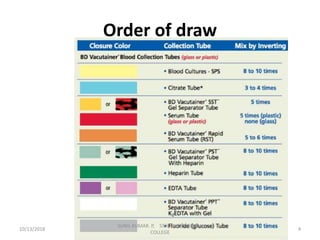
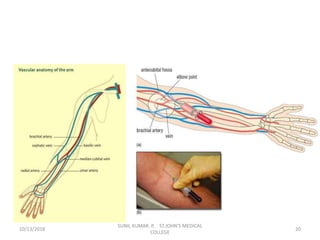
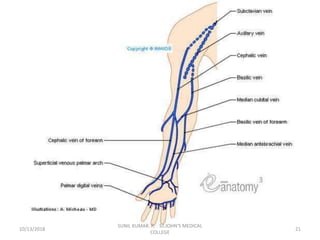
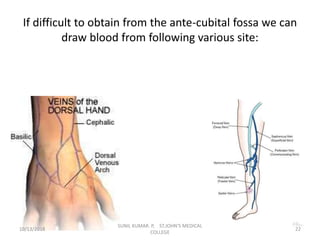
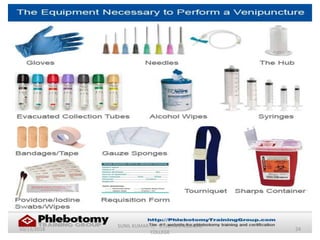
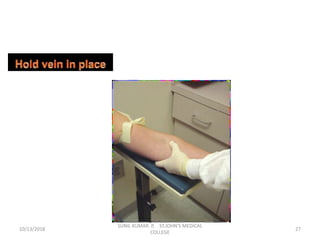
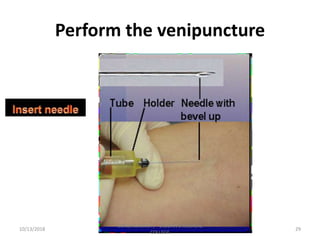
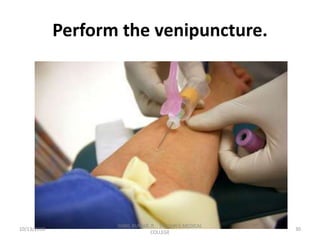
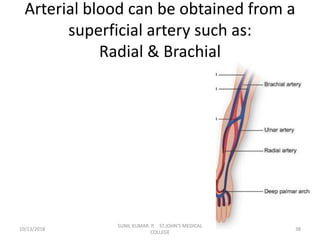
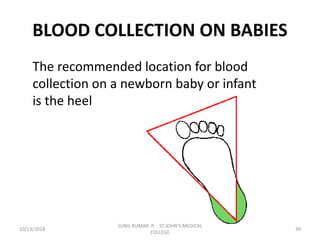
This document provides information about blood collection procedures. It discusses phlebotomy, the order of draw for blood collection, sources of blood like venous, arterial and capillary blood. It describes different blood collection tubes and their uses. The key methods of blood collection covered are skin prick or finger stick, venipuncture and arterial collection. Specific steps for each method and proper handling of samples are outlined.