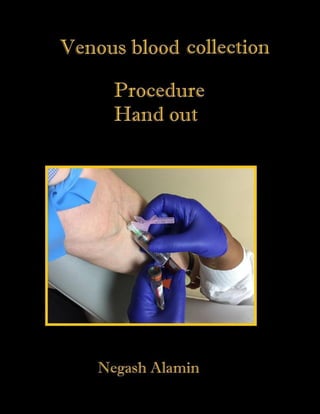
Venous blood collection, or venipuncture, allows for collection of large blood volumes from the median cubital vein in the antecubital fossa for numerous clinical tests. The procedure involves cleaning the site, applying a tourniquet, inserting a vacutainer needle to fill test tubes, removing the needle and applying pressure to stop bleeding. Proper collection permits complete blood counts, cell analyses, and other tests to aid clinical evaluation and diagnosis.