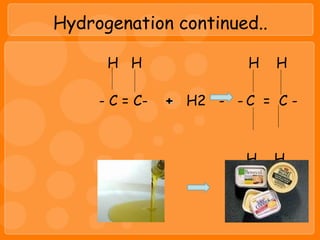
Lipids include fats and oils, which are composed of triglycerides made of a glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acid molecules. Fats are solid at room temperature while oils are liquid. Lipids provide energy and are a component of cell membranes. They are digested into fatty acids and glycerol in the stomach and small intestine and absorbed via the lymphatic system. Excess lipids are stored as adipose tissue and used as an energy reserve.