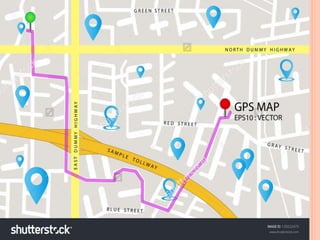
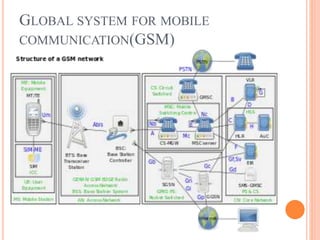
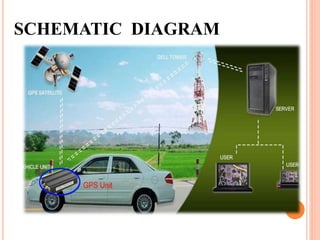
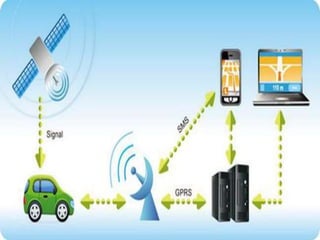
The document discusses a system that uses GPS and GSM technologies to track vehicles and other assets. GPS satellites provide location data that is transmitted via GSM networks. This allows asset owners to monitor locations in real-time through a web application. The system provides security benefits like recovering stolen vehicles and monitoring high-value goods. It could also optimize delivery routes and track animals. Combined GPS and GSM technologies enable low-cost, real-time asset monitoring with potential applications in transportation, security, and logistics.