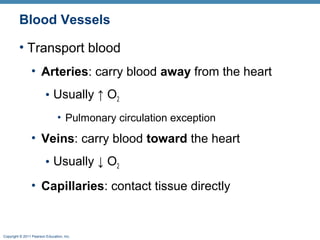
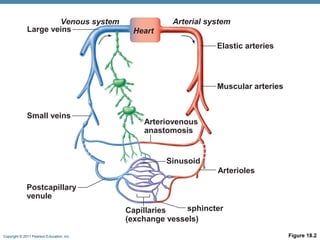
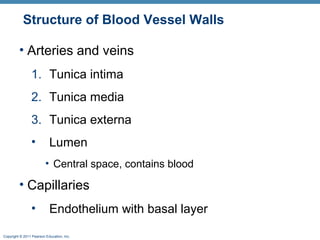
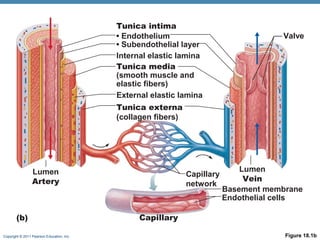
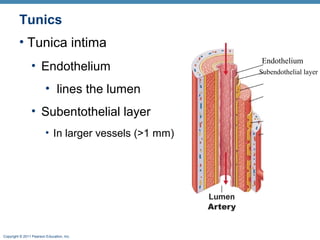
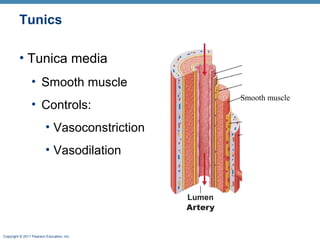
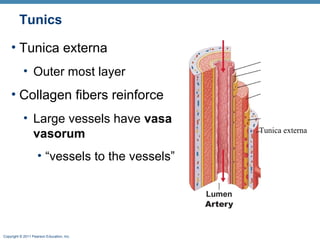
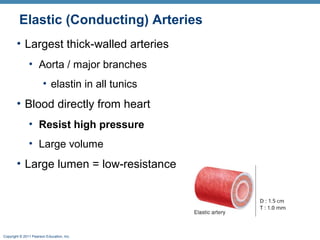
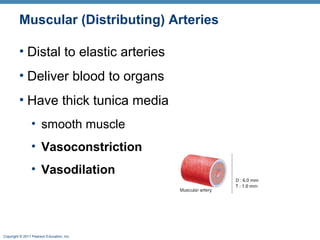
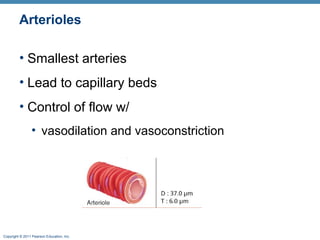
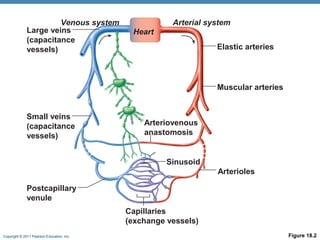
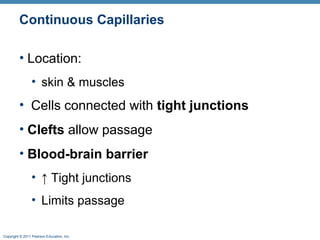
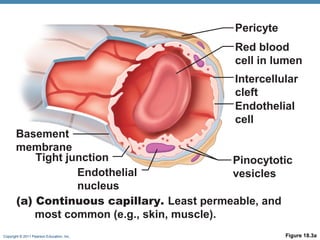
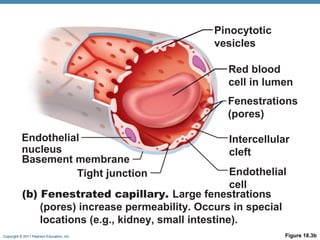
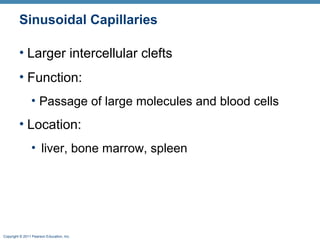
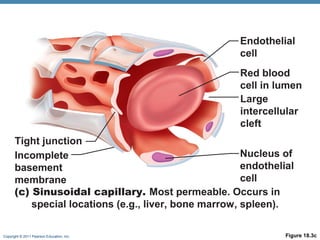
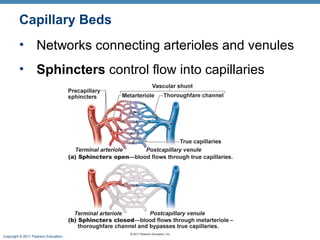
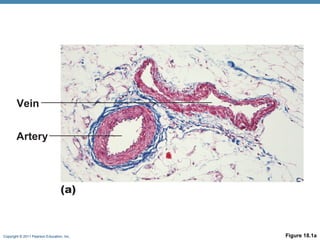
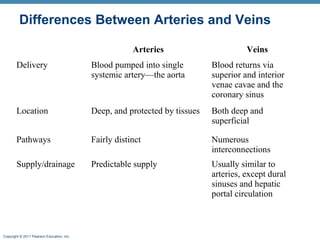
The document summarizes the structure and function of the cardiovascular system. It describes the three main types of blood vessels - arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, and capillaries facilitate gas and nutrient exchange with tissues. The walls of blood vessels are composed of three tunics - the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa. Arteries and veins have these three layers, while capillaries have a single layer of endothelium. The document also discusses the adaptations of different vessel types for their roles in circulation.