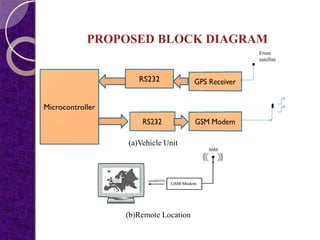
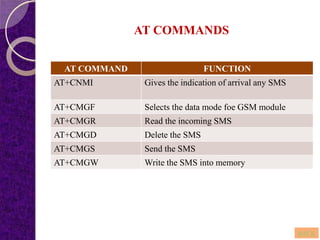
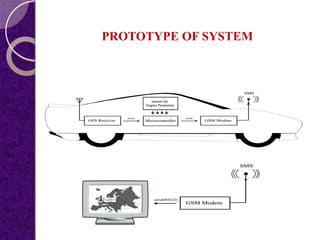
This document summarizes a student project on a GPS and GSM-based vehicle theft control system. The system uses GPS to track the exact location of a vehicle through latitude and longitude coordinates. The GPS location is sent via GSM modem to a remote location and displayed on Google Earth. The proposed system aims to both monitor and locate a vehicle to ensure security by integrating GPS and GSM technologies.